Collagraph and woodcut are printmaking techniques that involve creating images by carving or assembling materials on a surface to transfer ink onto paper. Collagraph uses various textures and materials glued to a base, offering rich, tactile results, while woodcut relies on carving designs into wooden blocks for bold, graphic prints. Explore the article to discover how these methods can expand your artistic expression.
Table of Comparison
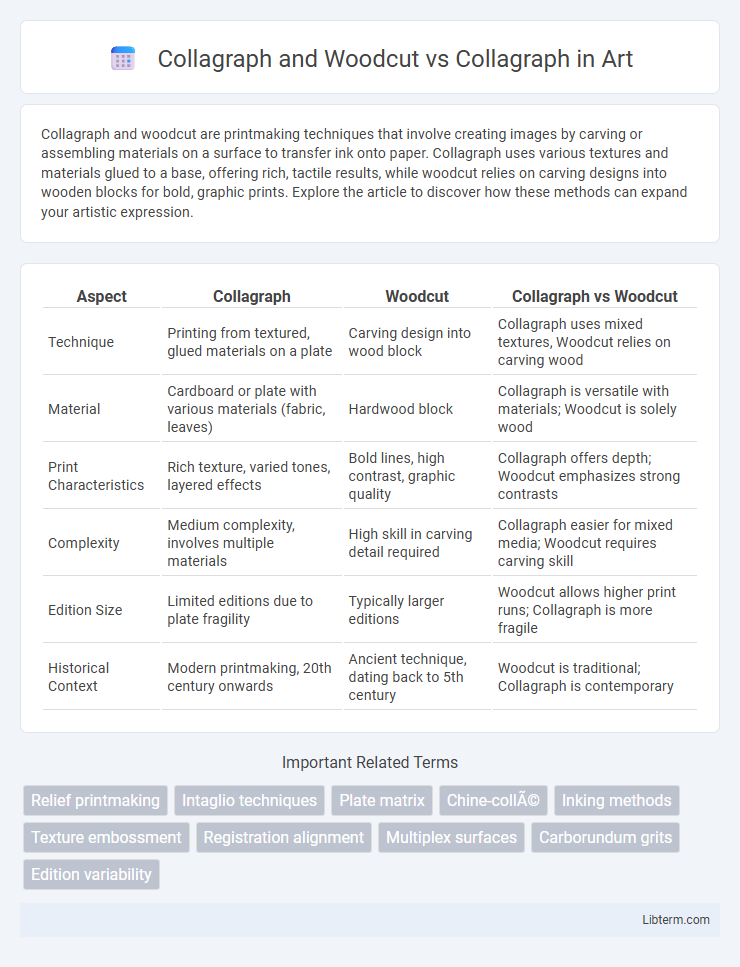
| Aspect | Collagraph | Woodcut | Collagraph vs Woodcut |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technique | Printing from textured, glued materials on a plate | Carving design into wood block | Collagraph uses mixed textures, Woodcut relies on carving wood |
| Material | Cardboard or plate with various materials (fabric, leaves) | Hardwood block | Collagraph is versatile with materials; Woodcut is solely wood |
| Print Characteristics | Rich texture, varied tones, layered effects | Bold lines, high contrast, graphic quality | Collagraph offers depth; Woodcut emphasizes strong contrasts |
| Complexity | Medium complexity, involves multiple materials | High skill in carving detail required | Collagraph easier for mixed media; Woodcut requires carving skill |
| Edition Size | Limited editions due to plate fragility | Typically larger editions | Woodcut allows higher print runs; Collagraph is more fragile |
| Historical Context | Modern printmaking, 20th century onwards | Ancient technique, dating back to 5th century | Woodcut is traditional; Collagraph is contemporary |
Introduction to Collagraph and Woodcut Techniques
Collagraph and woodcut are printmaking techniques that utilize different materials and processes to create textured prints. Collagraph involves building up a collage of materials on a rigid surface, such as cardboard or wood, which is then inked and pressed onto paper to produce varied textures and tonal effects. Woodcut, on the other hand, is a relief printing technique where the artist carves an image into the surface of a wooden block, with the raised areas representing the inked design, resulting in bold contrasts and linear patterns.
What is Collagraph Printing?
Collagraph printing is a versatile printmaking technique where materials of varying textures are glued onto a rigid surface, such as cardboard or wood, and then inked and pressed onto paper. Unlike woodcut, which involves carving into a wooden block to create a relief surface, collagraph allows for a collage-based approach combining different textures for more intricate and layered prints. This method offers artists greater flexibility in producing detailed, tactile images by layering inks and materials instead of solely relying on carving depth and lines.
Explaining the Woodcut Printmaking Method
Woodcut printmaking involves carving an image into a wooden block, where the raised areas hold ink while the recessed parts remain ink-free, allowing for bold and high-contrast prints. This relief printing technique contrasts with collagraph, which uses boards assembled from various textured materials to create a plate. Woodcut emphasizes precise carving skills and produces sharp, graphic lines compared to collagraph's textured and layered effects.
Key Differences Between Collagraph and Woodcut
Collagraph and woodcut differ primarily in technique and material; collagraph involves assembling various textured materials on a plate to create a collage, while woodcut requires carving an image directly into a wood block. In collagraph, the plate can be built up with adhesive elements and then inked, allowing for a wide range of textures and tonal variations, whereas woodcut relies on removing parts of the wood to create a relief image, producing bold, high-contrast prints. The key difference lies in collagraph's flexibility in materials and surface texture against woodcut's traditional, carved wooden matrix.
Materials and Tools: Collagraph vs Woodcut
Collagraph printing utilizes a variety of textured materials such as cardboard, fabric, leaves, and textured papers glued onto a rigid plate, often complemented by acrylic mediums and varnishes for durability and depth. In contrast, woodcut relies primarily on carving tools like gouges and knives to carve designs into a smooth wooden block, with careful selection of hardwoods such as cherry or maple to ensure fine detail and durability. While collagraph offers versatility in material choice allowing for diverse textures, woodcut demands skilled carving on specific wood types to create precise linear patterns.
Artistic Effects: Texture and Detail Comparison
Collagraph printmaking offers rich texture and depth through its layered, collage-like plates, creating dynamic, tactile surfaces that enhance visual complexity. Woodcut prints deliver bold, high-contrast imagery with distinct, sharp lines but usually exhibit less nuanced texture compared to collagraphs. The difference in artistic effects lies in collagraph's versatility for detailed textures versus woodcut's emphasis on crisp outlines and graphic clarity.
Creative Possibilities in Collagraph vs Woodcut
Collagraph offers broader creative possibilities compared to woodcut by allowing artists to experiment with a wide variety of textures and relief depths using glued materials like fabric, paper, and found objects. In contrast, woodcut is limited to carving into wood, which restricts texture variation and detail precision. The versatility of collagraph enables richer surface effects and layering, expanding artistic expression beyond the linear and bold contrasts typical of woodcut prints.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technique
Collagraph printing offers the advantage of rich texture and versatility by using mixed media materials to create plates, allowing for varied tonal effects and intricate details, but it can be time-consuming and requires careful preparation to avoid fragile plate damage. Woodcut, a traditional relief printmaking technique, provides bold, graphic contrasts and durability of the wooden block for repeated prints, yet it is limited by less subtlety in textures and can be physically demanding due to carving. Collagraph's flexibility in material choice contrasts with woodcut's robustness and ease of replication, making each suitable for different artistic goals depending on desired texture complexity and production scale.
Choosing Between Collagraph and Woodcut
Choosing between collagraph and woodcut depends on the desired texture and detail in printmaking; collagraph allows for a wide range of textures through the use of various materials glued to the plate, making it ideal for rich, tactile surfaces. Woodcut, an ancient relief printing technique, emphasizes strong, bold lines and contrasts, suitable for artists seeking graphic clarity and simplified shapes. For versatility in experimentation and mixed-media effects, collagraph is preferable, while woodcut excels in traditional, high-contrast imagery.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Printmaking Process
Choosing between collagraph and woodcut depends on the desired texture and detail in the artwork; collagraph offers rich, tactile surfaces through varied materials, while woodcut emphasizes bold, graphic lines created by carving. Artists seeking complex layering and mixed materials benefit from the versatility of collagraph, whereas those aiming for traditional, stark contrasts may prefer woodcut. Ultimately, understanding the distinct characteristics and technical requirements of each process ensures the selection aligns with the creative vision and production goals.
Collagraph and Woodcut Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com