Woodcut is a traditional printmaking technique that involves carving an image into a wooden block, applying ink, and pressing it onto paper to create bold, textured prints. This method has been used for centuries to produce intricate artworks and illustrations with distinct contrast and detail. Discover how woodcut techniques evolved and how you can create your own stunning prints in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
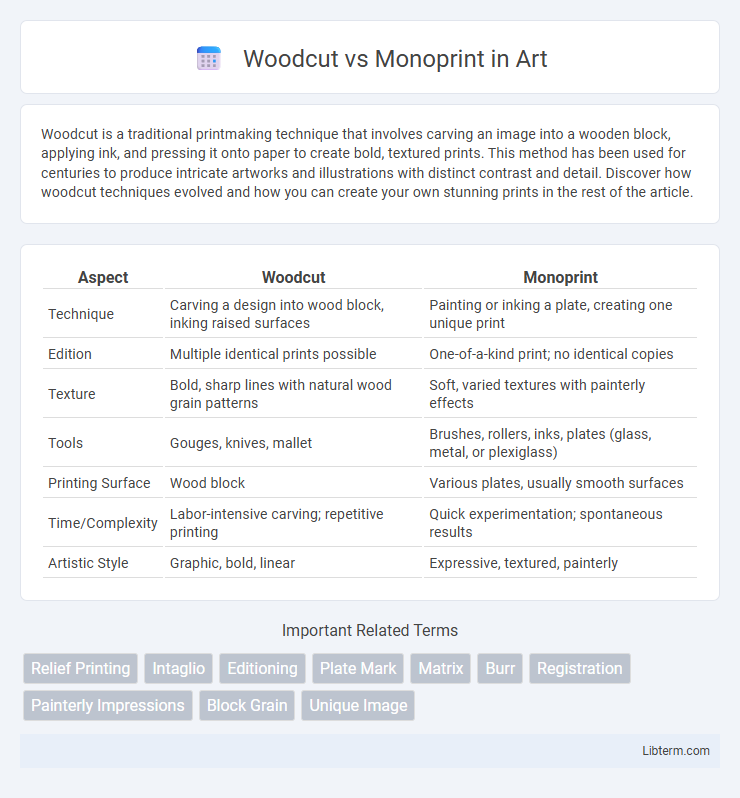
| Aspect | Woodcut | Monoprint |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Carving a design into wood block, inking raised surfaces | Painting or inking a plate, creating one unique print |
| Edition | Multiple identical prints possible | One-of-a-kind print; no identical copies |
| Texture | Bold, sharp lines with natural wood grain patterns | Soft, varied textures with painterly effects |
| Tools | Gouges, knives, mallet | Brushes, rollers, inks, plates (glass, metal, or plexiglass) |
| Printing Surface | Wood block | Various plates, usually smooth surfaces |
| Time/Complexity | Labor-intensive carving; repetitive printing | Quick experimentation; spontaneous results |
| Artistic Style | Graphic, bold, linear | Expressive, textured, painterly |
Introduction to Woodcut and Monoprint Techniques
Woodcut is a relief printmaking technique where artists carve images into a wooden block, leaving raised areas to receive ink and transfer the design onto paper. Monoprint involves creating a unique, one-of-a-kind print by applying ink or paint onto a smooth surface and then pressing paper onto it, producing a singular image with no exact duplicates. Both methods offer distinct textures and artistic expressions, with woodcut emphasizing bold lines and monoprint showcasing fluid, painterly effects.
Historical Origins and Development
Woodcut, originating in China during the Tang Dynasty around the 7th century, is one of the oldest printmaking techniques, characterized by carving images into wooden blocks to create multiple reproductions. Monoprint, developed in the 17th century Europe, particularly Italy, introduced a unique approach by allowing only a single impression from a painted or inked plate, emphasizing spontaneity and individuality. The historical development of woodcuts laid the foundation for mass print distribution, while monoprints emerged as a more experimental and expressive art form within printmaking traditions.
Materials and Tools Required
Woodcut requires a wooden block, carving tools such as gouges and knives, and oil-based or water-based inks for printing. Monoprint involves a smooth, non-absorbent surface like glass or plexiglass, printing inks or paints, and tools like brayers, brushes, or rollers to create unique impressions. Both techniques benefit from a printing press or hand-burnishing tools to transfer ink onto paper.
Step-by-Step Creation Processes
Woodcut printing involves carving an image into a wooden block, applying ink to the raised surfaces, and pressing it onto paper to transfer the design. Monoprinting uses a smooth surface like glass or metal where artists apply ink or paint, manipulate it with brushes or tools, and then press paper onto the surface to create a single, unique print. The woodcut process emphasizes detailed carving and repeatability, while monoprint prioritizes spontaneity and uniqueness in each impression.
Visual Characteristics and Aesthetic Qualities
Woodcut prints exhibit bold, sharp lines and strong contrasts due to carved relief surfaces, resulting in a graphic, textured appearance with clear, repeating patterns. Monoprints offer unique, painterly visuals with soft, blended colors and spontaneous textures, creating one-of-a-kind images marked by fluidity and expressive depth. The tactile, structured quality of woodcuts contrasts with the unpredictable, dynamic aesthetic of monoprints, reflecting distinct artistic techniques and visual impacts.
Advantages of Woodcut Printing
Woodcut printing offers distinct advantages such as durability of the carved blocks, allowing for multiple high-quality prints with consistent detail. The technique produces bold, graphic images with strong contrast, ideal for clear and impactful visual communication. Woodcut's tactile texture and traditional craftsmanship appeal to collectors and artists seeking authentic, timeless artwork.
Unique Features of Monoprinting
Monoprinting stands out for its ability to produce one-of-a-kind prints by varying ink application and pressure on a smooth surface, unlike woodcut which uses carved wooden blocks for repeated patterns. It allows artists to experiment with textures, colors, and layering techniques, resulting in spontaneous and unpredictable outcomes. This versatility makes monoprinting ideal for expressing individual artistic expressions and dynamic visual effects.
Artistic Applications and Styles
Woodcut techniques excel in producing bold, graphic images with strong lines and textures ideal for traditional and narrative art styles, often emphasizing contrast and intricate patterns. Monoprint offers unique, one-of-a-kind prints with fluid, painterly effects that suit experimental and abstract artistic expressions, allowing spontaneous variations in color and form. Both methods embrace tactile processes but differ in visual outcomes: woodcut embodies structured repetition, while monoprint thrives on singular, expressive impressions.
Notable Artists and Influential Works
Albrecht Durer remains a seminal figure in woodcut art, with masterpieces like "The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse" showcasing intricate detail and masterful line work. In contrast, monoprint pioneers such as Edgar Degas explored expressive possibilities through works like "Woman at a Window," highlighting unique textures and spontaneous effects. The distinct approaches of these artists emphasize woodcut's precision and monoprint's singular experimental quality within printmaking history.
Choosing Between Woodcut and Monoprint
Choosing between woodcut and monoprint techniques depends on the desired artistic outcome and production process. Woodcut offers high durability and distinct, bold textures suitable for multiple reproductions, while monoprint provides unique, one-of-a-kind impressions with varied textures and spontaneity. Artists seeking reproducibility and strong graphic qualities often prefer woodcut; those valuing experimental effects and singular prints typically opt for monoprint.
Woodcut Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com