Files are essential digital containers used to store, organize, and manage data on your computer or cloud services. Proper file naming and organization improve retrieval efficiency and ensure your important documents remain accessible and secure. Explore the rest of this article to learn expert tips on effective file management and optimization strategies.
Table of Comparison
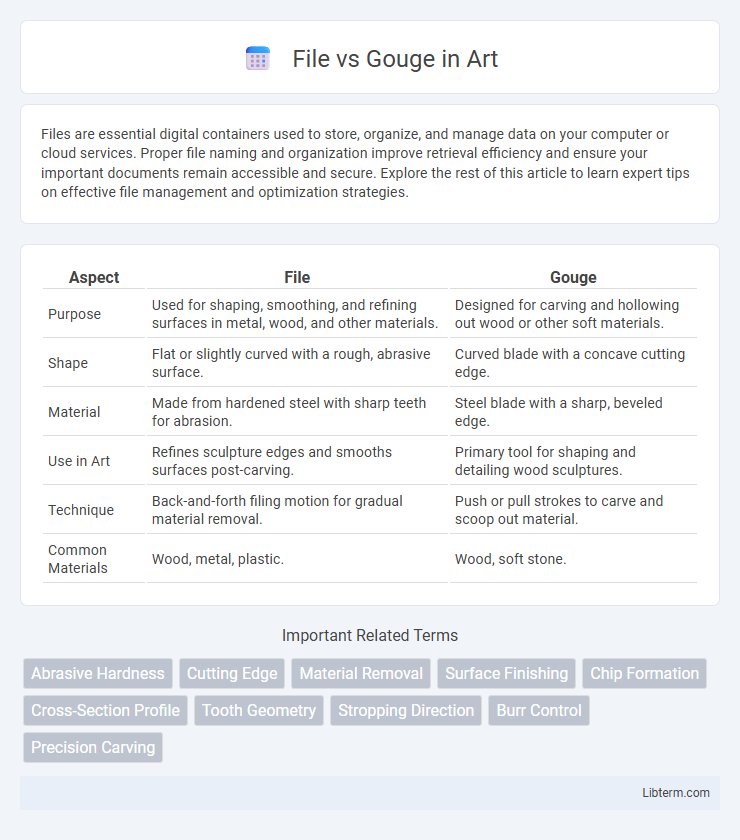
| Aspect | File | Gouge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used for shaping, smoothing, and refining surfaces in metal, wood, and other materials. | Designed for carving and hollowing out wood or other soft materials. |
| Shape | Flat or slightly curved with a rough, abrasive surface. | Curved blade with a concave cutting edge. |
| Material | Made from hardened steel with sharp teeth for abrasion. | Steel blade with a sharp, beveled edge. |
| Use in Art | Refines sculpture edges and smooths surfaces post-carving. | Primary tool for shaping and detailing wood sculptures. |
| Technique | Back-and-forth filing motion for gradual material removal. | Push or pull strokes to carve and scoop out material. |
| Common Materials | Wood, metal, plastic. | Wood, soft stone. |
Introduction to Files and Gouges
Files and gouges are essential hand tools used in shaping and carving materials like wood and metal. Files consist of hardened steel with a series of sharp, parallel ridges or teeth designed to abrade and smooth surfaces by removing small amounts of material. Gouges feature a curved, chisel-like blade ideal for scooping and hollowing out wood, enabling detailed carving and shaping with precision.
Definition and Basic Functions
A file is a hand tool consisting of a hardened steel bar with sharp, parallel ridges used for smoothing, shaping, and removing small amounts of material from metal, wood, or plastic surfaces. A gouge is a chisel-like cutting tool featuring a curved, concave blade designed for carving or hollowing out material, commonly used in woodworking, sculpture, and linoleum cutting. Files provide precise surface leveling and finishing, whereas gouges enable deep material removal and detailed shaping.
Historical Development
File and gouge tools have evolved distinctly through historical development, with files originating in the Bronze Age as basic hand tools for shaping metal and stones, while gouges trace back to ancient woodworking practices for carving and hollowing wood. Files were refined during the Industrial Revolution, incorporating hardened steel to improve durability and efficiency in metalworking. Gouges advanced through centuries with variations in blade curvature and size, tailored to specialized tasks in sculpture and cabinetry, reflecting regional craftsmanship trends.
Key Differences between File and Gouge
A file is a hand tool with a flat or rounded surface containing numerous small, closely spaced cutting edges used primarily for smoothing or shaping metal, wood, or plastic. A gouge features a curved, U-shaped or V-shaped blade designed for carving or scooping material, commonly employed in woodworking and sculpture for creating concave contours. The key differences lie in their blade shape and intended function: files refine surfaces with abrasive action, while gouges remove material through scooping motions.
Common Materials and Construction
Files and gouges are essential tools in woodworking and metalworking, each designed for specific material removal techniques. Files typically consist of hardened steel with parallel ridges or teeth, optimized for shaping metals such as steel, aluminum, and brass, as well as hardwoods and plastics; they feature various cuts like single and double-cut for different finish qualities. Gouges, with their curved or U-shaped hardened steel blades, excel in carving softer materials like wood, clay, and wax, enabling precise scooping and shaping used extensively in fine woodworking and sculpting.
Typical Uses for Files
Files are commonly used for shaping, smoothing, and finishing metal, wood, and plastic surfaces with precision and control. Typical applications include deburring sharp edges, refining tool profiles, and fitting parts by removing small amounts of material. In contrast, gouges are primarily employed in woodworking and sculpting for carving out recesses and creating detailed textures.
Typical Uses for Gouges
Gouges are primarily used in woodworking and carving to create curved cuts, hollows, and intricate details that flat files cannot achieve. Their curved cutting edges enable precise shaping of concave surfaces, making them ideal for sculpting bowls, decorative patterns, and relief work. Unlike files which smooth and level flat surfaces, gouges remove larger amounts of material quickly, enhancing efficiency in woodcraft and fine detailing tasks.
Pros and Cons of Using Files
Files provide precise material removal and fine surface finishing, making them ideal for shaping and smoothing metal, wood, or plastic in detailed work. Their durability and range of shapes and sizes offer versatility for various tasks, but using files can be time-consuming and requires manual effort, which may lead to inconsistent results if not skilled. Compared to gouges, files lack the ability to rapidly remove large amounts of material, limiting their effectiveness for rough carving or deep cuts.
Pros and Cons of Using Gouges
Gouges offer superior efficiency when carving curved or detailed wood surfaces due to their curved cutting edge, providing precision and smoother cuts compared to flat files. However, gouges require more skill and control to avoid overcutting, and they can be less versatile than files, which perform better on flat or mildly contoured surfaces. The maintenance of gouges can be more demanding, needing frequent sharpening to preserve their curved cutting edge for optimal performance.
Choosing Between File and Gouge
Choosing between a file and a gouge depends on the specific woodworking task and desired finish. Files are ideal for smoothing and refining flat or slightly curved surfaces, providing precision in shaping metal or wood edges. Gouges excel in carving deeper grooves and rounded contours, making them essential for detailed sculpting and removing larger material amounts.
File Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com