Glazing enhances the energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal of windows by incorporating multiple glass panes or specialized coatings that reduce heat transfer and improve insulation. Modern glazing techniques can significantly lower your energy bills while providing increased comfort and noise reduction. Discover how different glazing options can transform your space in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
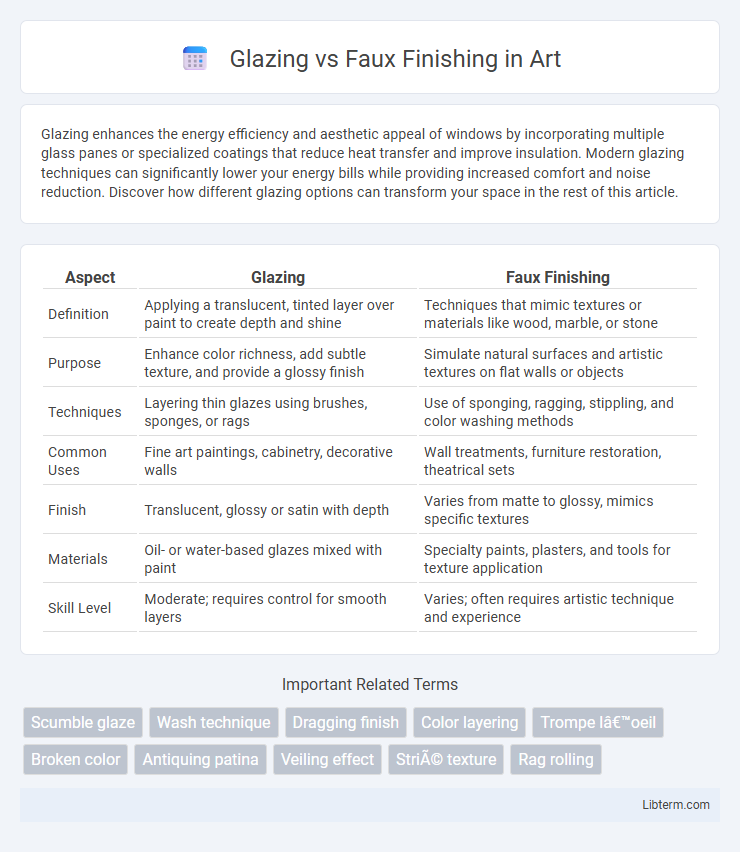
| Aspect | Glazing | Faux Finishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a translucent, tinted layer over paint to create depth and shine | Techniques that mimic textures or materials like wood, marble, or stone |
| Purpose | Enhance color richness, add subtle texture, and provide a glossy finish | Simulate natural surfaces and artistic textures on flat walls or objects |
| Techniques | Layering thin glazes using brushes, sponges, or rags | Use of sponging, ragging, stippling, and color washing methods |
| Common Uses | Fine art paintings, cabinetry, decorative walls | Wall treatments, furniture restoration, theatrical sets |
| Finish | Translucent, glossy or satin with depth | Varies from matte to glossy, mimics specific textures |
| Materials | Oil- or water-based glazes mixed with paint | Specialty paints, plasters, and tools for texture application |
| Skill Level | Moderate; requires control for smooth layers | Varies; often requires artistic technique and experience |
Introduction to Glazing and Faux Finishing
Glazing involves applying a translucent layer of paint or glaze over a base coat to create depth, texture, and subtle color variations in surfaces like walls, furniture, and cabinetry. Faux finishing replicates the appearance of materials such as wood, marble, or stone through techniques like sponging, ragging, or stippling, enhancing interior design with artistic effects. Both glazing and faux finishing offer versatile, customizable options to transform plain surfaces into visually rich, decorative elements.
What is Glazing?
Glazing is a decorative painting technique that involves applying a transparent or semi-transparent layer of color over a base coat to create depth, richness, and subtle texture on surfaces. This method enhances architectural details and adds an elegant, aged, or multidimensional effect to walls, furniture, or cabinetry by manipulating light reflection. Glazes are typically made by mixing paint with a glazing medium, allowing extended workability for smooth blending and precise application.
What is Faux Finishing?
Faux finishing is a decorative painting technique that mimics the appearance of materials such as marble, wood, or stone through layers of paint and glaze. Unlike glazing, which primarily enhances the underlying surface with translucent color, faux finishing creates textured and patterned effects to replicate natural surfaces. This technique involves multiple steps including base coating, layering, and texturing to achieve a realistic finish.
Key Differences Between Glazing and Faux Finishing
Glazing involves applying a transparent or semi-transparent layer over a base coat to create depth and subtle color variations, often enhancing architectural elements like trim or cabinetry. Faux finishing mimics the appearance of materials such as wood, marble, or stone, using various techniques like sponging, ragging, or color washing to create textured, decorative surfaces. The key difference lies in glazing's emphasis on translucency and subtlety versus faux finishing's goal of replicating distinct textures and complex visual effects.
Techniques Used in Glazing
Glazing techniques involve applying a transparent or semi-transparent layer of paint over a base coat to create depth, texture, and subtle color variations, often using brushes, sponges, or rags for application. Common methods include dry brushing, where minimal paint is used, and combing, which creates linear patterns, while layering multiple glaze coats enhances the visual richness and dimension. This technique contrasts with faux finishing, which mimics materials like marble or wood through more opaque and decorative paint treatments.
Techniques Used in Faux Finishing
Faux finishing techniques involve the application of multiple layers of paints and glazes using methods such as sponging, rag rolling, and color washing to create textured effects that mimic natural surfaces like marble, wood, or stone. Tools like brushes, trowels, and specialty rollers play a crucial role in achieving the desired depth and dimension characteristic of faux finishes. Mastery of layering and blending pigments allows for customized patterns and rich visual interest beyond traditional glazing methods.
Surface Preparation for Glazing and Faux Finishing
Surface preparation for glazing requires thorough cleaning, sanding, and priming to ensure a smooth base that enhances the transparency and depth of the glaze. Faux finishing demands meticulous surface repair and smoothing, often involving spackling and sanding to create an even canvas for techniques like sponging or ragging. Proper preparation in both methods is crucial for adhesion and achieving the desired visual texture and finish.
Pros and Cons of Glazing
Glazing enhances surfaces by adding depth and richness to paint, offering a subtle, translucent finish that can smooth imperfections and create visual interest. It is easy to apply and allows for layering effects, but it requires precise technique and longer drying times, which may increase project duration. However, glazing can be vulnerable to damage in high-traffic areas and may not provide the durability or texture variety that faux finishing techniques offer.
Pros and Cons of Faux Finishing
Faux finishing offers a versatile range of decorative techniques that can mimic textures like marble, wood, or stone, providing a cost-effective alternative to expensive materials. Pros include its ability to add depth, character, and a unique artistic touch to walls, enhancing interior aesthetics without structural changes. Cons involve the skill-intensive application process, potential for inconsistent results, and challenges in repair or touch-up compared to traditional paint or glazing methods.
Choosing the Right Method: Glazing vs Faux Finishing
Choosing between glazing and faux finishing depends on the desired texture and depth for your surface. Glazing offers a translucent, layered effect ideal for subtle color variation and enhancing architectural details, while faux finishing mimics materials like wood, marble, or stone, creating bold, decorative impacts. Consider the room's style, lighting, and repair ease when selecting the method to achieve the perfect aesthetic and durability.
Glazing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com