Texturing enhances 3D models by adding detailed surface qualities that create realism and depth. By applying different textures, you can simulate materials like wood, metal, or fabric, making your designs visually engaging and lifelike. Explore the rest of the article to learn how mastering texturing can transform your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
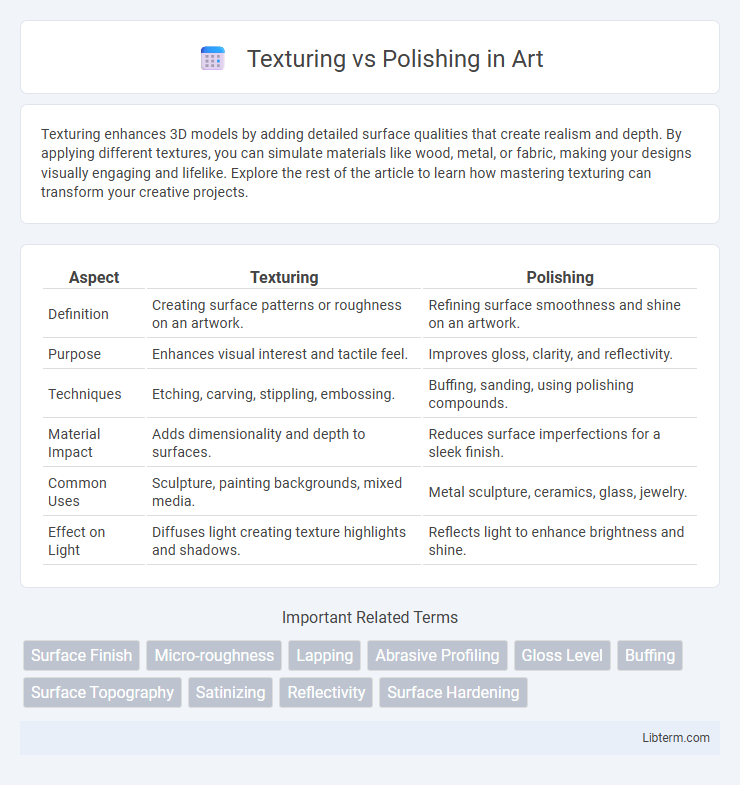
| Aspect | Texturing | Polishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating surface patterns or roughness on an artwork. | Refining surface smoothness and shine on an artwork. |
| Purpose | Enhances visual interest and tactile feel. | Improves gloss, clarity, and reflectivity. |
| Techniques | Etching, carving, stippling, embossing. | Buffing, sanding, using polishing compounds. |
| Material Impact | Adds dimensionality and depth to surfaces. | Reduces surface imperfections for a sleek finish. |
| Common Uses | Sculpture, painting backgrounds, mixed media. | Metal sculpture, ceramics, glass, jewelry. |
| Effect on Light | Diffuses light creating texture highlights and shadows. | Reflects light to enhance brightness and shine. |
Understanding Texturing and Polishing
Texturing involves creating controlled surface roughness on materials to enhance adhesion, aesthetics, or functionality, often achieved through methods like blasting, grinding, or chemical etching. Polishing is the process of smoothing and refining surfaces to achieve high reflectivity and reduce imperfections, typically using abrasive compounds or mechanical buffs. Understanding the distinct purposes and techniques of texturing and polishing is essential for optimizing material performance in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and electronics.
Key Differences Between Texturing and Polishing
Texturing alters a surface's microgeometry to create patterns or roughness, enhancing grip, appearance, or paint adhesion, while polishing smooths surfaces to a high gloss by removing microscopic irregularities. Texturing involves processes like sandblasting or etching, whereas polishing uses abrasives or chemical treatments to achieve reflectivity and smoothness. Key differences lie in their functional goals: texturing prioritizes tactile feel and aesthetic variation, polishing focuses on visual clarity and reduced friction.
Applications of Texturing in Various Industries
Texturing enhances surface properties such as grip, aesthetics, and friction control, making it vital in industries like automotive for improving tire traction and part durability, electronics for better heat dissipation and touch sensitivity, and medical devices to promote tissue integration and reduce infection risk. In manufacturing, textured surfaces enable better adhesion of coatings and paints, while architecture leverages texturing for both decorative appeal and functional benefits like slip resistance. These diverse applications demonstrate how texturing optimizes performance, safety, and design across multiple sectors.
The Importance of Surface Polishing
Surface polishing significantly enhances the durability and aesthetic appeal of materials by creating a smooth, reflective finish that reduces surface roughness and minimizes corrosion risks. Unlike texturing, which adds patterns or roughness for decorative or functional purposes, polishing improves material performance by decreasing friction and preventing contaminants from adhering. High-quality surface polishing is essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics, where precision and longevity are critical.
Techniques Used in Texturing Processes
Texturing techniques include sandblasting, shot peening, and acid etching, each imparting specific surface characteristics that enhance adhesion or aesthetic appeal. Mechanical methods use abrasive tools or rollers to create patterns or roughness, while chemical processes rely on reactive agents to alter surface topology at a microscopic level. These methods optimize material performance by increasing surface area, improving paint bonding, or controlling friction properties in industrial applications.
Popular Methods of Achieving Polished Surfaces
Popular methods of achieving polished surfaces include mechanical polishing, which uses abrasive materials like sandpaper or polishing pads to smoothen textures, and chemical polishing, involving chemical solutions that dissolve surface irregularities. Electro-polishing is another advanced technique that removes microscopic layers electrically, enhancing surface reflectivity and corrosion resistance. These methods are favored in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics for producing shiny, reflective finishes with minimized surface roughness.
Impact on Material Performance: Texture vs Polished Finish
Texturing increases surface roughness, enhancing adhesion and paint retention but can reduce fatigue resistance and wear performance. Polished finishes create a smooth, reflective surface that improves corrosion resistance and reduces friction, leading to better durability in dynamic applications. Material performance depends on the balance between surface texture and polishing, where textured surfaces suit protective coatings and polished finishes benefit mechanical efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of Texturing
Texturing enhances surface roughness to improve adhesion, reduce glare, and create aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for applications like automotive finishes and industrial coatings. Its main advantage lies in increasing friction and masking surface imperfections, although it may compromise smoothness and make cleaning more challenging. Limitations of texturing include potential wear over time and difficulty in achieving uniform patterns on complex geometries compared to polishing.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Polishing
Polishing enhances surface smoothness and shine, improving aesthetic appeal and reducing friction, which can extend the lifespan of materials by minimizing wear. However, it can remove surface layers, potentially weakening the material or removing protective coatings, and might be more time-consuming and costly compared to texturing. Unlike texturing, which adds grip and hides imperfections, polishing prioritizes sleekness and clean lines, sometimes at the expense of durability and cost-efficiency.
Choosing Between Texturing and Polishing for Your Project
Choosing between texturing and polishing depends on the desired surface finish and functional requirements of your project. Texturing enhances grip, reduces glare, and hides imperfections, making it ideal for industrial or decorative surfaces needing durability and slip resistance. Polishing creates a smooth, reflective surface that improves aesthetics and ease of cleaning, suitable for high-end furniture, automotive parts, and metal components requiring a sleek finish.
Texturing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com