Gouache wash creates vibrant, opaque layers perfect for adding depth and texture to your artwork. This technique uses diluted gouache paint to achieve smooth, even washes that enhance color intensity without losing opacity. Explore the rest of the article to master gouache wash techniques and elevate your painting skills.
Table of Comparison
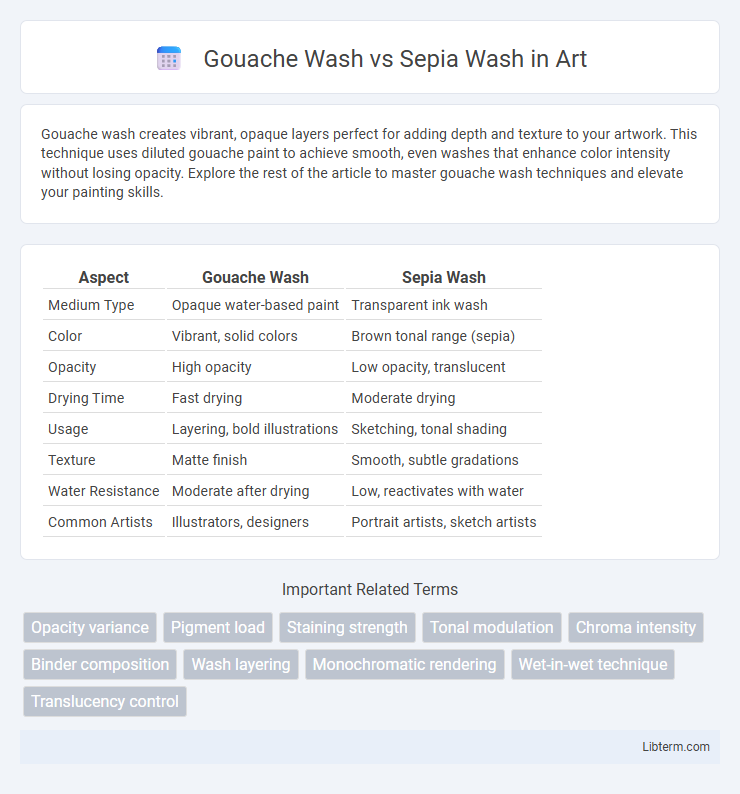
| Aspect | Gouache Wash | Sepia Wash |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Type | Opaque water-based paint | Transparent ink wash |
| Color | Vibrant, solid colors | Brown tonal range (sepia) |
| Opacity | High opacity | Low opacity, translucent |
| Drying Time | Fast drying | Moderate drying |
| Usage | Layering, bold illustrations | Sketching, tonal shading |
| Texture | Matte finish | Smooth, subtle gradations |
| Water Resistance | Moderate after drying | Low, reactivates with water |
| Common Artists | Illustrators, designers | Portrait artists, sketch artists |
Introduction to Gouache Wash and Sepia Wash
Gouache wash is a water-based painting technique that uses opaque, pigment-rich gouache paint diluted with water to create smooth, matte layers and subtle tonal variations. Sepia wash involves applying diluted sepia ink or watercolor pigment, producing warm, brown monochromatic tones often used for antique or vintage effects. Both techniques emphasize layering and shading to achieve depth, but gouache offers stronger opacity while sepia wash provides a translucent, earthy aesthetic.
Defining Characteristics of Gouache Wash
Gouache wash is characterized by its opaque, matte finish and vibrant color payoff, allowing for solid, uniform coverage that can be easily layered and reworked. It dries quickly to a smooth, velvety texture, making it ideal for achieving bold, flat areas of color or subtle gradients with controlled transparency. In contrast, sepia wash typically offers a translucent, warm brown tone associated with antique or vintage illustrations, emphasizing tonal variation rather than opacity.
Unique Qualities of Sepia Wash
Sepia wash offers a warm, vintage aesthetic characterized by its rich brown tones that evoke classic ink drawings and antique photographs, setting it apart from the vibrant opacity of gouache wash. The translucency of sepia wash allows for subtle gradients and depth, making it ideal for creating atmospheric effects and textured backgrounds. Its archival quality and natural pigment composition enhance durability and provide a timeless feel, favored in traditional and fine art applications.
Historical Background of Gouache and Sepia Techniques
Gouache wash, rooted in ancient Mediterranean and European art traditions, gained prominence during the Renaissance for its opaque, matte finish that artists used to achieve vibrant, solid colors in illustrations and manuscripts. Sepia wash, derived from the ink made from the cuttlefish's ink sac, has been historically favored since antiquity for its warm brown tones, commonly used in sketches and drawings by Old Masters like Leonardo da Vinci and Rembrandt. Both techniques evolved as essential mediums for artists seeking distinct tonal and textural effects in visual storytelling throughout art history.
Materials and Tools Needed for Each Wash
Gouache wash requires high-quality gouache paints, synthetic or natural watercolor brushes, and smooth or textured watercolor paper to achieve vibrant, opaque layers with controlled blending. Sepia wash uses sepia pigment or ink, typically in liquid or powder form, applied with soft brushes or even quills on absorbent paper like watercolor or laid paper to create warm, transparent tones and fine gradients. Both techniques benefit from palettes for mixing, water containers, and blotting materials, but the choice of pigment and paper texture significantly influences the final wash effect.
Color and Tonal Range Comparison
Gouache wash offers vibrant, opaque colors with a broad tonal range, allowing for rich layering and smooth gradients, while sepia wash provides a monochromatic, warm brown palette characterized by subtle tonal variations and a more vintage, muted effect. Gouache pigments tend to be more saturated and versatile for creating both bold and delicate tones, whereas sepia wash excels in producing soft highlights and deep shadows within a limited color spectrum. Artists often choose gouache for dynamic color expression and sepia for atmospheric, nostalgic compositions.
Application Techniques: Gouache vs Sepia
Gouache wash involves applying opaque, water-based pigment layers that allow for smooth blending and vibrant color variations, making it ideal for bold, matte finishes. Sepia wash consists of diluted sepia ink or watercolor, creating translucent, warm-toned layers that emphasize shading and subtle tonal gradients in artwork. Techniques with gouache focus on layering and reworking while sepia wash techniques prioritize controlled washes and glazing to achieve depth and texture.
Artistic Effects and Use Cases
Gouache wash delivers vibrant, opaque layers with a matte finish, ideal for bold, graphic effects and smooth color transitions in illustration and design projects. Sepia wash offers warm, earthy tones with transparent, fluid strokes that evoke a vintage or antique aesthetic, perfect for classical sketches, portraits, and historical-themed artwork. Artists choose gouache for modern, vivid compositions and sepia for subtle, atmospheric studies emphasizing texture and tonal depth.
Pros and Cons of Gouache Wash and Sepia Wash
Gouache wash offers vibrant opacity and excellent coverage, making it ideal for creating bold highlights and corrections, but it can be less transparent and harder to layer smoothly compared to sepia wash. Sepia wash provides warm, earthy tones with natural transparency, allowing for subtle gradations and vintage effects, yet it may lack the intensity needed for striking contrasts and can fade over time if not properly sealed. Choosing between gouache and sepia washes depends on the desired visual impact and textural qualities of the artwork.
Choosing the Right Wash for Your Artwork
Gouache wash provides vibrant, opaque colors ideal for bold, layered artwork, while sepia wash offers a warm, monochromatic tone perfect for vintage or classical pieces. Choosing the right wash depends on the mood and texture desired; gouache enhances brightness and detail, whereas sepia creates subtle shading and aged effects. Artists seeking strong color contrasts should opt for gouache, while those aiming for nostalgic or delicate atmospheres benefit from sepia wash.
Gouache Wash Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com