Traditional painting embodies timeless techniques using natural materials like oils, acrylics, and watercolors to create rich, textured artwork. Mastering brushstrokes and color blending brings depth and emotion to each piece, reflecting cultural heritage and artistic expression. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how you can develop your skills and appreciate the value of traditional painting.
Table of Comparison
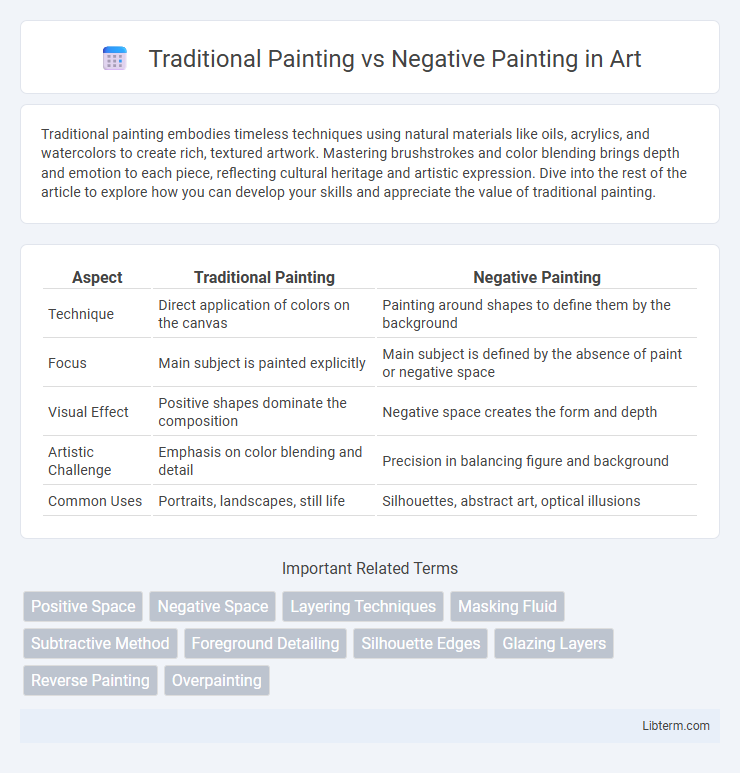
| Aspect | Traditional Painting | Negative Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Direct application of colors on the canvas | Painting around shapes to define them by the background |
| Focus | Main subject is painted explicitly | Main subject is defined by the absence of paint or negative space |
| Visual Effect | Positive shapes dominate the composition | Negative space creates the form and depth |
| Artistic Challenge | Emphasis on color blending and detail | Precision in balancing figure and background |
| Common Uses | Portraits, landscapes, still life | Silhouettes, abstract art, optical illusions |
Introduction to Traditional and Negative Painting
Traditional painting involves applying pigments directly onto a surface to depict objects, landscapes, or abstract compositions using techniques such as oil, acrylic, or watercolor. Negative painting, by contrast, emphasizes the space around and between subjects, painting the background or negative space to define the main forms indirectly. Both techniques require mastery of color theory and composition but differ fundamentally in approach and visual impact.
Historical Background of Both Techniques
Traditional painting traces its origins to ancient civilizations, where artists utilized direct application of pigments to surfaces, evident in Egyptian tombs and Renaissance masterpieces. Negative painting, with roots in prehistoric rock art and indigenous practices, involves painting around the subject to define it through contrasting backgrounds rather than direct rendering. Both techniques evolved through cultural exchanges and technological advancements, reflecting diverse artistic philosophies across historical periods.
Core Principles of Traditional Painting
Traditional painting centers on applying pigments directly to a surface to create forms and colors through techniques such as layering, blending, and brushwork. It emphasizes precise representation, balance, and the manipulation of light and shadow to achieve depth and realism. Core principles include composition, color theory, and texture, all aimed at portraying subjects with clarity and intentionality.
Understanding the Concept of Negative Painting
Negative painting emphasizes the use of the background space to create shapes and forms, contrasting with traditional painting, which relies on directly applying color to depict objects. This technique involves painting around the subject to define it, enhancing visual interest through the interplay of positive and negative space. Understanding negative painting requires recognizing how outlines and forms emerge from the untouched or carefully painted surrounding area rather than the object itself.
Materials and Tools Used in Both Styles
Traditional painting employs brushes, canvas, and pigments like oil, acrylic, or watercolor to build images by applying color directly onto the surface. Negative painting involves using resist materials such as wax or gutta and dyes or inks, where the artist paints around the subject to define shapes by contrast rather than filling them in. Both styles require precise control of mediums, but traditional painting emphasizes additive color application while negative painting relies on selective preservation of the base material's color.
Visual Effects and Artistic Outcomes
Traditional painting emphasizes layering colors directly onto the canvas to create form and depth, resulting in vibrant and detailed visuals with clear subject focus. Negative painting utilizes the space around the subject by painting the background or surrounding areas, enhancing contrast and highlighting shapes through absence of direct coloration. This technique produces dynamic compositions where the interplay of positive and negative spaces drives artistic expression and visual intrigue.
Techniques and Step-by-Step Processes
Traditional painting techniques involve applying layers of pigment directly onto a surface to create an image, often starting with a sketch, followed by underpainting, layering, and detailing to build color and texture. Negative painting, in contrast, focuses on painting around the subject rather than the subject itself, emphasizing the background or negative space to define shapes and forms, which requires careful planning and control of edges. The step-by-step process for traditional painting typically begins with drawing outlines, adding base colors, shading, and highlighting, whereas negative painting starts by blocking in background tones, gradually revealing the subject through surrounding color transitions and contrasts.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Approach
Traditional painting offers rich texture and depth through layering pigments, allowing precise control over color blending and brushwork, which suits realistic and detailed artwork. Challenges include longer drying times and difficulty correcting mistakes without affecting underlying layers. Negative painting emphasizes defining shapes by painting around them, enhancing contrast and creating unique visual effects, but it demands careful planning and lacks the flexibility to easily alter forms once painted.
Renowned Artists and Key Examples
Renowned artists in traditional painting include Leonardo da Vinci, known for the "Mona Lisa," and Vincent van Gogh, famous for "Starry Night," characterized by direct application of colors to depict subjects. Negative painting, rooted in Indigenous and folk art traditions, uses the background to define shapes and forms, with examples such as the Pomo basketry patterns and traditional Indian Warli art. Key distinctions between traditional and negative painting lie in technique and perspective, with celebrated practitioners exemplifying each method's cultural and artistic significance.
Deciding Which Technique Suits Your Art Style
Traditional painting emphasizes adding colors and details to create an image, ideal for artists who prefer layering and direct representation. Negative painting focuses on painting around the subject to define shapes and space, suited for those who enjoy abstract or fluid compositions. Choose traditional methods for precise control and realism, while negative painting supports creativity in form and background interaction.
Traditional Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com