Stylistic variation enhances your writing by introducing diverse sentence structures, tones, and word choices that keep readers engaged and convey your message more effectively. Employing a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences prevents monotony and highlights key points with clarity and rhythm. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical techniques for mastering stylistic variation in your writing.
Table of Comparison
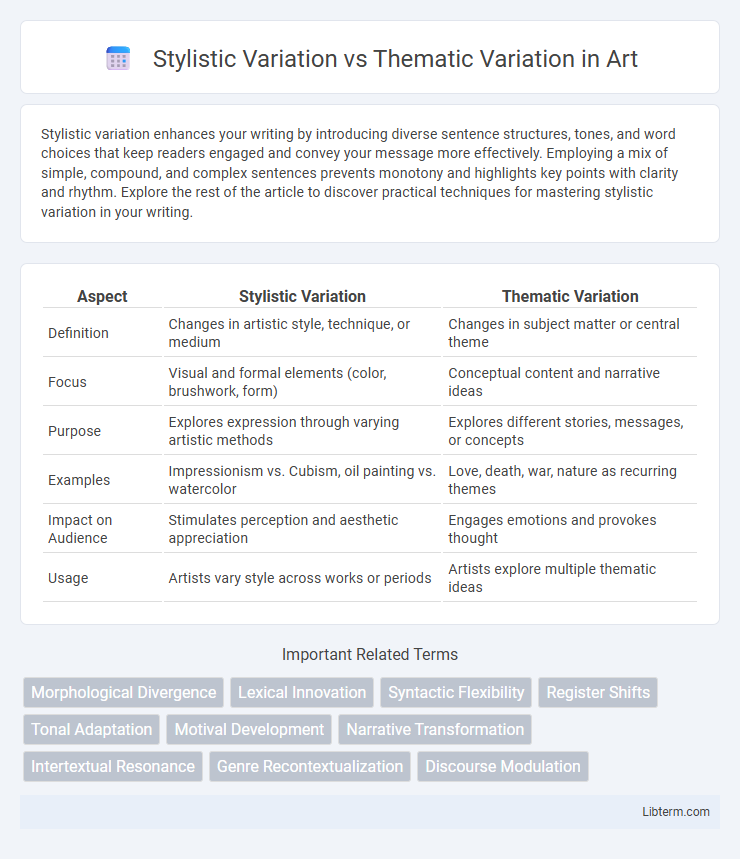
| Aspect | Stylistic Variation | Thematic Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Changes in artistic style, technique, or medium | Changes in subject matter or central theme |
| Focus | Visual and formal elements (color, brushwork, form) | Conceptual content and narrative ideas |
| Purpose | Explores expression through varying artistic methods | Explores different stories, messages, or concepts |
| Examples | Impressionism vs. Cubism, oil painting vs. watercolor | Love, death, war, nature as recurring themes |
| Impact on Audience | Stimulates perception and aesthetic appreciation | Engages emotions and provokes thought |
| Usage | Artists vary style across works or periods | Artists explore multiple thematic ideas |
Introduction to Stylistic and Thematic Variation
Stylistic variation refers to changes in language use that reflect differences in social context, audience, or purpose, involving adjustments in tone, diction, and syntax to suit specific communicative settings. Thematic variation focuses on shifts in content and subject matter within a text or discourse, emphasizing topic development and the organization of ideas to maintain coherence and interest. Understanding stylistic and thematic variation is essential for analyzing how language adapts to varying contexts and how information is structured effectively.
Defining Stylistic Variation
Stylistic variation refers to the deliberate changes in language use driven by social context, purpose, and audience, influencing factors such as vocabulary, syntax, and tone. It differs from thematic variation, which centers on shifts in subject matter or topical focus within a discourse. Understanding stylistic variation is essential for analyzing how speakers or writers adjust their language to convey identity, social roles, or situational nuances.
Defining Thematic Variation
Thematic variation refers to the subtle shifts and contrasts in musical themes or subjects within a composition, enhancing its expressive depth and structural complexity. It involves modifying elements such as melody, rhythm, or harmony while maintaining the core thematic identity to create diversified yet cohesive musical narratives. This variation contrasts with stylistic variation, which centers on changing interpretative aspects like articulation and dynamics rather than thematic content.
Key Differences Between Stylistic and Thematic Variation
Stylistic variation refers to changes in language use influenced by context, purpose, or audience, affecting tone, diction, and syntax, while thematic variation focuses on shifts in subject matter or themes within a text. The key difference lies in stylistic variation shaping how a message is conveyed, emphasizing form and expression, whereas thematic variation centers on what content or ideas are presented. Understanding these differences aids in analyzing discourse structure and communicative intent across different texts.
Importance in Literary Analysis
Stylistic variation enhances literary analysis by revealing how authors manipulate language, tone, and narrative techniques to evoke emotions and create distinct voices. Thematic variation deepens understanding by highlighting the evolution of central ideas and motifs across a work, uncovering layers of meaning and cultural context. Examining both variations provides a comprehensive insight into the interplay between form and content, enriching interpretation and critical appreciation.
Examples of Stylistic Variation in Literature
Stylistic variation in literature is evident through diverse narrative techniques such as the use of stream of consciousness in James Joyce's *Ulysses* or the fragmented syntax and playful language in e.e. cummings' poetry, which contrast the more uniform thematic variation focused on subject matter differences. Authors employ stylistic devices like metaphor, diction, and varied sentence structures to evoke distinct moods and voice, seen in Virginia Woolf's lyrical prose and Ernest Hemingway's succinct dialogue. These stylistic choices create unique reading experiences while maintaining coherence within the overarching themes explored in the works.
Examples of Thematic Variation in Literature
Thematic variation in literature involves exploring different underlying subjects or messages within a work, often reflecting changes in the author's perspective or societal context. Examples include William Blake's "Songs of Innocence and Experience," where contrasting themes of innocence and experience reveal dual viewpoints on human nature. Another example is Virginia Woolf's "To the Lighthouse," which shifts themes from the passage of time to the complexities of family relationships and personal memory.
Impact on Reader Interpretation
Stylistic variation influences reader interpretation by altering tone, mood, and voice, thereby shaping emotional engagement and the perceived personality of the text. Thematic variation directs attention to different subject matters or ideas within a work, guiding readers toward contrasting insights and deeper meaning. Together, these variations create a dynamic reading experience that enhances cognitive and emotional responses, affecting overall comprehension and resonance.
Stylistic and Thematic Variation Across Genres
Stylistic variation across genres involves changes in language features such as tone, vocabulary, and sentence structure tailored to the specific communicative purpose of each genre. Thematic variation centers on the content and subject matter, where genres address distinct topics and themes relevant to their audience and context. Effective genre analysis requires examining both stylistic and thematic elements to understand how texts achieve their intended impact.
Conclusion: Integrating Stylistic and Thematic Insights
Integrating stylistic and thematic insights enhances the depth of literary analysis by revealing how language choices and underlying themes interact to shape meaning. Understanding stylistic variation illuminates the author's voice and tone, while thematic variation uncovers the evolving subject matter and message. Together, these perspectives provide a comprehensive framework for interpreting texts with greater nuance and complexity.
Stylistic Variation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com