Expressionism emphasizes intense emotional experience over physical reality, using bold colors and distorted forms to convey inner feelings. This art movement, flourishing in the early 20th century, challenged traditional aesthetics by prioritizing subjective perspective and psychological depth. Discover how expressionism transformed art and influenced modern creativity by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
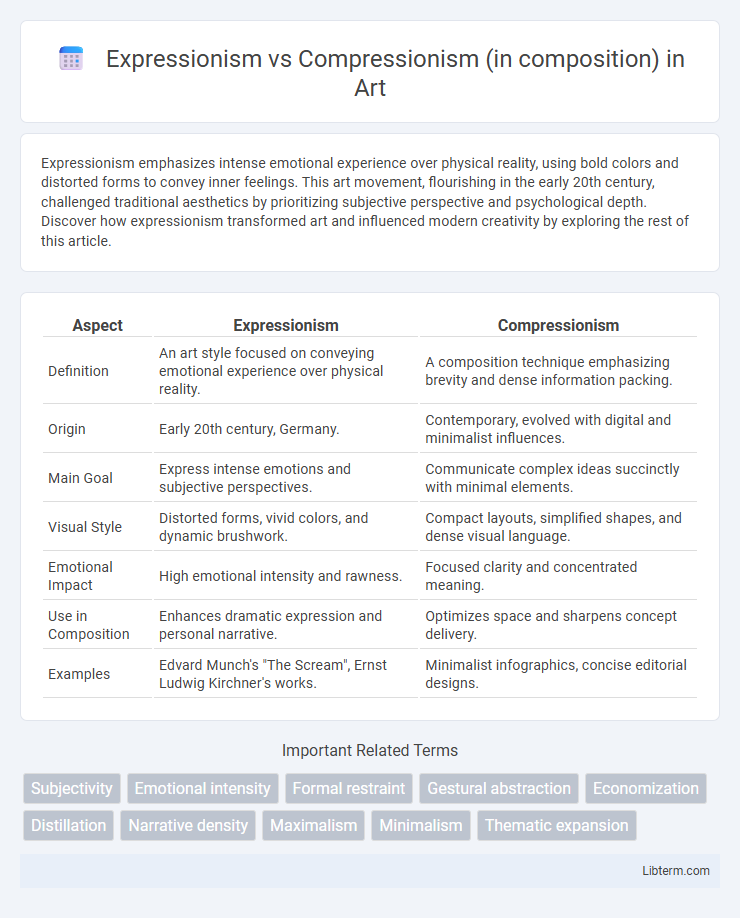
| Aspect | Expressionism | Compressionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An art style focused on conveying emotional experience over physical reality. | A composition technique emphasizing brevity and dense information packing. |
| Origin | Early 20th century, Germany. | Contemporary, evolved with digital and minimalist influences. |
| Main Goal | Express intense emotions and subjective perspectives. | Communicate complex ideas succinctly with minimal elements. |
| Visual Style | Distorted forms, vivid colors, and dynamic brushwork. | Compact layouts, simplified shapes, and dense visual language. |
| Emotional Impact | High emotional intensity and rawness. | Focused clarity and concentrated meaning. |
| Use in Composition | Enhances dramatic expression and personal narrative. | Optimizes space and sharpens concept delivery. |
| Examples | Edvard Munch's "The Scream", Ernst Ludwig Kirchner's works. | Minimalist infographics, concise editorial designs. |
Understanding Expressionism in Composition
Expressionism in composition emphasizes intense emotional expression through dissonance, atonality, and unconventional structures, seeking to convey inner psychological states rather than external reality. Composers like Arnold Schoenberg pioneered Expressionism, utilizing techniques such as twelve-tone rows to break free from traditional harmony and tonality. This approach contrasts with Compressionism, which prioritizes concise, tightly structured musical ideas over the expansive emotional exploration typical of Expressionist works.
Defining Compressionism: A Modern Approach
Compressionism in composition emphasizes brevity and intensity by distilling musical ideas into concise, impactful motifs that convey emotion with minimal elaboration. Unlike Expressionism, which often explores extended, complex emotional narratives through dissonance and dynamic contrasts, Compressionism seeks clarity and immediacy, focusing on streamlined structures and sharp contrasts. This modern approach blends traditional compositional techniques with innovative textures to create music that is both accessible and profound.
Historical Origins and Influences
Expressionism in composition emerged in early 20th-century Europe, rooted in the rejection of traditional tonality and influenced by the psychological and emotional intensity of artists like Arnold Schoenberg and Alban Berg. Compressionism, a less widely recognized movement, developed as a reaction to Expressionism, emphasizing economy of material and structural clarity, drawing inspiration from neoclassicism and minimalism in the mid-20th century. Both movements reflect contrasting responses to modernism, with Expressionism focusing on emotional depth and Compressionism prioritizing restraint and precision.
Key Characteristics of Expressionism
Expressionism in composition emphasizes intense emotional expression, dissonance, and unconventional structures to convey inner turmoil and subjective experiences. It often employs atonality, abrupt dynamic shifts, and complex rhythms to create a dramatic, sometimes unsettling atmosphere. This style contrasts with Compressionism, which focuses on brevity, clarity, and density of musical ideas within a compact framework.
Core Features of Compressionism
Compressionism in composition emphasizes concise, dense musical structures that prioritize economy of material and intense emotional impact within minimal duration. Unlike Expressionism, which explores expanded harmonic language and extreme emotional expression through dissonance and fragmented motifs, Compressionism condenses ideas to their essential elements, focusing on clarity, sharp contrasts, and rhythmic precision. Core features include compressed thematic development, streamlined textures, and a focus on structural unity over elaborate elaboration.
Techniques and Methods Compared
Expressionism in composition emphasizes intense emotional expression through atonality, dissonance, and dynamic contrasts, utilizing techniques like Sprechstimme and free rhythm to break traditional harmonic and structural boundaries. Compressionism, conversely, focuses on distilling musical ideas into concise, tightly structured forms, often employing repetitive motifs, minimalist textures, and precise rhythmic patterns to create clarity and intensity. While Expressionism explores expansive psychological depth and chaos, Compressionism prioritizes economy of means and concentrated musical narratives.
Influential Composers and Works
Expressionism in composition is characterized by atonal and dissonant styles, prominently advanced by Arnold Schoenberg with works like "Pierrot Lunaire," which revolutionized early 20th-century music through its emotional intensity and innovative use of Sprechstimme. Compressionism, often linked to composers such as Gyorgy Ligeti, emphasizes dense textures and micro-polyphonic techniques, exemplified in pieces like "Atmospheres," which create immersive sonic landscapes through intricate layering and rhythmic complexity. Both movements significantly shaped modern music, contrasting emotional expressionism with structural condensation in their compositional approaches.
Emotional Impact: Expressiveness vs. Economy
Expressionism in composition emphasizes vivid emotional intensity and dramatic expressiveness, using extended techniques and dynamic contrasts to evoke profound feelings. Compressionism prioritizes economy and precision, focusing on minimalistic elements that convey emotions succinctly without excess, achieving impactful restraint. Both styles harness emotional impact uniquely--Expressionism through expansive, raw expressiveness, and Compressionism through concentrated, distilled emotional clarity.
Critical Reception and Legacy
Expressionism in composition received mixed critical reception due to its intense emotional distortion and dissonance, which some audiences found challenging, while others praised its innovative exploration of psychological depth. Compressionism, characterized by its concise structures and concentrated thematic material, was lauded for its clarity and precision but occasionally criticized for perceived austerity. Both movements significantly influenced modern music, with Expressionism shaping avant-garde and experimental approaches, and Compressionism contributing to minimalist and neo-classical trends.
Choosing Between Expressionism and Compressionism
Choosing between Expressionism and Compressionism in composition hinges on the desired emotional impact and structural clarity; Expressionism emphasizes intense, raw emotions and individual perception through bold, often dissonant soundscapes, while Compressionism prioritizes concise, structured elements that condense thematic material into dense, tightly woven motifs. Composers inclined toward vivid, expansive emotional exploration favor Expressionism, whereas those seeking precision, balance, and thematic economy lean toward Compressionism. Understanding each style's core principles enables composers to strategically align their creative goals with the appropriate compositional approach.
Expressionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com