Oil paint offers rich, vibrant colors and a versatile medium for artists seeking depth and texture in their work. Its slow drying time allows for detailed blending and layering to achieve complex effects. Explore the rest of this article to master techniques and maximize your oil painting skills.
Table of Comparison
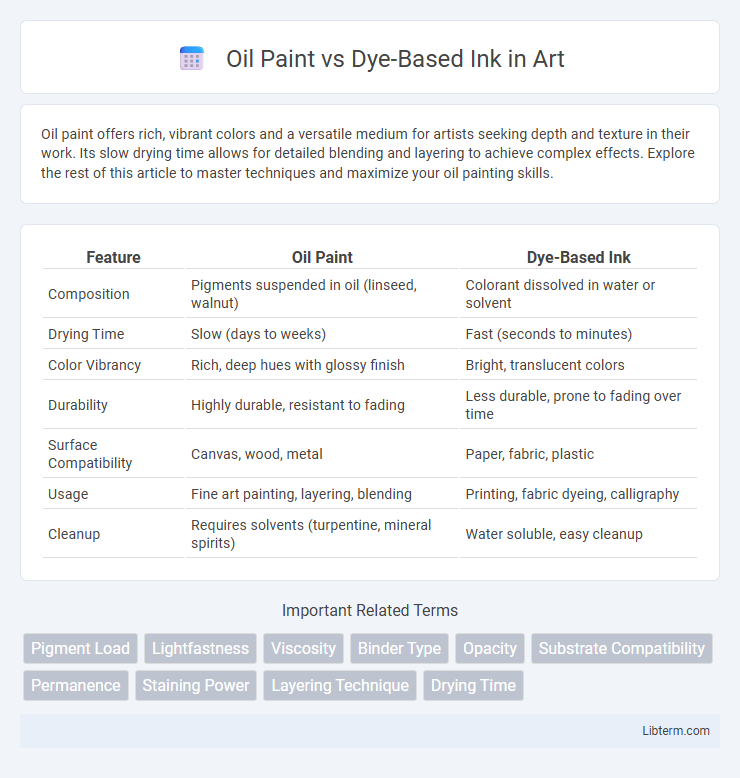
| Feature | Oil Paint | Dye-Based Ink |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pigments suspended in oil (linseed, walnut) | Colorant dissolved in water or solvent |
| Drying Time | Slow (days to weeks) | Fast (seconds to minutes) |
| Color Vibrancy | Rich, deep hues with glossy finish | Bright, translucent colors |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to fading | Less durable, prone to fading over time |
| Surface Compatibility | Canvas, wood, metal | Paper, fabric, plastic |
| Usage | Fine art painting, layering, blending | Printing, fabric dyeing, calligraphy |
| Cleanup | Requires solvents (turpentine, mineral spirits) | Water soluble, easy cleanup |
Introduction to Oil Paint and Dye-Based Ink
Oil paint consists of pigment particles suspended in drying oils like linseed, providing rich color depth and slow drying times ideal for blending and texture creation on canvas. Dye-based ink, composed of colorants dissolved in a liquid carrier, offers vibrant transparency and rapid drying, primarily suited for high-resolution printing and detailed artwork on paper. Each medium's chemical composition affects durability, application techniques, and final visual effects, influencing artists' choices based on project requirements.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Oil paint consists primarily of pigment particles suspended in drying oils such as linseed oil, which polymerize to form a durable, flexible film, making it resistant to water and light degradation. Dye-based inks, on the other hand, contain soluble colorants dissolved in a liquid solvent, typically water or alcohol, allowing for vibrant colors that penetrate paper fibers but exhibit less resistance to UV light and moisture. The chemical structure of oil paints involves long-chain fatty acid esters that undergo oxidative cross-linking, whereas dye-based inks rely on molecular dyes that do not form a solid film, resulting in differences in longevity and water resistance.
Color Vibrancy and Longevity
Oil paint exhibits superior color vibrancy due to its rich pigmentation and ability to retain intensity over time, making it ideal for artwork requiring lasting brilliance. Dye-based ink, while capable of producing bright colors initially, tends to fade faster when exposed to light and environmental factors, reducing overall longevity. The chemical stability of oil paints ensures that colors remain vivid for decades, whereas dye-based inks are more susceptible to degradation and color shift.
Application Techniques Compared
Oil paint requires layering and blending techniques that allow for rich texture and depth, making it ideal for detailed, tactile artwork. Dye-based ink, prized for its vibrant color saturation and fast drying time, is commonly applied through brushing, dipping, or printing, offering precision in fine lines and smooth gradients. Both mediums demand different drying considerations, with oil paint requiring extended curing periods and dye-based ink drying almost instantly, affecting workflow and finishing methods.
Surface Compatibility
Oil paint adheres well to non-porous surfaces such as canvas, wood, and metal due to its thick, viscous texture and slow drying time, allowing for deeper saturation and durability. Dye-based inks penetrate porous materials like paper and fabric, delivering vibrant colors but risking bleed or feathering on smooth, sealed surfaces. Surface preparation plays a crucial role; primed or treated surfaces enhance oil paint adhesion, while coated papers minimize dye ink spread for crisp, detailed results.
Drying Time and Workflow
Oil paint typically requires several days to dry due to its slow oxidation process, significantly impacting workflow by necessitating longer waiting periods between layers. Dye-based ink dries rapidly by absorption and evaporation, facilitating faster production cycles and immediate handling. Choosing between oil paint and dye-based ink influences project timelines, with oil paint favoring detailed, layered work and dye-based ink optimizing efficiency and speed.
Durability and Fade Resistance
Oil paint exhibits superior durability and fade resistance compared to dye-based ink, making it ideal for long-lasting applications. Its pigment particles are suspended in oil, which creates a robust barrier against UV rays and environmental factors that typically cause fading in dye-based inks. Dye-based inks tend to absorb into substrates and degrade faster when exposed to light and moisture, reducing their longevity in outdoor and high-traffic settings.
Artistic Styles and Usage
Oil paint offers rich, textured layers ideal for classical and impressionistic artistic styles, allowing for prolonged blending and detailed brushwork. Dye-based inks provide vibrant, translucent colors suited to illustration, calligraphy, and digital art reproduction, favoring precision and quick drying times. The choice between oil paint and dye-based ink depends on the desired finish, texture, and medium compatibility in various art forms.
Maintenance and Preservation
Oil paint offers superior longevity and resistance to fading due to its chemical stability and slow drying process, making it ideal for artworks requiring long-term preservation. Dye-based inks, while vibrant and quick-drying, are more prone to color degradation and require careful storage away from direct sunlight and humidity to maintain their appearance. Proper maintenance of oil paintings involves controlled environments with stable temperature and humidity, whereas dye-based ink prints benefit from archival-quality paper and UV-protective coatings to extend lifespan.
Cost and Accessibility
Oil paint typically has a higher upfront cost due to the quality of pigments and the complexity of production, making it less accessible for beginners or casual artists. Dye-based inks are generally more affordable and widely available, often found in standard ink cartridges and craft supplies. The affordability and ease of use of dye-based inks make them a popular choice for everyday projects and mass production printing.
Oil Paint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com