Motion capture technology records and translates human movement into digital data, enhancing realism in animation, video games, and film production. It captures subtle body mechanics, facial expressions, and gestures to create lifelike characters and immersive experiences. Explore the full article to discover how motion capture can transform your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
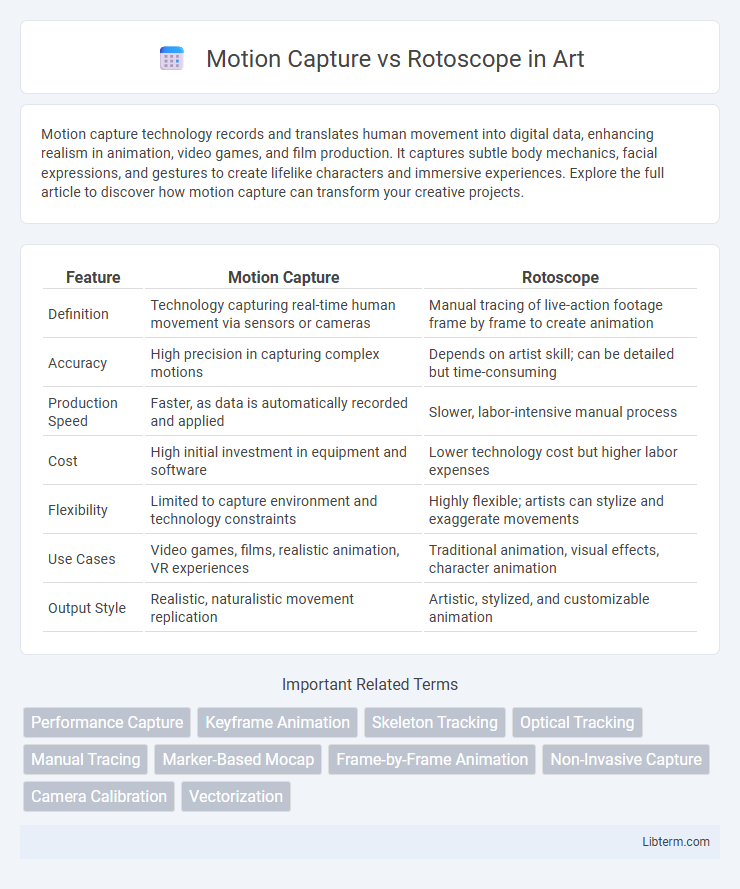
| Feature | Motion Capture | Rotoscope |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology capturing real-time human movement via sensors or cameras | Manual tracing of live-action footage frame by frame to create animation |
| Accuracy | High precision in capturing complex motions | Depends on artist skill; can be detailed but time-consuming |
| Production Speed | Faster, as data is automatically recorded and applied | Slower, labor-intensive manual process |
| Cost | High initial investment in equipment and software | Lower technology cost but higher labor expenses |
| Flexibility | Limited to capture environment and technology constraints | Highly flexible; artists can stylize and exaggerate movements |
| Use Cases | Video games, films, realistic animation, VR experiences | Traditional animation, visual effects, character animation |
| Output Style | Realistic, naturalistic movement replication | Artistic, stylized, and customizable animation |
Introduction to Motion Capture and Rotoscope
Motion capture captures real-life movements by tracking sensors on actors, translating physical gestures into digital animations with precise accuracy, often utilized in gaming and film industries for realistic character actions. Rotoscoping involves manually tracing over footage frame-by-frame to create animated sequences or visual effects, providing animators greater artistic control but requiring significant time and skill. Both techniques serve animation and VFX but differ in approach: motion capture leverages technology for efficiency and realism, while rotoscoping emphasizes craftsmanship and detailed frame manipulation.
Understanding the Basics: What is Motion Capture?
Motion capture (mocap) is a technology that records real-life movements of actors or objects using sensors and cameras to create realistic animations. It captures detailed motion data, allowing for precise replication of human body movements in digital characters. This technique is widely used in film, video games, and virtual reality to achieve lifelike performance and enhance visual storytelling.
What is Rotoscope? A Brief Overview
Rotoscope is an animation technique where animators trace over live-action footage frame by frame to create realistic movement and detail. This method allows for precise control over the final animation, enabling artists to enhance or stylize the original motion. Unlike motion capture, which records actors' movements digitally using sensors, rotoscope relies on manual tracing to blend live-action and animated elements seamlessly.
Technology Behind Motion Capture
Motion capture technology uses sensors and cameras to record real-time movements of actors or objects, translating physical actions into digital data for accurate animation. This process relies on optical or inertial systems, with optical capture employing multiple high-speed cameras to track reflective markers placed on subjects. The captured data is then processed through sophisticated software algorithms, enabling precise replication of movements in 3D character models.
Techniques and Tools Used in Rotoscope
Rotoscope techniques involve manually tracing over footage frame by frame to create realistic animations, often using specialized software like Adobe After Effects or Silhouette. This method requires skilled artists to refine motion paths and keyframes, enabling precise control over animated elements. Compared to motion capture, which relies on sensor suits and 3D tracking technology, rotoscoping remains a highly customizable tool for integrating hand-drawn elements with live-action footage.
Key Differences Between Motion Capture and Rotoscope
Motion capture records real actors' movements using sensors or cameras to generate precise 3D data, enabling realistic animation, while rotoscope involves manually tracing over live-action footage frame by frame for stylistic 2D animation. Motion capture excels in speed and capturing complex, subtle motions, whereas rotoscope offers greater artistic control and customization at the cost of labor-intensive work. Key differences include the nature of data acquisition--digital sensor-based versus hand-drawn--and the resulting output, with motion capture producing fluid, lifelike 3D animations and rotoscope yielding detailed, handcrafted 2D visuals.
Advantages of Motion Capture in Animation
Motion capture offers precise and realistic character movements by capturing an actor's performance directly, enhancing animation authenticity compared to rotoscope techniques. It significantly reduces production time and labor costs by automating complex motion replication, enabling faster iterations. Advanced motion capture systems also support real-time visualization, allowing immediate adjustments and improved creative control in animation projects.
Benefits of Rotoscope for Creative Projects
Rotoscope offers unparalleled control and artistic flexibility, enabling animators to trace live-action footage frame-by-frame for highly detailed and stylized effects. This technique allows precise manipulation of motion and expression, enhancing the creative vision beyond the limitations of motion capture data. By blending realistic movement with imaginative design, rotoscoping elevates storytelling in animation, visual effects, and experimental film projects.
Real-World Applications: When to Use Each Method
Motion capture excels in creating realistic animations for video games, virtual reality, and films by capturing precise human movements through sensors and cameras, making it ideal for complex, dynamic scenes requiring lifelike motion. Rotoscope is preferred in visual effects and animation for its frame-by-frame manual tracing technique, allowing artists to achieve stylized or exaggerated movements, particularly useful in blending live-action footage with animated elements. Choosing between motion capture and rotoscope depends on project requirements: motion capture suits high-fidelity, naturalistic performances, while rotoscope is advantageous for artistic control and integrating animated characters into live video.
Future Trends: Motion Capture and Rotoscope in Modern Media
Motion capture technology is rapidly advancing with AI integration, enabling more precise and realistic character movements in modern media productions. Rotoscoping is evolving through automated software powered by machine learning, reducing manual frame-by-frame tracing while maintaining artistic control. Both techniques are increasingly blended in virtual production workflows, enhancing efficiency and creative flexibility in film, gaming, and VR experiences.
Motion Capture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com