Photorealistic portraiture captures every detail with remarkable accuracy, creating images that mirror real life down to the finest texture and light reflection. This art form blends advanced techniques and digital tools to achieve a level of realism that blurs the line between photography and painting. Explore the full article to discover how photorealistic portraits can transform your visual storytelling.
Table of Comparison
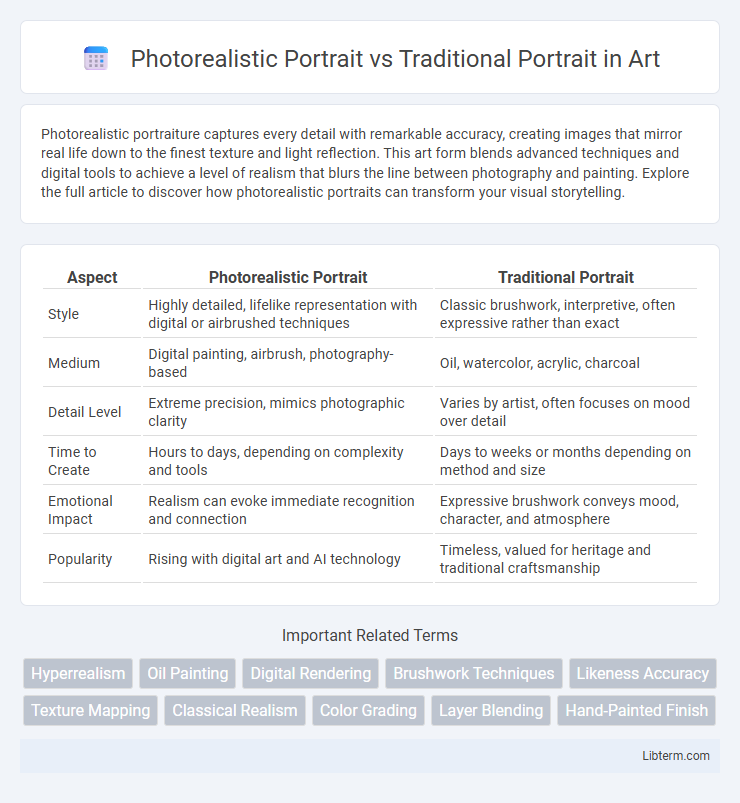
| Aspect | Photorealistic Portrait | Traditional Portrait |
|---|---|---|
| Style | Highly detailed, lifelike representation with digital or airbrushed techniques | Classic brushwork, interpretive, often expressive rather than exact |
| Medium | Digital painting, airbrush, photography-based | Oil, watercolor, acrylic, charcoal |
| Detail Level | Extreme precision, mimics photographic clarity | Varies by artist, often focuses on mood over detail |
| Time to Create | Hours to days, depending on complexity and tools | Days to weeks or months depending on method and size |
| Emotional Impact | Realism can evoke immediate recognition and connection | Expressive brushwork conveys mood, character, and atmosphere |
| Popularity | Rising with digital art and AI technology | Timeless, valued for heritage and traditional craftsmanship |
Introduction to Photorealistic and Traditional Portraits
Photorealistic portraits employ advanced techniques to replicate a photograph's intricate details, textures, and lighting with remarkable accuracy, often created using digital tools or hyper-realistic painting methods. Traditional portraits emphasize artistic interpretation through mediums like oil, watercolor, or charcoal, capturing the subject's essence with expressive brushstrokes and stylistic elements. The distinction lies in photorealistic works striving for lifelike precision, while traditional portraits prioritize emotional depth and artistic flair.
Defining Photorealistic Portraiture
Photorealistic portraiture is a highly detailed art form that replicates the visual nuances of a photograph using traditional mediums such as pencil, charcoal, or paint. This style emphasizes precise shading, texture, and color accuracy to create lifelike representations of subjects. Unlike traditional portraits that may incorporate impressionistic or stylistic interpretations, photorealistic portraits aim for exact visual fidelity and realism.
Understanding Traditional Portrait Techniques
Traditional portrait techniques emphasize mastering foundational skills such as accurate anatomy, chiaroscuro lighting, and brushwork to capture the subject's essence and personality. Artists often use mediums like oil, charcoal, or pastels to build texture and depth through layering and blending, reflecting centuries of artistic heritage. This approach contrasts with photorealistic portraits that rely heavily on digital tools or photographic references to achieve hyperrealistic detail.
Historical Evolution of Portrait Art
Photorealistic portrait art emerged in the late 20th century, driven by advances in photography and digital technology that enable artists to capture intricate details and lifelike textures with precision. Traditional portrait art, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece, relies on manual techniques using mediums like oil, charcoal, and pastels to convey personality and status through stylized or idealized representation. Over time, the shift from traditional to photorealistic portraits reflects a broader historical evolution where evolving tools and cultural values influence the emphasis on realism and technological integration in portraiture.
Key Differences in Style and Approach
Photorealistic portraits emphasize hyper-realistic detail and accuracy, often created using digital tools or meticulous brushwork that mimics photographic precision. Traditional portraits prioritize expressive brushstrokes, texture, and the artist's interpretation, reflecting historical techniques and emotional depth. The key difference lies in photorealism's focus on exact visual replication, whereas traditional portraits embrace stylistic individuality and artistic nuance.
Tools and Mediums Used in Both Types
Photorealistic portraits utilize advanced digital tools such as graphics tablets, software like Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter, and high-resolution digital brushes to achieve lifelike detail and texture. Traditional portraits rely on classical mediums including oil paints, charcoal, graphite, and pastels applied on canvas or paper, emphasizing manual techniques for shading and color blending. Both methods demand mastery of lighting, anatomy, and composition, though digital tools allow for greater precision and the ability to easily edit or layer elements compared to the permanence of traditional media.
Visual Impact: Realism versus Artistic Interpretation
Photorealistic portraits emphasize meticulous detail and lifelike accuracy, capturing every nuance to create a striking sense of realism that can evoke strong emotional responses. Traditional portraits, meanwhile, prioritize artistic interpretation through brushwork, color, and composition, offering a unique, subjective perspective that often highlights the artist's style and emotional connection to the subject. The visual impact of photorealism lies in its precision and immediacy, while traditional portraits communicate depth through creative expression and abstraction.
Skillset and Training Requirements
Photorealistic portrait artists require advanced proficiency in digital tools such as Photoshop and graphic tablets, alongside traditional drawing skills to achieve hyper-realistic textures and lighting effects. Traditional portrait artists rely heavily on classical techniques including charcoal, oil painting, and meticulous brushwork, demanding extensive training in anatomy, color theory, and fine motor skills. Mastery in photorealistic art often involves continuous software adaptation and digital workflow efficiency, while traditional portraiture emphasizes years of study in hands-on materials and historical art styles.
Popularity and Market Trends
Photorealistic portraits have surged in popularity due to advancements in digital art technology, appealing to collectors seeking lifelike accuracy and modern aesthetics. Traditional portraits maintain steady demand, particularly among buyers valuing classic techniques and historical authenticity. Market trends indicate a growing preference for photorealistic works in contemporary art auctions and online platforms, while traditional art continues to hold significant value in galleries and private collections.
Choosing the Right Style for Your Portrait
Selecting between photorealistic and traditional portrait styles depends on the desired emotional impact and artistic expression. Photorealistic portraits emphasize precise detail and lifelike accuracy using digital or hyperrealistic techniques, ideal for capturing true-to-life representations. Traditional portraits, often created with classical mediums like oil or charcoal, convey mood and personality through brushstrokes and interpretative elements, making them perfect for conveying artistry and timeless character.
Photorealistic Portrait Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com