Screen printing offers vibrant, long-lasting designs ideal for custom apparel and promotional products. This versatile technique uses a stencil and mesh screen to transfer ink onto various surfaces with precision and durability. Explore the full article to learn how screen printing can enhance Your branding and creative projects.
Table of Comparison
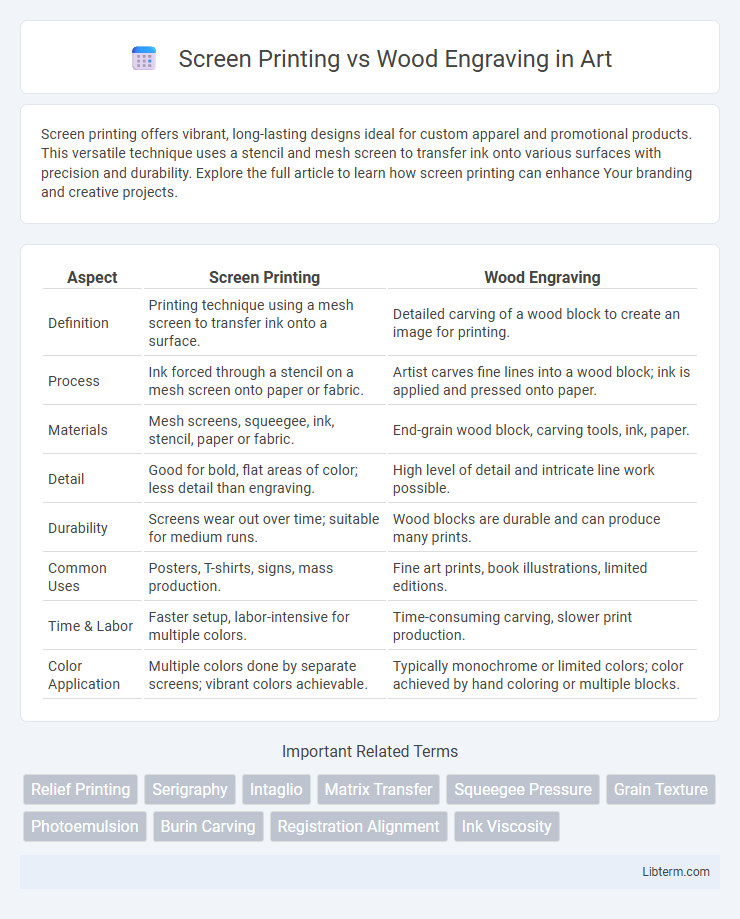
| Aspect | Screen Printing | Wood Engraving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Printing technique using a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a surface. | Detailed carving of a wood block to create an image for printing. |
| Process | Ink forced through a stencil on a mesh screen onto paper or fabric. | Artist carves fine lines into a wood block; ink is applied and pressed onto paper. |
| Materials | Mesh screens, squeegee, ink, stencil, paper or fabric. | End-grain wood block, carving tools, ink, paper. |
| Detail | Good for bold, flat areas of color; less detail than engraving. | High level of detail and intricate line work possible. |
| Durability | Screens wear out over time; suitable for medium runs. | Wood blocks are durable and can produce many prints. |
| Common Uses | Posters, T-shirts, signs, mass production. | Fine art prints, book illustrations, limited editions. |
| Time & Labor | Faster setup, labor-intensive for multiple colors. | Time-consuming carving, slower print production. |
| Color Application | Multiple colors done by separate screens; vibrant colors achievable. | Typically monochrome or limited colors; color achieved by hand coloring or multiple blocks. |
Introduction to Screen Printing and Wood Engraving
Screen printing is a versatile printing technique where ink is pushed through a stenciled mesh screen onto a surface, allowing for vibrant color application on textiles, paper, and ceramics. Wood engraving involves carving fine, detailed images into the end grain of hardwood blocks, producing high-definition prints with intricate line work ideal for book illustrations and fine art. Both methods offer distinct tactile and visual qualities suited to different artistic and commercial purposes.
Historical Background of Each Technique
Screen printing originated in ancient China during the Song Dynasty, evolving through Japanese Edo period craftsmanship before gaining widespread use in the early 20th century for commercial and artistic purposes. Wood engraving, developed in the late 18th century by Thomas Bewick in England, refined traditional woodcut techniques with fine detail by engraving the end grain of hardwood blocks, revolutionizing book illustration and printmaking. Both techniques have distinct historical trajectories, with screen printing rooted in textile and stencil arts, while wood engraving advanced print clarity and detail in publishing.
Materials and Tools Required
Screen printing requires a mesh screen, squeegee, photo emulsion, ink, and a flat surface such as fabric or paper, making it versatile for various materials like textiles, posters, and signage. Wood engraving demands a fine-grained hardwood block such as boxwood, specialized gravers or burins, and ink for transferring intricate designs onto paper or cardstock. The choice of materials and tools directly influences the detail, texture, and durability of the finished artwork in each printing technique.
Process Overview: How Screen Printing Works
Screen printing involves pushing ink through a fine mesh stencil onto a substrate, allowing for vibrant and durable designs on fabric, paper, or plastic. This process relies on a screen stretched over a frame with blocked-out areas that prevent ink passage, creating the desired image. Multiple layers of ink can be applied for detailed, multi-colored prints, making screen printing ideal for mass production and custom artwork.
Process Overview: How Wood Engraving Works
Wood engraving involves carving intricate designs into the end grain of hardwood blocks using specialized tools like burins, allowing for high detail and durability. The engraved areas remain raised to hold ink when pressed against paper, producing fine, crisp prints with distinct textures. This relief printing technique contrasts with screen printing, which uses a mesh stencil to transfer ink through open areas, offering broader coverage but less precision.
Visual Results and Artistic Styles
Screen printing produces vibrant, bold colors with sharp edges, making it ideal for graphic, pop art, and commercial designs. Wood engraving offers intricate detail and rich textures through fine lines and shading, suited for traditional, vintage, and illustrative styles. Visual results in screen printing emphasize flat color areas, while wood engraving highlights depth and tactile contrast.
Durability and Longevity of Printed Works
Screen printing offers high durability with thick ink layers that resist fading and cracking over time, making it ideal for long-lasting designs on fabrics and surfaces. Wood engraving produces detailed, tactile prints that age gracefully, but the fine lines and shallow grooves are more susceptible to wear and abrasion with extensive handling. Preservation of wood engraving prints often requires careful framing or protection, whereas screen printed works typically endure harsher conditions without significant degradation.
Applications and Common Uses
Screen printing excels in producing vibrant, durable designs on textiles, posters, and promotional materials, making it a staple in fashion, advertising, and product branding. Wood engraving is predominantly used for intricate illustrations, fine art prints, and detailed book covers, favored in traditional publishing and collectible art industries. Both techniques cater to different markets: screen printing targets mass production and commercial use, while wood engraving suits artisanal, high-detail applications.
Pros and Cons of Screen Printing vs Wood Engraving
Screen printing offers vibrant color accuracy and is cost-effective for large-volume production, but it lacks the fine detail achievable in wood engraving. Wood engraving provides intricate, high-resolution designs with a classic, tactile quality, though it is more time-consuming and expensive compared to screen printing. Screen printing excels in versatility across materials, while wood engraving is best suited for artisanal, limited-edition pieces with a premium finish.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Screen printing offers vibrant, durable colors ideal for mass production on fabrics and posters, while wood engraving provides intricate, timeless details perfect for limited editions and fine art prints. Evaluate project scope, material texture, and desired aesthetic: screen printing suits bold, colorful designs on flat surfaces, whereas wood engraving excels in detailed, monochromatic images on paper or wood. Consider production volume, cost, and artistic style to select the technique that best aligns with your project's goals and budget.
Screen Printing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com