Glazing enhances your home's energy efficiency and aesthetic appeal by improving insulation and allowing natural light to flow in. Choosing the right type of glass can reduce heat loss, minimize noise, and increase security. Discover how to select the perfect glazing options for your needs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
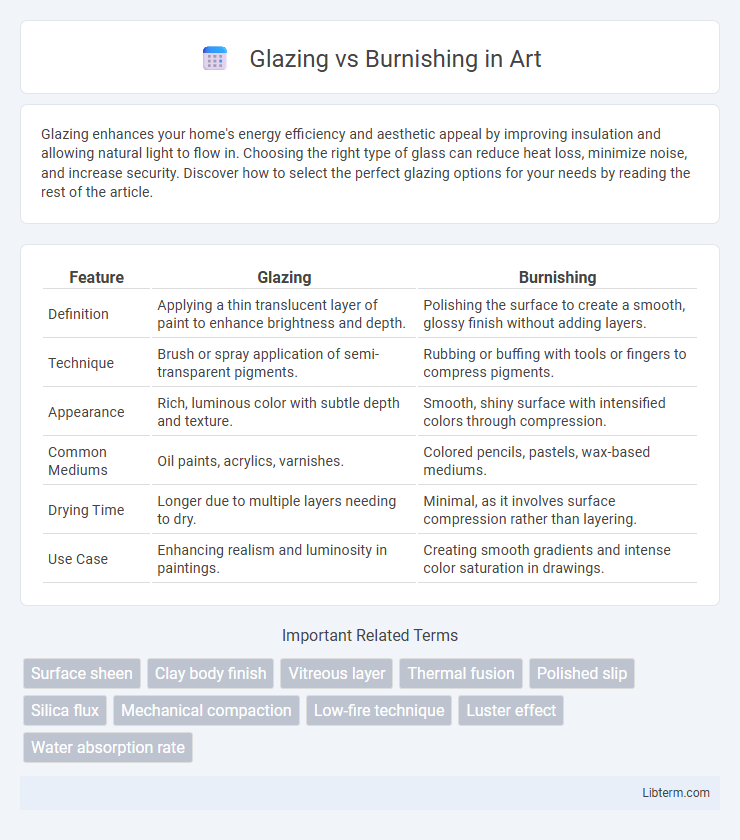
| Feature | Glazing | Burnishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Applying a thin translucent layer of paint to enhance brightness and depth. | Polishing the surface to create a smooth, glossy finish without adding layers. |
| Technique | Brush or spray application of semi-transparent pigments. | Rubbing or buffing with tools or fingers to compress pigments. |
| Appearance | Rich, luminous color with subtle depth and texture. | Smooth, shiny surface with intensified colors through compression. |
| Common Mediums | Oil paints, acrylics, varnishes. | Colored pencils, pastels, wax-based mediums. |
| Drying Time | Longer due to multiple layers needing to dry. | Minimal, as it involves surface compression rather than layering. |
| Use Case | Enhancing realism and luminosity in paintings. | Creating smooth gradients and intense color saturation in drawings. |
Introduction to Glazing and Burnishing
Glazing involves applying a thin, translucent layer of glass or ceramic coating to enhance surface durability and achieve a glossy finish. Burnishing is a mechanical polishing process that uses friction to create a smooth, shiny surface on metal or ceramic materials by compressing and smoothing the material's peaks. Both techniques optimize surface aesthetics and protection but differ in application method, with glazing relying on coating application and burnishing on physical surface manipulation.
What is Glazing?
Glazing is a finishing technique often used in ceramics and painting that involves applying a smooth, glossy coating to a surface to enhance its appearance and durability. This process typically requires the application of a liquid glaze followed by firing at high temperatures, which fuses the glaze to the surface, creating a glass-like protective layer. Glazing improves resistance to moisture, scratches, and stains, while also enriching color depth and surface texture.
What is Burnishing?
Burnishing is a finishing technique that involves polishing a surface by rubbing it with a hard, smooth tool to create a shiny, smooth texture. Unlike glazing, which adds a coating or layer, burnishing compacts and smooths the original material, enhancing its durability and appearance without altering its color or composition. This method is commonly used in ceramics, metalwork, and leathercraft to achieve a high-gloss finish through mechanical polishing.
Key Differences Between Glazing and Burnishing
Glazing involves applying a smooth, glossy coating that enhances surface shine and provides protective benefits, often used in ceramics and woodworking. Burnishing is a mechanical polishing technique that compacts and smooths a surface by friction, improving sheen without adding extra material. Key differences include glazing's reliance on coatings for finish and protection, while burnishing uses physical pressure to achieve polish and durability directly on the base material.
Advantages of Glazing
Glazing enhances surface smoothness by applying a fine layer of glass-like coating, resulting in increased durability and resistance to moisture and stains. This technique also improves the aesthetic appeal of materials by providing a glossy finish that highlights color depth and texture. Unlike burnishing, glazing offers superior protection against environmental wear, extending the longevity of ceramic and tile surfaces.
Benefits of Burnishing
Burnishing enhances surface durability by creating a hard, polished finish that resists scratches and wear better than glazing. This process compacts the material's surface, improving its strength and longevity while providing a smooth texture that requires less maintenance. Burnishing also often results in a more environmentally friendly finish by reducing the need for additional coatings or sealants commonly required in glazing.
Applications in Different Industries
Glazing is commonly used in ceramics, automotive, and construction industries to provide a glossy, protective surface that enhances durability and aesthetic appeal. Burnishing finds applications primarily in metalworking and manufacturing sectors, where it improves surface finish, hardness, and wear resistance of metals without removing material. Both techniques are essential in industries like aerospace and electronics for achieving specific surface properties tailored to performance and longevity requirements.
Choosing the Right Technique
Choosing the right technique between glazing and burnishing depends on the desired finish and material type. Glazing applies a translucent layer that enhances color depth and surface protection, ideal for ceramics and pottery. Burnishing compresses the material surface, creating a smooth, shiny finish without additional coatings, best suited for leather and metalwork.
Glazing vs Burnishing: Cost and Efficiency
Glazing typically requires lower initial investment and specialized equipment but demands more time for application and curing, resulting in moderate operational costs. Burnishing, while often involving higher upfront expenses due to heavy machinery use, offers faster processing and immediate finish, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing labor costs. Choosing between glazing and burnishing depends on balancing material costs, desired finish quality, and production speed to optimize budget and workflow.
Conclusion: Which Is Best for Your Project?
Glazing offers a glossy, protective finish ideal for enhancing color depth and durability in ceramic or wood projects, making it suitable for high-traffic or moisture-prone areas. Burnishing provides a smooth, matte surface by compressing the material's particles, perfect for organic, rustic aesthetics and low-maintenance finishes on pottery or concrete surfaces. Choosing between glazing and burnishing depends on the desired texture, durability requirements, and the specific use case of your project.
Glazing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com