Hide glue, a traditional adhesive made from animal collagen, has been used for centuries in woodworking, bookbinding, and musical instrument repair due to its strong bonding properties and reversibility with heat and moisture. This natural glue offers advantages such as easy application, excellent gap-filling ability, and safe removal for delicate restoration tasks. Discover how hide glue can be the perfect solution for your next project by exploring its benefits and best practices in the full article.
Table of Comparison
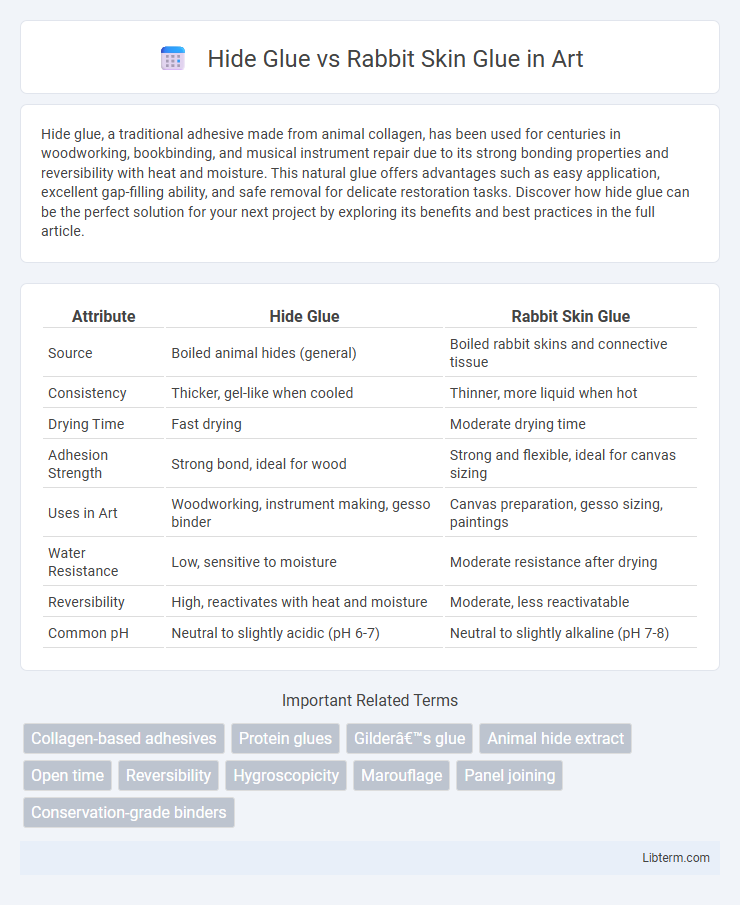
| Attribute | Hide Glue | Rabbit Skin Glue |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Boiled animal hides (general) | Boiled rabbit skins and connective tissue |
| Consistency | Thicker, gel-like when cooled | Thinner, more liquid when hot |
| Drying Time | Fast drying | Moderate drying time |
| Adhesion Strength | Strong bond, ideal for wood | Strong and flexible, ideal for canvas sizing |
| Uses in Art | Woodworking, instrument making, gesso binder | Canvas preparation, gesso sizing, paintings |
| Water Resistance | Low, sensitive to moisture | Moderate resistance after drying |
| Reversibility | High, reactivates with heat and moisture | Moderate, less reactivatable |
| Common pH | Neutral to slightly acidic (pH 6-7) | Neutral to slightly alkaline (pH 7-8) |
Introduction to Hide Glue and Rabbit Skin Glue
Hide glue, derived from collagen in animal hides, offers excellent adhesive strength and reversibility, making it ideal for fine woodworking and antique restoration. Rabbit skin glue, extracted specifically from rabbit collagen, is valued for its flexible yet strong bond and is commonly used in traditional gesso grounds and art practices. Both glues provide strong adhesion but differ in texture, drying times, and ideal applications within woodworking and artistic projects.
Historical Uses of Animal Glues
Hide glue and rabbit skin glue have been historically pivotal in woodworking, art restoration, and musical instrument making due to their strong adhesive properties and reversibility. Hide glue, derived from bovine collagen, was extensively used in furniture making and violin crafting since ancient times for its excellent clamp strength and ease of repair. Rabbit skin glue, commonly used in traditional painting and gilding, provided a flexible adhesive layer that prevented cracking and enhanced the durability of canvases and gold leaf applications.
Composition and Sourcing Differences
Hide glue is derived from collagen extracted from animal skins, primarily cattle hides, and processed through boiling and purification, resulting in a gel-like adhesive with high clarity and moderate setting time. Rabbit skin glue, specifically formulated from the collagen of rabbit skins, offers superior flexibility and elasticity, making it a preferred choice for traditional gesso preparation in fine art applications. Sourcing variations influence the purity and protein content of each glue type, with rabbit skin glue typically producing a stronger, more resilient bond due to its higher collagen concentration.
Adhesive Properties and Strength
Hide glue offers excellent initial tack and strong adhesion, making it ideal for woodworking and instrument repair due to its reversible bond with heat and moisture. Rabbit skin glue, known for higher elasticity and superior tensile strength, is preferred in canvas sizing and gilding because it provides durable, flexible adhesion resistant to cracking. Both animal-based adhesives exhibit strong bonding properties but differ in flexibility and application-specific strength requirements.
Application Techniques and Workability
Hide glue offers excellent adhesive strength with fast tack and a working time of about 10-15 minutes, ideal for precise joint alignments in woodworking and instrument making. Rabbit skin glue, softer and more flexible, provides longer open time--typically 20-30 minutes--making it suitable for canvas priming and delicate restorations where extended working time is needed. Both glues require warming before application to ensure optimal viscosity and bonding, yet rabbit skin glue demands careful moisture control to prevent brittleness or mold growth over time.
Reversibility and Repair Considerations
Hide glue offers excellent reversibility, making it ideal for antique furniture restoration where future repairs are anticipated; it softens with heat and moisture, allowing easy disassembly without damaging wood fibers. Rabbit skin glue, while also reversible, tends to be more brittle when dry and less forgiving during repairs, requiring careful handling to avoid cracking or weakening the bond. Both glues are favored in conservation, but hide glue's superior flexibility and reactivation properties provide significant advantages for long-term repair strategies.
Suitability for Woodworking
Hide glue provides excellent initial tack and strong bond strength, making it ideal for delicate woodworking tasks such as veneer application and instrument making where reversibility is important. Rabbit skin glue offers superior flexibility and is particularly suited for traditional wood joinery and gesso grounds due to its strong adhesion and ability to absorb paint layers effectively. Both glues perform well on wood but differ in drying speed and moisture resistance, influencing the choice based on specific woodworking requirements.
Uses in Fine Art and Gilding
Hide glue offers exceptional flexibility and strong adhesion, making it ideal for panel paintings and wood joinery in fine art, especially for tempera and traditional gesso grounds. Rabbit skin glue, prized for its strong tensile strength and superior sizing properties, is commonly used as a primer on canvas and supports precise gilding applications where a stable, absorbent base is critical. Both glues are animal-based and prized for archival quality, but rabbit skin glue's ability to create a resilient surface suits intricate gold leaf application better than the more brittle hide glue.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Impact
Hide glue and rabbit skin glue, both traditional animal-based adhesives, differ significantly in health, safety, and environmental impact. Hide glue generally poses fewer allergenic risks and is less prone to emitting harmful fumes compared to rabbit skin glue, which can cause respiratory irritation and allergic reactions due to proteins and ammonia content. Environmentally, hide glue is biodegradable and sourced from bovine collagen often considered a byproduct of the meat industry, while rabbit skin glue, derived from rabbit connective tissues, raises concerns about animal welfare and sustainability due to the energy-intensive extraction process.
Choosing the Right Glue for Your Project
Choosing the right glue for your project depends on factors like drying time, flexibility, and surface type. Hide glue offers a strong, reversible bond ideal for furniture restoration and woodworking, while rabbit skin glue provides a flexible and absorbent adhesive perfect for canvas preparation and gesso grounds. Understanding the specific requirements of your project ensures optimal adhesion and long-lasting results with either hide glue or rabbit skin glue.
Hide Glue Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com