Casting plays a crucial role in shaping the success of theater, film, and television productions by carefully selecting actors who embody characters authentically and bring stories to life. The process involves evaluating talent, chemistry, and suitability to ensure the narrative resonates deeply with the audience. Discover how effective casting techniques can elevate your project by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
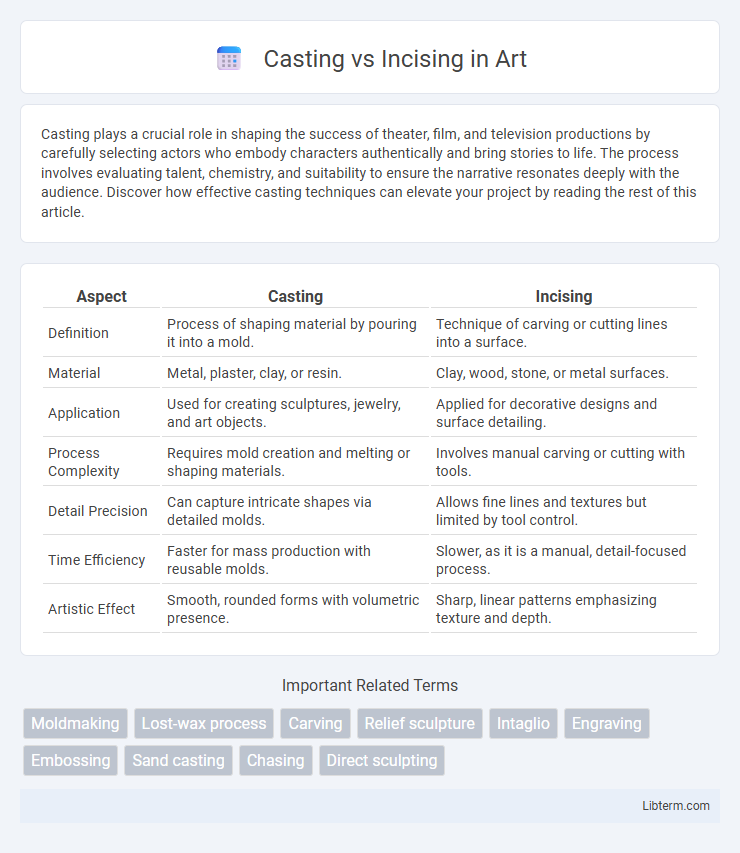
| Aspect | Casting | Incising |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of shaping material by pouring it into a mold. | Technique of carving or cutting lines into a surface. |
| Material | Metal, plaster, clay, or resin. | Clay, wood, stone, or metal surfaces. |
| Application | Used for creating sculptures, jewelry, and art objects. | Applied for decorative designs and surface detailing. |
| Process Complexity | Requires mold creation and melting or shaping materials. | Involves manual carving or cutting with tools. |
| Detail Precision | Can capture intricate shapes via detailed molds. | Allows fine lines and textures but limited by tool control. |
| Time Efficiency | Faster for mass production with reusable molds. | Slower, as it is a manual, detail-focused process. |
| Artistic Effect | Smooth, rounded forms with volumetric presence. | Sharp, linear patterns emphasizing texture and depth. |
Introduction to Casting vs Incising
Casting involves shaping materials by pouring molten metal or other substances into a mold to produce complex and precise forms. Incising, in contrast, is a subtractive technique that cuts or carves designs directly onto a surface, often used for detailed decoration or texturing. Both methods play crucial roles in art and manufacturing, offering distinct advantages for creating intricate objects.
Defining Casting and Incising
Casting involves shaping molten material, typically metal or plastic, by pouring it into a mold where it solidifies into a desired form. Incising is a technique that involves cutting or carving grooves, lines, or patterns into a surface, often used in ceramics, metalwork, or wood to create detailed designs. While casting shapes objects through mold solidification, incising modifies existing surfaces through precise cutting or engraving.
Historical Significance of Both Techniques
Casting and incising are foundational techniques that shaped ancient art and craftsmanship, with casting enabling the mass production of bronze artifacts in civilizations like Mesopotamia and China, thus advancing metallurgical technology. Incising, widely used in pottery and metalwork across cultures such as the Greeks and Native Americans, allowed artisans to create intricate designs that conveyed cultural narratives and symbolized social status. Both techniques hold significant historical value as they reflect technological innovation and artistic expression pivotal to cultural identity and economic development in early human societies.
Materials Used in Casting vs Incising
Casting commonly utilizes materials such as molten metals like bronze, aluminum, and iron, as well as plastics and resins, which are poured into molds to create detailed shapes. Incising involves directly cutting or carving into solid surfaces like stone, wood, clay, or metal sheets, requiring tools appropriate for precise engraving or etching. The choice of materials profoundly influences the texture, durability, and application of the final artwork in both casting and incising techniques.
Process Overview: Casting
Casting involves pouring molten material, such as metal or plastic, into a pre-designed mold to solidify and form a desired shape. The process requires precise temperature control to ensure proper flow and cooling, which directly affects the final product's surface quality and structural integrity. Casting is ideal for producing complex geometries and large quantities with consistent dimensions.
Process Overview: Incising
Incising involves creating precise designs by cutting or carving into a surface, typically using sharp tools to remove material and form patterns or images. This technique allows for fine detail and texture, often applied on ceramics, metal, or wood before further processing such as firing or finishing. Incising is favored for its ability to produce intricate lines and depth, distinguishing it from casting, which shapes materials by pouring molten substance into molds.
Advantages of Casting
Casting offers superior detail reproduction and uniformity in metal fabrication, enabling complex shapes and fine textures that incising cannot easily achieve. This method allows for mass production with consistent quality, reducing labor costs and time per unit. Casting also supports a wider range of materials and thicknesses, enhancing versatility in industrial applications.
Benefits of Incising
Incising offers precise control for creating detailed textures and patterns on surfaces, enabling intricate artistic expression not achievable through casting. The process reduces material waste by allowing selective removal rather than complete molding, making it cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Incising also enhances tactile quality and depth, contributing to the uniqueness and authenticity of sculptures and decorative objects.
Key Differences Between Casting and Incising
Casting involves pouring molten material into a mold to form objects with complex shapes and smooth surfaces, while incising refers to cutting or engraving designs directly onto a surface. Casting allows for mass production and intricate three-dimensional forms, whereas incising produces detailed, often two-dimensional patterns on existing materials. The primary distinction lies in casting shaping the material from liquid form and incising modifying the surface of solid objects.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Selecting between casting and incising depends on the project's material, detail requirements, and production scale. Casting excels in creating complex, three-dimensional forms with uniformity and is ideal for metal or resin components. Incising offers precision in surface detail, perfect for ceramics or wood, where intricate patterns or textures enhance the final piece's aesthetic.
Casting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com