Sculpture transforms raw materials into dynamic three-dimensional artworks that engage viewers from every angle. Exploring techniques like carving, modeling, and assembling reveals the diverse methods artists use to express form, texture, and emotion. Dive deeper into the fascinating world of sculpture to enhance your appreciation and understanding.
Table of Comparison
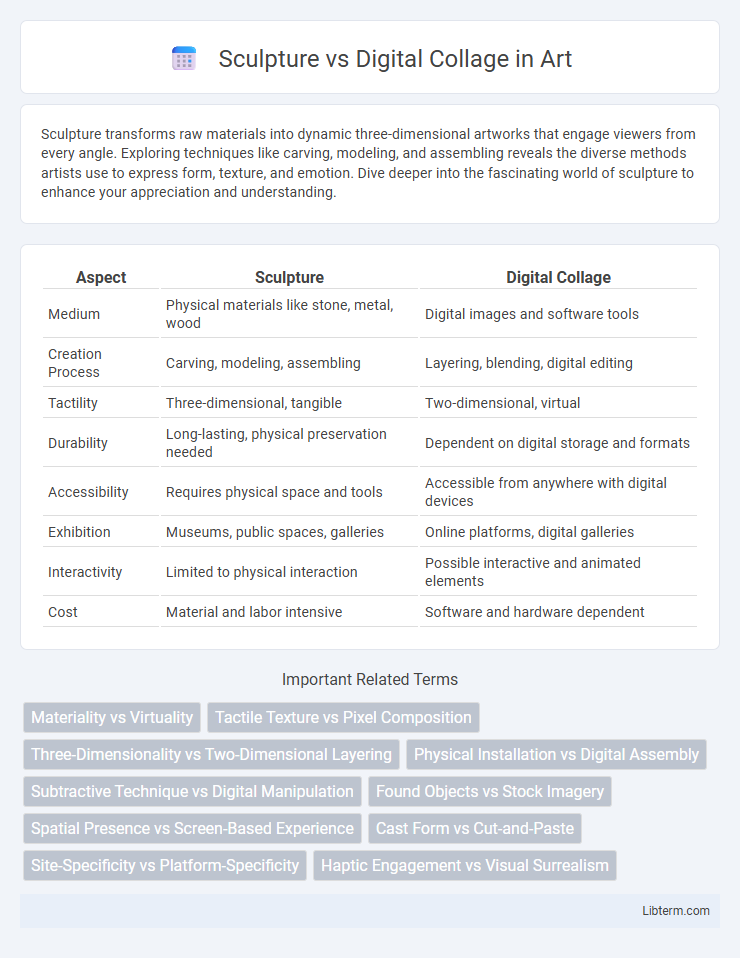
| Aspect | Sculpture | Digital Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials like stone, metal, wood | Digital images and software tools |
| Creation Process | Carving, modeling, assembling | Layering, blending, digital editing |
| Tactility | Three-dimensional, tangible | Two-dimensional, virtual |
| Durability | Long-lasting, physical preservation needed | Dependent on digital storage and formats |
| Accessibility | Requires physical space and tools | Accessible from anywhere with digital devices |
| Exhibition | Museums, public spaces, galleries | Online platforms, digital galleries |
| Interactivity | Limited to physical interaction | Possible interactive and animated elements |
| Cost | Material and labor intensive | Software and hardware dependent |
Introduction to Sculpture and Digital Collage
Sculpture is a three-dimensional art form that involves shaping materials such as stone, metal, or wood to create tangible objects with physical depth and texture. Digital collage combines various digital images, graphics, and textures using software tools to produce layered visual compositions on a flat screen. Both mediums explore creativity and expression, but sculpture emphasizes spatial presence, while digital collage focuses on virtual assemblage.
Defining Sculpture: Origins and Evolution
Sculpture, an ancient art form dating back to prehistoric times, involves shaping materials like stone, metal, and clay into three-dimensional works that occupy physical space. Its evolution spans classical realism in Greek and Roman eras to abstract and conceptual forms in modern art, reflecting cultural shifts and technological advancements. Unlike digital collage, which merges images digitally, sculpture emphasizes tactile craftsmanship and material presence.
Understanding Digital Collage: History and Techniques
Digital collage emerged in the late 20th century, blending traditional collage methods with modern technology to create layered, multimedia artworks. Artists utilize software like Adobe Photoshop to combine photographs, textures, and digital elements, enabling precise manipulation of images and seamless integration. This technique contrasts with sculpture's physicality by emphasizing virtual assembly and infinite editing possibilities, reflecting evolving artistic practices in the digital age.
Materials and Tools: Physical vs Virtual Creation
Sculpture relies on tangible materials such as clay, stone, metal, and wood, shaped using physical tools like chisels, hammers, and welding equipment, fostering a tactile interaction with the medium. Digital collage employs software platforms such as Adobe Photoshop or Procreate, utilizing virtual brushes, layering tools, and digital assets to manipulate images in a non-physical space. The physical creation of sculpture emphasizes texture and form through direct manipulation, whereas digital collage prioritizes flexibility and seamless integration of disparate visual elements in a virtual environment.
Artistic Processes: Hands-On vs Digital Manipulation
Sculpture involves a tactile, hands-on process where artists physically shape materials like clay, metal, or wood to create three-dimensional forms, emphasizing texture, weight, and spatial presence. Digital collage relies on digital manipulation, combining images and elements through software to produce layered, often flat compositions with precise control over color, scale, and blending. Both processes reflect distinct artistic approaches: one grounded in physical interaction and materiality, the other in virtual editing and compositional flexibility.
Expressive Possibilities: Comparing Aesthetic Outcomes
Sculpture offers tactile depth and dynamic spatial interaction, allowing artists to manipulate physical materials like clay, metal, or stone to create three-dimensional forms rich in texture and volume. Digital collage leverages software tools to combine images, textures, and colors with infinite layering flexibility, enabling quick experimentation and complex visual narratives that are impossible in physical mediums. Both techniques expand expressive possibilities by harnessing their unique aesthetic outcomes--sculpture embodies tangible presence and materiality, while digital collage excels in versatility and multimedia integration.
Accessibility and Audience Engagement
Sculpture offers a tangible, three-dimensional experience that allows audiences to engage physically and emotionally through touch and spatial interaction, often requiring physical presence in galleries or public spaces. Digital collage enhances accessibility by enabling creators to share work globally via online platforms, reaching diverse audiences instantly and encouraging interactive participation through digital comments and shares. Both mediums leverage unique accessibility features; sculpture fosters intimate, localized engagement while digital collage expands reach and interactive potential in the virtual realm.
Conservation and Longevity: Challenges and Solutions
Sculpture faces conservation challenges due to material degradation, environmental exposure, and physical damage, requiring specialized restoration techniques and climate-controlled environments to ensure longevity. Digital collage confronts issues such as file format obsolescence, data corruption, and hardware dependency, necessitating strategies like regular data migration, use of standardized formats, and robust digital archiving systems. Both art forms benefit from advancements in preservation technologies, but their conservation demands distinct expertise tailored to physical durability or digital integrity.
Cultural Impact and Contemporary Significance
Sculpture has historically shaped cultural identity through its tangible, three-dimensional form, embodying tradition and public memory across civilizations. Digital collage, emerging from technological innovation, challenges traditional aesthetics by blending diverse media, fostering new narratives and democratizing artistic expression globally. Both mediums significantly influence contemporary culture by reflecting societal values and expanding the boundaries of creativity in the digital age.
Choosing Your Medium: Factors to Consider
Choosing between sculpture and digital collage depends on factors like tactile engagement, spatial depth, and technical skills. Sculpture offers a three-dimensional, physical interaction with materials such as clay, metal, or wood, emphasizing texture and volume. Digital collage requires proficiency in software tools and allows for greater flexibility in composition, layering, and rapid iteration without material constraints.
Sculpture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com