Minimalism focuses on simplicity and intentional living by eliminating excess and prioritizing what truly matters. This approach can enhance your mental clarity, reduce stress, and create a more organized and peaceful environment. Discover how adopting minimalism can transform your lifestyle in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
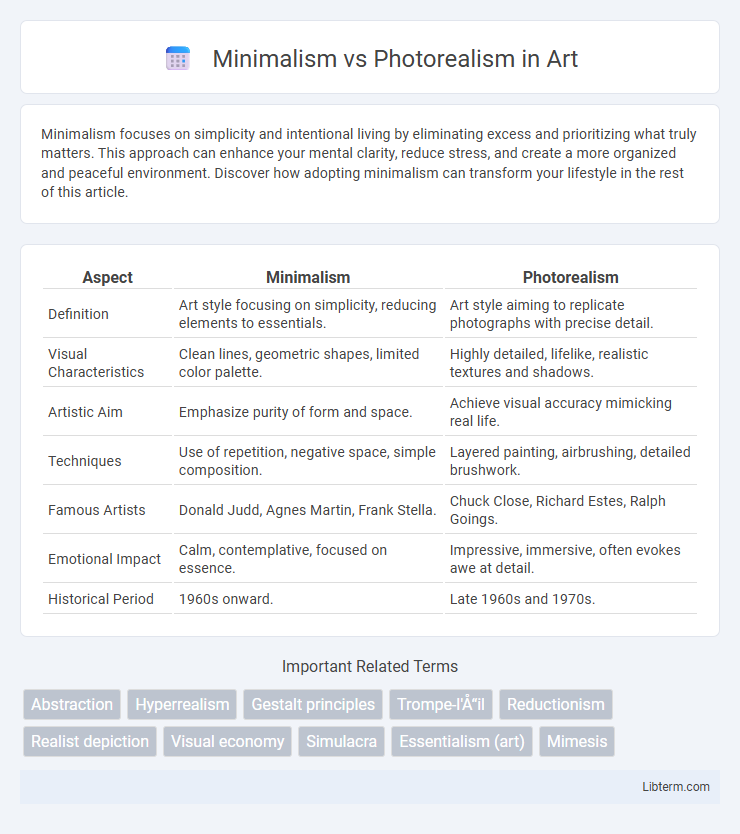
| Aspect | Minimalism | Photorealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style focusing on simplicity, reducing elements to essentials. | Art style aiming to replicate photographs with precise detail. |
| Visual Characteristics | Clean lines, geometric shapes, limited color palette. | Highly detailed, lifelike, realistic textures and shadows. |
| Artistic Aim | Emphasize purity of form and space. | Achieve visual accuracy mimicking real life. |
| Techniques | Use of repetition, negative space, simple composition. | Layered painting, airbrushing, detailed brushwork. |
| Famous Artists | Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, Frank Stella. | Chuck Close, Richard Estes, Ralph Goings. |
| Emotional Impact | Calm, contemplative, focused on essence. | Impressive, immersive, often evokes awe at detail. |
| Historical Period | 1960s onward. | Late 1960s and 1970s. |
Understanding Minimalism in Art and Design
Minimalism in art and design emphasizes simplicity, using limited elements such as basic shapes, monochromatic palettes, and clean lines to create a sense of clarity and focus. This movement prioritizes the essence of objects, stripping away extraneous details to highlight form and function. Minimalism's reductionist approach contrasts sharply with photorealism's detailed and highly representational techniques.
Defining Photorealism: Art That Imitates Life
Photorealism is an art movement characterized by the meticulous replication of photographic images, emphasizing extreme detail and precision to imitate real-life scenes. This style focuses on rendering textures, lighting, and reflections with high fidelity, often producing works indistinguishable from high-resolution photographs. Unlike Minimalism, which embraces simplicity and abstraction, Photorealism celebrates complexity and visual accuracy to capture the essence of everyday reality.
Core Principles of Minimalism
Minimalism emphasizes simplicity, using clean lines, limited color palettes, and basic geometric shapes to create visual clarity and emotional impact. It prioritizes the essence of subjects by removing unnecessary details, promoting a sense of order and tranquility. This core approach contrasts with photorealism, which focuses on intricate detail and exact replication of real-world imagery.
Techniques and Characteristics of Photorealism
Photorealism employs advanced techniques such as airbrushing, fine brushwork, and photographic projection to achieve an extreme level of detail and precision, replicating the exact appearance of photographs. Characterized by meticulous attention to light, texture, and reflections, photorealistic artworks emphasize realism and optical accuracy, often portraying everyday scenes with striking clarity. In contrast to minimalism's simplicity and abstraction, photorealism demands technical skill to produce images that challenge the boundaries between painting and photography.
Historical Evolution: Minimalism vs Photorealism
Minimalism emerged in the late 1950s as a reaction against abstract expressionism, emphasizing simplicity, geometric forms, and the reduction of color and detail to evoke pure artistic expression. Photorealism developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s, inspired by advancements in photography and a cultural shift toward hyper-realistic representation, focusing on meticulous detail and the illusion of photographic precision. Both movements reflect contrasting artistic philosophies: Minimalism's abstraction and Photorealism's detailed, almost mechanical reproduction of reality.
Emotional Impact: Simplistic vs Hyper-Realistic Art
Minimalism evokes emotional resonance through simplicity, using limited forms and colors to provoke introspection and calm, emphasizing mood over detail. Photorealism captures intricate visual reality with precise detail, creating intense emotional responses by mimicking real-life textures and lighting. The contrast lies in minimalism's abstraction fostering personal interpretation, while photorealism's exactness delivers immersive emotional immediacy.
Popular Artists: Minimalists and Photorealists
Minimalism is exemplified by artists like Donald Judd and Agnes Martin, who emphasize simplicity, geometric forms, and monochromatic palettes to evoke purity and clarity. Photorealism features figures such as Chuck Close and Richard Estes, who create highly detailed, lifelike paintings that replicate photographic precision and surface textures. Both movements challenge traditional art by focusing on different aspects: Minimalism on abstraction and essence, Photorealism on technical skill and visual accuracy.
Minimalism vs Photorealism in Modern Media
Minimalism in modern media emphasizes simplicity, using limited color palettes and abstract forms to evoke emotion and convey messages efficiently. Photorealism contrasts this by striving for hyper-detailed, lifelike imagery that captures every nuance of light and texture, often used in digital art, advertising, and video games to create immersive experiences. The tension between Minimalism's clarity and Photorealism's complexity defines a critical spectrum in contemporary visual culture and design trends.
Choosing Between Minimalism and Photorealism for Your Space
Choosing between minimalism and photorealism for your space depends on your aesthetic preferences and functional needs; minimalism emphasizes clean lines, simplicity, and a clutter-free environment, promoting tranquility and focus. Photorealism, on the other hand, offers highly detailed, lifelike imagery that can create dramatic visual impact and immersive atmospheres. Consider the room's purpose and lighting conditions, as minimalism suits open, bright areas that highlight negative space, while photorealism works well in spaces where rich detail and texture can be appreciated up close.
The Future of Artistic Expression: Minimalism or Photorealism?
The future of artistic expression increasingly balances between minimalism and photorealism, each offering distinct visual impact and emotional resonance. Minimalism emphasizes simplicity, clarity, and the essence of form, appealing to contemporary tastes for clean, thoughtful design that fosters introspection. In contrast, photorealism captures hyper-detailed representation, pushing technological advancements in digital and traditional media to create immersive realism, signaling a future where art replicates life with acute precision.
Minimalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com