Formalist theory emphasizes the analysis of a text's structure, style, and literary devices, focusing on how these elements create meaning independent of historical or biographical contexts. This approach dissects narrative techniques, language patterns, and symbolism to uncover deeper thematic insights within the work. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Formalist criticism can enhance your interpretation of literature.
Table of Comparison
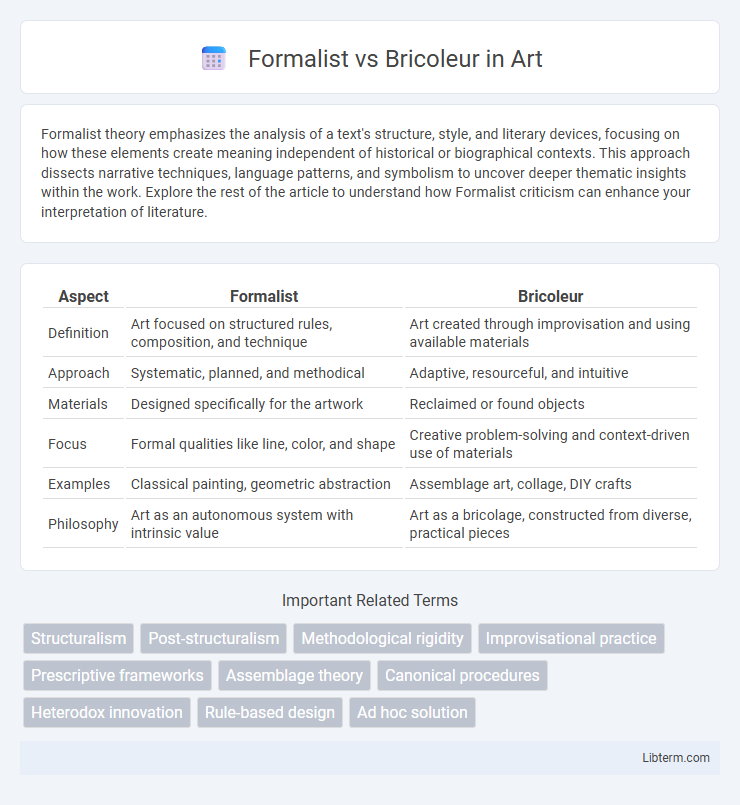
| Aspect | Formalist | Bricoleur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art focused on structured rules, composition, and technique | Art created through improvisation and using available materials |
| Approach | Systematic, planned, and methodical | Adaptive, resourceful, and intuitive |
| Materials | Designed specifically for the artwork | Reclaimed or found objects |
| Focus | Formal qualities like line, color, and shape | Creative problem-solving and context-driven use of materials |
| Examples | Classical painting, geometric abstraction | Assemblage art, collage, DIY crafts |
| Philosophy | Art as an autonomous system with intrinsic value | Art as a bricolage, constructed from diverse, practical pieces |
Defining Formalist and Bricoleur Approaches
Formalist approaches emphasize structured frameworks and pre-established methodologies to analyze and interpret data systematically, ensuring consistency and replicability in research. Bricoleur approaches rely on improvisation and the creative use of available tools and resources, adapting flexibly to evolving research contexts without strict adherence to predefined methods. The formalist method prioritizes logical rigor and clear procedural steps, while the bricoleur embraces methodological pluralism and contextual sensitivity in addressing complex problems.
Historical Background and Origins
The Formalist approach, rooted in early 20th-century structuralism, emphasizes universal rules and systematic frameworks derived from linguistic and anthropological studies by scholars like Ferdinand de Saussure. In contrast, the Bricoleur concept emerged from Claude Levi-Strauss's mid-20th-century work on myth and culture, highlighting a creative, improvisational method that uses available resources to solve problems. These origins reflect distinct epistemologies: Formalists seek coherent, fixed systems while Bricoleurs embrace adaptability and context-driven synthesis.
Core Principles of Formalism
Formalism centers on structured methods and consistent frameworks to solve problems, emphasizing systematic analysis and predefined rules. It prioritizes clear categorizations, logical sequencing, and adherence to theoretical models to ensure replicability and objectivity. Formalists value formal systems and algorithms to achieve precise and predictable outcomes in research or practice.
Key Characteristics of the Bricoleur Method
The Bricoleur method emphasizes improvisation and adaptability, utilizing available resources to solve problems creatively without relying on predefined rules or formal structures. Key characteristics include flexible thinking, practical problem-solving, and the ability to integrate diverse materials or concepts in innovative ways. This approach contrasts with the Formalist method by valuing contextual responsiveness and resourcefulness over rigid frameworks.
Comparative Analysis: Formalist vs Bricoleur
The Formalist approach emphasizes structured methodologies and predefined frameworks, ensuring consistency and replicability in research processes. In contrast, the Bricoleur employs a more adaptive and eclectic methodology, integrating diverse tools and perspectives to navigate complex, emergent problems. Comparative analysis reveals that Formalists prioritize systematic rigor, while Bricoleurs excel in flexibility and creativity, making each suitable for different research contexts depending on the need for precision or adaptability.
Strengths and Limitations of Formalism
Formalist approaches excel in providing structured, systematic analysis through clearly defined rules and frameworks, enabling consistent interpretation and reproducibility in diverse contexts. Their limitations lie in rigidity, often overlooking contextual nuances and the fluidity of meaning in dynamic environments. This can result in constrained adaptability and potential misinterpretation when applied to complex, real-world phenomena that require flexibility and creativity.
Advantages and Challenges of Bricoleur Thinking
Bricoleur thinking leverages diverse resources and creative problem-solving, enabling flexibility and innovation in complex or uncertain environments. This approach balances multiple perspectives and adapts quickly, fostering unique solutions that formalist methods may overlook. However, challenges include potential lack of coherence, difficulty in justifying decisions systematically, and risks of inconsistent outcomes due to reliance on improvisation.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Formalist approaches in real-world applications emphasize structured methodologies and predefined theoretical frameworks, often seen in engineering project management where precise protocols guide outcomes. Bricoleur strategies thrive in dynamic environments such as startup innovation or crisis response, where improvisation and resourcefulness are essential to adapt tools and processes on the fly. Case studies in software development highlight formalists using standardized models like Waterfall, while bricoleurs employ agile methods to iteratively navigate uncertainties and evolving requirements.
Impact on Creative and Academic Practices
Formalist approaches emphasize structured methodologies and defined frameworks, enhancing precision and replicability in academic research but potentially limiting creative flexibility. Bricoleur practices embrace improvisation and resourcefulness, fostering innovative problem-solving and adaptive thinking crucial for breakthrough creativity. The interplay between formalist rigor and bricoleur adaptability drives dynamic advancements in both scholarly inquiry and artistic expression.
Choosing Between Formalist and Bricoleur Strategies
Choosing between Formalist and Bricoleur strategies depends on project complexity and resource availability. Formalist approaches excel in structured environments with clear objectives and standardized methods, optimizing predictability and efficiency. Bricoleur strategies thrive in dynamic contexts, leveraging creativity and adaptability to repurpose existing resources and address unforeseen challenges.
Formalist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com