Illumination plays a crucial role in enhancing the ambiance and functionality of any space, influencing mood and productivity throughout the day. Strategic use of natural and artificial lighting can transform both residential and commercial environments, highlighting architectural features and optimizing energy efficiency. Explore the benefits and techniques of effective illumination to elevate Your living or working spaces.
Table of Comparison
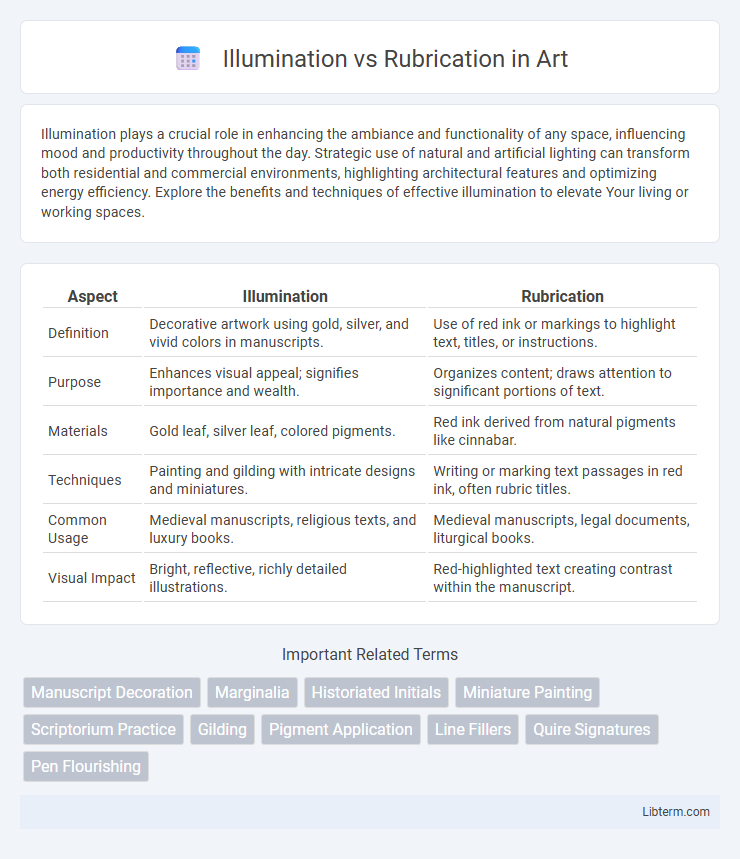
| Aspect | Illumination | Rubrication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative artwork using gold, silver, and vivid colors in manuscripts. | Use of red ink or markings to highlight text, titles, or instructions. |
| Purpose | Enhances visual appeal; signifies importance and wealth. | Organizes content; draws attention to significant portions of text. |
| Materials | Gold leaf, silver leaf, colored pigments. | Red ink derived from natural pigments like cinnabar. |
| Techniques | Painting and gilding with intricate designs and miniatures. | Writing or marking text passages in red ink, often rubric titles. |
| Common Usage | Medieval manuscripts, religious texts, and luxury books. | Medieval manuscripts, legal documents, liturgical books. |
| Visual Impact | Bright, reflective, richly detailed illustrations. | Red-highlighted text creating contrast within the manuscript. |
Understanding Illumination and Rubrication
Illumination refers to the intricate decoration of manuscripts using gold leaf, vibrant colors, and detailed illustrations to enhance visual appeal and convey symbolic meaning. Rubrication involves the addition of red ink titles, headings, or instructions within manuscripts to organize content and emphasize important sections. Both techniques play essential roles in medieval manuscripts, with illumination focusing on artistic embellishment and rubrication on textual clarity and navigation.
Historical Origins of Illumination and Rubrication
Illumination originated in the early medieval period as a technique to embellish manuscripts with gold leaf and vibrant colors, enhancing the visual impact and spiritual significance of religious texts. Rubrication, dating back to Late Antiquity, involved the use of red ink to highlight important sections, titles, and instructions in manuscripts, guiding readers through complex texts. Both practices emerged from monastic scriptoria, where scribes and artists collaborated to increase the readability and aesthetic appeal of hand-copied books in Western Europe.
Key Differences Between Illumination and Rubrication
Illumination refers to the decorative art of enhancing manuscripts with gold, silver, and vibrant colors, often featuring intricate designs and miniature illustrations, while rubrication involves the use of red ink to highlight headings, initial letters, or important text elements. Illumination aims to embellish the manuscript visually and symbolically, creating a luxurious appearance, whereas rubrication serves a functional purpose by organizing and guiding readers through the text. The key differences lie in their artistic complexity, color usage, and the roles they play within medieval manuscripts.
Techniques Used in Illumination
Illumination techniques involve applying gold leaf, vibrant pigments, and intricate brushwork to decorate manuscripts, enhancing their visual appeal and symbolism. Artists use layering and burnishing methods to create a shimmering effect, often combining natural minerals and organic dyes for rich, lasting colors. These meticulous processes contrast with rubrication, which primarily employs red ink for text highlighting without elaborate decoration.
Methods of Rubrication in Manuscripts
Rubrication in manuscripts involves applying red ink to highlight headings, instructions, or important text segments, primarily using quills or fine brushes for precise control. This method enhances readability and guides the reader through the text without extensive illustration, distinguishing it from full illumination which incorporates gold leaf and vibrant colors. Techniques include underlining, initial capitals, and marginal notes painted with vermilion or other red pigments derived from natural minerals or organic sources.
Cultural Significance of Illuminated Texts
Illuminated texts, adorned with intricate gold leaf and vivid colors, symbolize the fusion of art and spirituality in medieval culture, reflecting societal values and religious devotion. These manuscripts served not only as religious or scholarly tools but also as indicators of wealth, power, and prestige within elite circles. The elaborate designs and iconography embedded in illuminated texts embody cultural narratives and identity, preserving historical continuity through visual storytelling.
Role of Rubrication in Manuscript Organization
Rubrication plays a crucial role in manuscript organization by using red ink to highlight headings, instructions, and important sections, guiding readers through complex texts with clarity. This technique contrasts with illumination, which primarily focuses on decorative and illustrative embellishments in manuscripts. Rubrication enhances navigability and structure, making it easier to distinguish key textual elements within medieval and early modern manuscripts.
Materials and Tools for Illumination and Rubrication
Illumination involves the use of gold leaf, silver, and vibrant pigments made from minerals and plants applied with fine brushes crafted from squirrel or sable hair to create radiant manuscript decorations. Rubrication relies on red ink made from cinnabar or red lead, applied with quills or reed pens for precise lettering and emphasis in medieval texts. Both crafts require meticulous tools and specialized materials to enhance the visual impact of manuscripts.
Famous Examples of Illumination and Rubrication
Famous examples of illumination include the Book of Kells and the Tres Riches Heures du Duc de Berry, renowned for their intricate gold leaf accents and vibrant colors enhancing medieval manuscripts. Rubrication features prominently in texts like the Gutenberg Bible, where red ink headings and initial letters guide readers through the scriptural content. Both techniques serve distinct roles: illumination provides elaborate decorative artistry, while rubrication emphasizes textual organization and hierarchy.
Modern Applications in Digital and Print Design
Illumination and rubrication, historically rooted in manuscript decoration, influence modern digital and print design by inspiring intricate visual embellishments and color-coded text hierarchy. Digital tools now replicate illumination's elaborate gold leaf effects and vibrant motifs through advanced graphic software, enhancing user interface aesthetics and eBook illustrations. Rubrication's practice of red text for emphasis informs contemporary design strategies in branding, editorial layouts, and web typography to direct reader attention and improve content readability.
Illumination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com