Glaze and varnish are essential finishing touches that enhance the durability and appearance of various surfaces, such as wood, ceramics, and paintings. Glaze typically adds a glossy or satin sheen while providing a protective layer, whereas varnish offers a more robust coating that guards against moisture and wear. Explore the rest of this article to discover how choosing the right finish can transform your project and extend its lifespan.
Table of Comparison
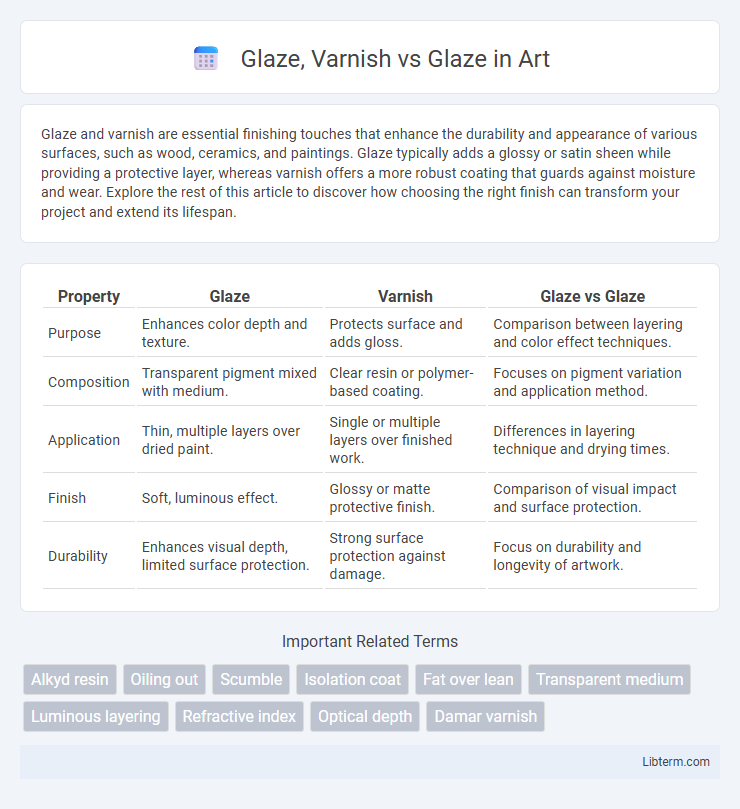
| Property | Glaze | Varnish | Glaze vs Glaze |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhances color depth and texture. | Protects surface and adds gloss. | Comparison between layering and color effect techniques. |
| Composition | Transparent pigment mixed with medium. | Clear resin or polymer-based coating. | Focuses on pigment variation and application method. |
| Application | Thin, multiple layers over dried paint. | Single or multiple layers over finished work. | Differences in layering technique and drying times. |
| Finish | Soft, luminous effect. | Glossy or matte protective finish. | Comparison of visual impact and surface protection. |
| Durability | Enhances visual depth, limited surface protection. | Strong surface protection against damage. | Focus on durability and longevity of artwork. |
Understanding Glaze: Definition and Purpose
Glaze is a transparent or translucent coating applied over a painted surface to add depth, richness, and a subtle sheen, enhancing the overall appearance and texture. Its primary purpose is to create effects such as softening details, increasing color complexity, and providing a protective layer without altering the underlying paint. Unlike varnish, which serves mainly as a protective finish, glaze is used for artistic expression and visual enhancement in painting and decorative finishes.
Key Characteristics of Glaze
Glaze is a transparent or semi-transparent coating that enhances the surface with depth, texture, and color richness, often used in ceramics and painting. It typically consists of glass-forming substances that fuse to the surface when heated, creating a durable, glossy, or matte finish. Unlike varnish, glaze primarily alters the appearance and texture rather than providing a thick protective layer, making it essential for decorative effects and surface sealing.
Introduction to Varnish: Definition and Uses
Varnish is a transparent, hard protective finish or film applied to wood, metal, or other materials to enhance durability and appearance while preventing damage from moisture and UV rays. Unlike glaze, which is often tinted or colored to add depth and texture, varnish primarily focuses on providing a clear, glossy, or matte seal that preserves the underlying surface. Common uses of varnish include furniture finishing, marine applications, and floor coatings, where long-lasting protection is essential.
Main Features of Varnish
Varnish is a high-performance HTTP accelerator designed for content-heavy dynamic websites, delivering fast content caching and increased web server efficiency. Key features include advanced caching mechanisms, flexible configuration with Varnish Configuration Language (VCL), and support for edge-side includes (ESI) to assemble web pages from their cached parts. Its ability to handle thousands of requests per second with minimal latency makes it ideal for optimizing website performance and scalability.
Glaze vs Varnish: Core Differences
Glaze and varnish serve distinct purposes in finishing surfaces, with glaze primarily used to enhance texture and depth by adding a translucent layer of color, while varnish provides a protective coating that seals and safeguards the material from damage. Varnish is typically clear and durable, offering resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV rays, whereas glaze emphasizes aesthetic appeal by highlighting details and creating a subtle sheen or shadow effect. Understanding the core differences between glaze and varnish is essential for selecting the right finish based on whether protection or decorative enhancement is the priority.
Application Techniques: Glaze vs Varnish
Glaze application involves using a thin, translucent layer of paint or stain that enhances texture and depth, often applied with brushes or sponges for subtle blending effects. Varnish, in contrast, is typically applied in multiple transparent coats using a clean brush or spray to create a durable, protective finish with varying levels of gloss. Understanding the differences in drying time, layering, and surface preparation is crucial for mastering the distinct techniques required for glaze versus varnish application.
Durability and Protection: Which Lasts Longer?
Glaze provides a thin, smooth coating that enhances the surface shine but generally offers less durability and protection compared to varnish. Varnish forms a thicker, harder protective layer, making it more resistant to scratches, moisture, and UV damage, thus lasting significantly longer. For long-term surface protection and durability, varnish is the superior choice over glaze.
Aesthetic Effects: Finish and Appearance Comparison
Glaze provides a translucent, glossy finish that enhances depth and richness by allowing underlying colors to show through, creating a layered, luminous effect ideal for artistic surfaces. Varnish, by comparison, offers a protective clear coat with variable gloss levels, ranging from matte to high-gloss, primarily emphasizing surface durability rather than depth. When focusing on aesthetic effects, glaze significantly alters the visual texture and color dynamics, while varnish mainly preserves the existing appearance with subtle enhancement of sheen and vibrancy.
Suitable Surfaces for Glaze and Varnish
Glaze is suitable for porous surfaces like wood and plaster, enhancing texture and depth by seeping into the material. Varnish is ideal for non-porous surfaces such as metal, ceramics, and painted wood, providing a protective, glossy, or matte finish. Both treatments can be selected based on the surface's absorbency and desired aesthetic effect.
Choosing the Right Option: Glaze or Varnish?
Choosing between glaze and varnish depends on the desired finish and protection level for your surface. Glaze offers a translucent, decorative effect that enhances texture and depth, ideal for artistic or resurfacing projects. Varnish provides a durable, clear protective coat that resists moisture, scratches, and UV damage, making it suitable for high-traffic or outdoor applications.
Glaze, Varnish Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com