Museums serve as vital cultural institutions preserving history, art, and science, offering immersive experiences that deepen your understanding of the world. They showcase diverse collections and exhibits that engage visitors through interactive displays and educational programs. Explore the full article to discover how museums enrich your knowledge and inspire lifelong learning.
Table of Comparison
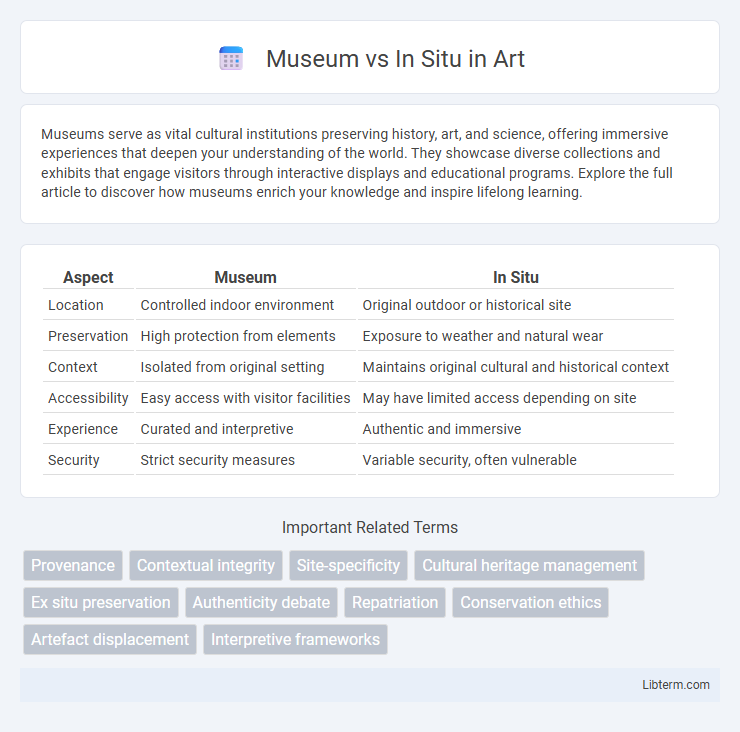
| Aspect | Museum | In Situ |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Controlled indoor environment | Original outdoor or historical site |
| Preservation | High protection from elements | Exposure to weather and natural wear |
| Context | Isolated from original setting | Maintains original cultural and historical context |
| Accessibility | Easy access with visitor facilities | May have limited access depending on site |
| Experience | Curated and interpretive | Authentic and immersive |
| Security | Strict security measures | Variable security, often vulnerable |
Introduction to Museum and In Situ Preservation
Museum preservation involves the careful collection, documentation, and display of artifacts in controlled environments designed to prevent deterioration, ensuring long-term protection and public accessibility. In situ preservation refers to maintaining cultural heritage and archaeological sites in their original locations, allowing for the protection of context and integrity while minimizing disturbance. Both methods are essential for conserving historical objects, with museums prioritizing artifact conservation and display, whereas in situ preservation emphasizes maintaining the authenticity of cultural landscapes.
Definitions and Key Differences
A museum is a curated space that preserves, displays, and interprets artifacts for public education and cultural enrichment, whereas in situ refers to objects or sites preserved in their original location without removal. Key differences include the context of preservation--museums relocate items for controlled environment and accessibility, while in situ emphasizes maintaining the artifact or archaeological site within its natural or historical setting. Museums enable close examination and broader public engagement, whereas in situ conservation prioritizes authenticity and environmental interaction.
Historical Context of Artifact Conservation
Museum conservation preserves artifacts within controlled environments, ensuring long-term protection from environmental factors such as humidity, light, and temperature fluctuations. In situ conservation maintains artifacts in their original locations, emphasizing the preservation of historical and cultural context while minimizing disruption to the surrounding environment. The choice between museum and in situ conservation depends on balancing artifact integrity, accessibility for research, and cultural significance within historical contexts.
Advantages of Museum-Based Preservation
Museum-based preservation offers controlled environmental conditions that protect artifacts from natural deterioration such as humidity, temperature fluctuations, and biological threats. Advanced conservation techniques and access to expert curators ensure the longevity and integrity of cultural and historical objects. Centralized collections also facilitate research, education, and public accessibility, enhancing cultural heritage appreciation.
Benefits of In Situ Conservation
In situ conservation preserves ecosystems and natural habitats, maintaining biodiversity and allowing species to evolve naturally within their environment. This approach supports ecological processes, genetic diversity, and the survival of endangered species by protecting them in their native context. It also facilitates ongoing scientific research and education by providing real-time data on species interactions and environmental changes.
Challenges Faced by Museums
Museums face challenges such as preserving artifacts while ensuring public accessibility, managing limited space for growing collections, and mitigating environmental factors that can cause deterioration. Conservation efforts require advanced technologies and expert knowledge to maintain the integrity of objects removed from their original contexts. Balancing educational outreach with ethical considerations about artifact removal contrasts sharply with in situ preservation, which maintains cultural heritage in its authentic setting but limits direct public interaction.
Limitations of In Situ Methods
In situ methods for cultural heritage preservation face limitations such as environmental exposure, which can accelerate deterioration due to fluctuating humidity, temperature, and pollution. Restricted access to fragile or remote sites hinders thorough documentation and conservation efforts, resulting in incomplete data capture. Furthermore, the inability to control external factors in situ often compromises the accuracy of analysis compared to the controlled conditions available in museums.
Case Studies: Museum vs In Situ Approaches
Case studies comparing museum and in situ approaches demonstrate distinct preservation outcomes and community impacts. Museums excel in artifact conservation and global accessibility, as illustrated by the British Museum's preservation of Egyptian relics, while in situ methods, seen in the Lascaux Cave, prioritize maintaining historical context and fostering local engagement. Analysis shows that integrating both approaches can optimize heritage conservation by balancing artifact protection with environmental and cultural authenticity.
Impact on Research and Education
Museums provide controlled environments with curated collections that facilitate detailed research, offering access to preserved artifacts and historical contexts essential for academic study and public education. In situ preservation allows researchers to study artifacts and sites in their original location, providing critical insights into spatial relationships and cultural context that are often lost when objects are removed. Both approaches complement each other by combining physical preservation with contextual understanding, enhancing multidisciplinary research and immersive learning experiences.
Future Trends in Heritage Preservation
Future trends in heritage preservation emphasize integrating Museum and In Situ approaches through advanced technologies such as 3D scanning, augmented reality, and digital archiving to enhance accessibility and education. The use of AI-driven conservation techniques supports real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of artifacts both within museum environments and at original sites. Collaborative frameworks involving local communities, governments, and global organizations are driving sustainable preservation strategies that balance cultural significance with environmental challenges.
Museum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com