Subtext reveals the underlying meaning beneath spoken words and actions, enriching narratives with deeper layers of emotion and intention that often go unnoticed. It guides your interpretation by highlighting unspoken tensions, desires, or conflicts within characters or conversations. Explore the rest of this article to discover how mastering subtext can transform your communication and storytelling skills.
Table of Comparison
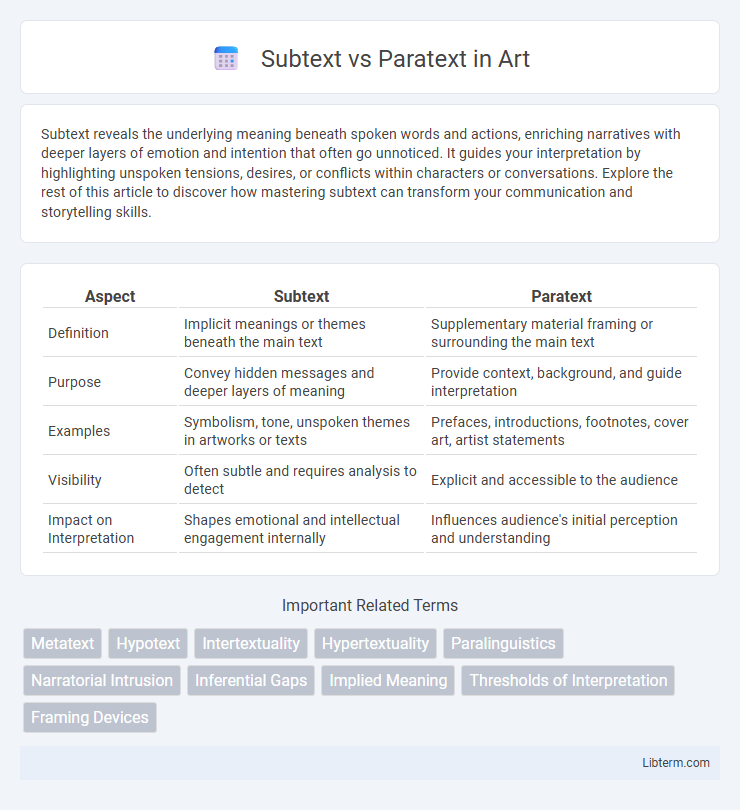
| Aspect | Subtext | Paratext |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Implicit meanings or themes beneath the main text | Supplementary material framing or surrounding the main text |
| Purpose | Convey hidden messages and deeper layers of meaning | Provide context, background, and guide interpretation |
| Examples | Symbolism, tone, unspoken themes in artworks or texts | Prefaces, introductions, footnotes, cover art, artist statements |
| Visibility | Often subtle and requires analysis to detect | Explicit and accessible to the audience |
| Impact on Interpretation | Shapes emotional and intellectual engagement internally | Influences audience's initial perception and understanding |
Understanding Subtext: Hidden Meanings in Texts
Subtext refers to the underlying meanings and implicit messages conveyed through tone, context, and character behavior, which are not explicitly stated in the text. Understanding subtext requires interpreting signals such as dialogue nuances, symbolism, and situational irony to grasp the deeper themes and emotional undercurrents. Unlike paratext, which includes external elements like titles and forewords framing the text, subtext operates within the narrative, enriching the reader's experience by revealing hidden layers of meaning.
Defining Paratext: The Textual Threshold
Paratext encompasses all the materials surrounding the main text, such as titles, prefaces, footnotes, and cover art, which function as a textual threshold guiding readers' interpretation and engagement. Gerard Genette, who coined the term, emphasizes that paratext serves as a mediator between the text and the reader, framing the reception and meaning of the primary content. This boundary shapes how the text is perceived, providing context, authority, and interpretive cues beyond the core narrative or argument.
Key Differences Between Subtext and Paratext
Subtext refers to the underlying meaning or implicit message conveyed beneath the explicit content of a text, often revealed through dialogue, tone, or character actions. Paratext encompasses the external elements surrounding the main text, such as prefaces, footnotes, titles, and cover art, which frame the reader's interpretation and provide contextual information. The key difference lies in subtext being an intrinsic part of the narrative conveying hidden meanings, while paratext serves as extrinsic material guiding or influencing how the text is perceived.
The Role of Subtext in Literature and Media
Subtext in literature and media functions as the underlying meaning or implicit message that enriches the narrative beyond the explicit dialogue or plot, allowing audiences to interpret characters' true intentions and themes. It enhances emotional depth and complexity, inviting readers or viewers to engage more critically with the content by revealing hidden motives, cultural nuances, or symbolic significance. The effective use of subtext distinguishes sophisticated storytelling, providing a layered experience that stimulates deeper reflection and connection.
Paratextual Elements: Covers, Titles, and Prefaces
Paratextual elements such as covers, titles, and prefaces shape readers' expectations and frame the interpretation of the main text by providing context and guiding the reading experience. Book covers often use visual design and imagery to signal genre, theme, and tone, while titles encapsulate key concepts or motifs that highlight the text's significance. Prefaces offer authors the opportunity to address readers directly, explain the work's purpose, or situate it within broader literary or cultural conversations, enriching the understanding before engaging with the core narrative.
How Subtext Shapes Reader Interpretation
Subtext subtly influences reader interpretation by embedding underlying meanings beyond the explicit narrative, prompting deeper cognitive engagement with the text. It operates through tone, symbolism, and implicit themes, guiding readers to infer emotions, motivations, and societal critiques. This nuanced layer enriches the reading experience by encouraging personal reflection and diverse perspectives on the story's core messages.
The Influence of Paratext on Audience Expectations
Paratext, including book covers, blurbs, and author interviews, shapes audience expectations by providing context that frames the main text's interpretation. These elements guide readers' perceptions before engaging with the content, influencing emotional response and thematic understanding. Subtext operates within the narrative itself, while paratext functions externally, directing audience anticipation and reception.
Analyzing Subtext in Popular Works
Analyzing subtext in popular works reveals underlying themes and unspoken societal commentary that deepen audience engagement and interpretation. Subtext operates beneath the explicit narrative, utilizing symbolism, dialogue nuance, and character behavior to convey complex emotions and ideologies. Examining these elements in renowned literature, films, and television series uncovers hidden meanings that enrich the textual experience beyond surface-level storytelling.
Paratext’s Impact on Book and Film Marketing
Paratext elements such as book covers, film trailers, author interviews, and promotional posters significantly influence audience perception and engagement by framing the primary text's meaning and generating anticipation. These materials function as marketing tools that shape consumer expectations, enhance brand visibility, and drive sales or viewership. Effective paratextual strategies increase market reach and create emotional connections, distinguishing products in competitive literary and cinematic markets.
Combining Subtext and Paratext in Effective Storytelling
Combining subtext and paratext enhances storytelling by enriching narrative depth and audience engagement through subtle cues and contextual framing. Subtext conveys underlying meanings and emotions within dialogue or scenes, while paratext includes external materials like titles, author notes, and cover art that guide interpretation. Integrating these elements effectively allows storytellers to create layered experiences that resonate on multiple levels, fostering deeper understanding and emotional connection.
Subtext Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com