Digital art transforms creativity through technology, allowing artists to produce vibrant and intricate works using software and digital tools. This medium offers unparalleled flexibility, from precise edits to limitless experimentation, making it accessible to both beginners and professionals. Explore the rest of the article to discover how digital art can enhance your creative journey.
Table of Comparison
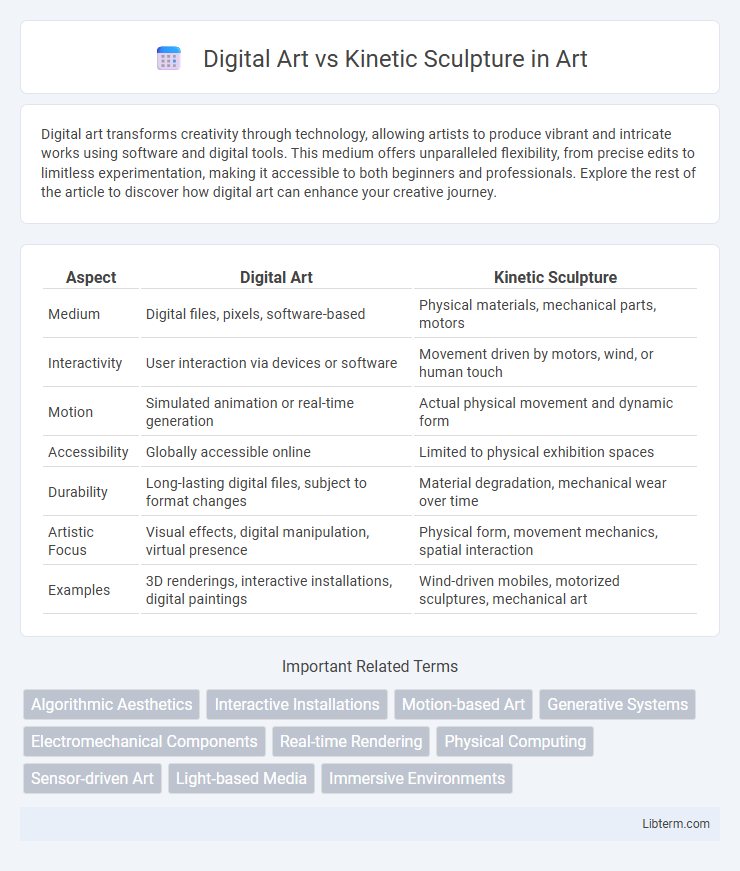
| Aspect | Digital Art | Kinetic Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Digital files, pixels, software-based | Physical materials, mechanical parts, motors |
| Interactivity | User interaction via devices or software | Movement driven by motors, wind, or human touch |
| Motion | Simulated animation or real-time generation | Actual physical movement and dynamic form |
| Accessibility | Globally accessible online | Limited to physical exhibition spaces |
| Durability | Long-lasting digital files, subject to format changes | Material degradation, mechanical wear over time |
| Artistic Focus | Visual effects, digital manipulation, virtual presence | Physical form, movement mechanics, spatial interaction |
| Examples | 3D renderings, interactive installations, digital paintings | Wind-driven mobiles, motorized sculptures, mechanical art |
Introduction to Digital Art and Kinetic Sculpture
Digital art leverages computer technology and software to create images, animations, and interactive installations, emphasizing virtual aesthetics and multimedia integration. Kinetic sculpture incorporates movement as a fundamental element, using mechanical, electrical, or natural forces to create dynamic, evolving artworks that engage physical space. Both art forms challenge traditional static expressions by introducing motion and interactivity, expanding the scope of contemporary artistic experiences.
Historical Evolution of Both Art Forms
Digital art emerged in the late 20th century with the advent of computer technology, allowing artists to create and manipulate images using software and digital tools. Kinetic sculpture dates back to the early 20th century, pioneered by artists like Alexander Calder, who introduced mobile sculptures that incorporated movement as a fundamental element. Both art forms reflect a shift from static traditional art toward dynamic expressions, with digital art evolving alongside rapid technological advancements and kinetic sculpture rooted in mechanization and motion.
Core Principles and Techniques
Digital art employs software algorithms, pixels, and virtual tools to create visually dynamic compositions, emphasizing manipulation of digital media and interactivity. Kinetic sculpture integrates mechanical components and physical movement, relying on principles of motion, balance, and spatial dynamics to engage viewers through tangible, changing forms. Both art forms explore time and transformation but utilize distinct mediums--digital code versus engineered motion--to evoke sensory experiences.
Materiality: Physical vs. Virtual Expressions
Digital art leverages virtual platforms and software to create intangible, dynamic images and experiences that exist primarily in digital form, emphasizing pixels and code over physical substance. Kinetic sculpture embodies physicality through mechanical movement and tactile materials such as metal, wood, and plastic, creating tangible, interactive artworks that occupy and engage space. The contrast between digital art's virtual expression and kinetic sculpture's material presence highlights differing sensory and experiential interactions in contemporary creative practices.
Interaction and Viewer Engagement
Digital art leverages interactive technologies such as touchscreens, sensors, and augmented reality to create immersive experiences that adapt to viewer input, enhancing engagement through personalized interaction. Kinetic sculpture captivates audiences by incorporating movement driven by motors, wind, or manual manipulation, offering a tangible and dynamic sensory experience that invites physical or visual interaction. Both mediums prioritize viewer participation, but digital art emphasizes virtual responsiveness while kinetic sculpture focuses on physical motion and spatial presence to foster connection.
Technological Influences and Innovations
Digital art harnesses cutting-edge software, virtual reality, and AI algorithms to create immersive, interactive experiences that evolve in real-time. Kinetic sculpture integrates advanced materials, robotics, and sensor technologies, enabling dynamic movement and responsive behavior within physical environments. Innovations in microcontrollers and automation systems drive both mediums toward increasingly sophisticated, multisensory expressions.
Aesthetic Differences and Artistic Intent
Digital art emphasizes virtual and screen-based experiences, using pixels, algorithms, and software to create dynamic visuals and interactive environments. Kinetic sculpture relies on physical movement, employing mechanical components, motors, or natural forces to produce changing forms and spatial interaction. The artistic intent in digital art often explores themes of virtuality and data manipulation, while kinetic sculpture focuses on the tangible relationship between motion, space, and viewer perception.
Cultural Impact and Contemporary Relevance
Digital art reshapes cultural narratives by integrating technology with creative expression, reaching global audiences through virtual platforms and interactive media. Kinetic sculpture emphasizes physical movement and tangible interaction, engaging viewers in dynamic experiences that challenge traditional art forms. Both mediums influence contemporary culture by expanding artistic boundaries and reflecting societal shifts toward innovation and multisensory engagement.
Challenges and Future Directions
Digital art faces challenges related to rapid technological obsolescence and the need for consistent digital preservation practices to maintain artwork accessibility over time. Kinetic sculpture encounters mechanical wear and energy inefficiency while integrating advanced materials and interactive technologies to enhance viewer engagement. Future directions include merging augmented reality with kinetic elements and developing blockchain-based provenance systems to authenticate digital and kinetic artworks securely.
Conclusion: Bridging Digital and Kinetic Art
Digital art harnesses technology to create immersive, interactive experiences, while kinetic sculpture emphasizes physical movement and mechanical innovation. Bridging these forms integrates digital sensors and programming with tangible materials, expanding creative possibilities and audience engagement. This fusion redefines contemporary art by blending virtual dynamics with real-world motion.
Digital Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com