Generative art uses algorithms and computational processes to create unique, evolving pieces that blend creativity with technology. This innovative approach allows artists to explore new forms, patterns, and aesthetics that traditional methods cannot achieve. Discover how generative art can transform your understanding of creativity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
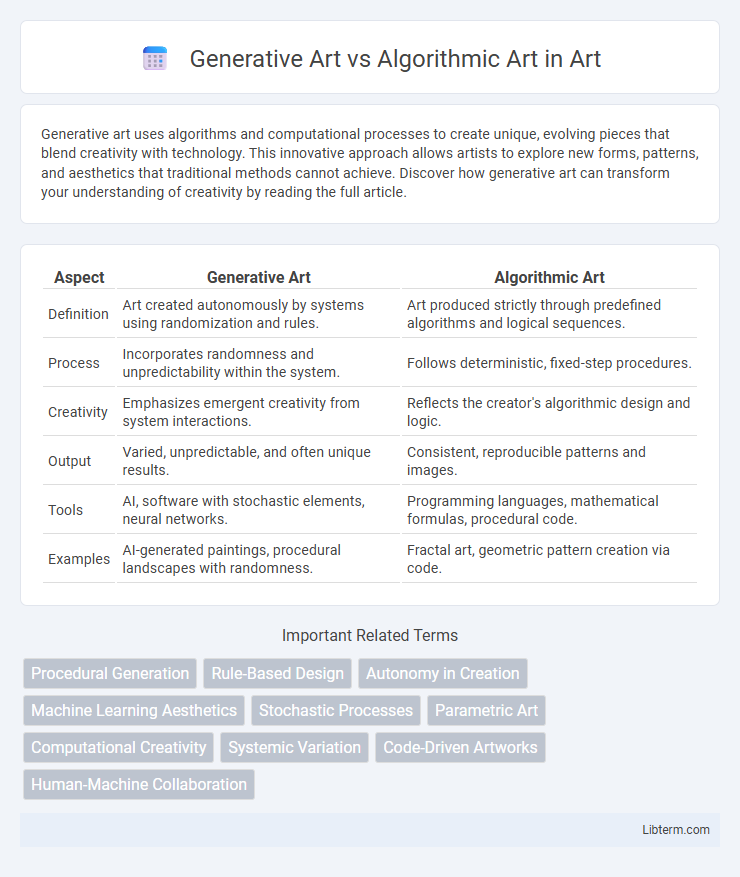
| Aspect | Generative Art | Algorithmic Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created autonomously by systems using randomization and rules. | Art produced strictly through predefined algorithms and logical sequences. |
| Process | Incorporates randomness and unpredictability within the system. | Follows deterministic, fixed-step procedures. |
| Creativity | Emphasizes emergent creativity from system interactions. | Reflects the creator's algorithmic design and logic. |
| Output | Varied, unpredictable, and often unique results. | Consistent, reproducible patterns and images. |
| Tools | AI, software with stochastic elements, neural networks. | Programming languages, mathematical formulas, procedural code. |
| Examples | AI-generated paintings, procedural landscapes with randomness. | Fractal art, geometric pattern creation via code. |
Understanding Generative Art
Generative Art involves the creation of artwork through autonomous systems driven by algorithms, often incorporating randomness and iterative processes to produce unique, evolving pieces. This form of art emphasizes the role of computational creativity, where artists design rules and parameters but the final output emerges unpredictably from the system's interaction. Unlike purely algorithmic art, which follows strict procedural code to create fixed results, generative art thrives on the interplay between control and chance, enabling dynamic and complex visual expressions.
Defining Algorithmic Art
Algorithmic art is a form of digital artwork created through explicit instructions and mathematical algorithms, where artists design precise code to generate visual patterns or structures. Unlike generative art, which incorporates randomness and autonomous systems producing unpredictable outcomes, algorithmic art follows deterministic processes with repeatable results. This discipline emphasizes the formalization of artistic concepts into algorithms that define shape, color, and composition in a systematic manner.
Key Differences Between Generative and Algorithmic Art
Generative art utilizes autonomous systems, often employing randomness or artificial intelligence, to create unique and unpredictable artworks, while algorithmic art strictly follows predefined mathematical rules and formulas to generate precise, repeatable patterns. Generative art emphasizes creativity through evolving processes and machine interaction, whereas algorithmic art focuses on logical structure and exact replication of coded instructions. The core difference lies in generative art's incorporation of variability and surprise versus algorithmic art's reliance on deterministic outputs from explicit algorithms.
Historical Evolution of Computer-Driven Art
Generative art and algorithmic art emerged as distinct yet interconnected forms of computer-driven creativity during the mid-20th century, with pioneers like Georg Nees and Frieder Nake utilizing early programming languages to create visual compositions. Generative art emphasizes autonomous systems and randomness, evolving alongside advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, whereas algorithmic art relies on predefined computational rules and mathematical algorithms to produce precise patterns and structures. The historical evolution of computer-driven art reflects the transition from manual coding and plotter outputs to sophisticated software tools, enabling artists to explore complex generative processes and redefine artistic expression in the digital age.
How Algorithms Influence Artistic Creation
Algorithms play a crucial role in both Generative Art and Algorithmic Art by defining the rules and parameters that guide the creative process. In Generative Art, algorithms introduce randomness and variation, enabling artists to explore unexpected visual outcomes through system-driven creativity. Algorithmic Art relies more on precise mathematical formulas and logic to produce structured, often repeatable patterns that emphasize the computational foundation of artistic creation.
The Role of Randomness and Control
Generative art relies heavily on randomness to create unpredictable and unique outcomes, allowing the artist to set initial parameters while the algorithm introduces variability. Algorithmic art emphasizes precise control through predefined rules and deterministic processes, minimizing randomness to produce consistent patterns or sequences. Balancing randomness and control defines the creative process, where generative art explores open-ended possibilities and algorithmic art executes specific designs.
Prominent Artists and Landmark Works
Generative art features artists like Harold Cohen, creator of the AARON program, and Casey Reas, co-founder of Processing, whose works blend code with artistic expression to produce evolving visual compositions. Algorithmic art includes pioneers such as Manfred Mohr, known for his geometric digital pieces, and Vera Molnar, whose early computer-generated drawings explore algorithmic aesthetics. Landmark works include Cohen's AARON-generated paintings, Reas's Process Series, Mohr's P-511/D structures, and Molnar's systematic graphical experiments, each exemplifying the distinct approaches within generative and algorithmic art.
Tools and Technologies Used
Generative art leverages AI-driven tools and machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow and RunwayML to create dynamic, evolving visuals based on pre-trained models and neural networks. Algorithmic art primarily utilizes traditional programming languages such as Processing, Python, or JavaScript, combined with mathematical algorithms and procedural code to generate precise, rule-based patterns and structures. Both approaches benefit from advancements in GPUs and cloud computing, enabling complex computations and real-time rendering for sophisticated artistic expressions.
Impact on the Modern Art Scene
Generative art, driven by autonomous systems that create unique outputs, has introduced unprecedented creativity and variability to the modern art scene, enabling artists to explore new forms and interactive experiences. Algorithmic art relies on predefined rules and mathematical processes, emphasizing precision and reproducibility, which has influenced digital art's integration with scientific and technological disciplines. Both forms have expanded the boundaries of artistic expression, challenging traditional concepts of authorship and fostering collaboration between artists, programmers, and machines.
Future Possibilities in Art Generation
Generative art harnesses AI models and machine learning algorithms to create novel, evolving visual compositions, while algorithmic art relies on predefined rules and mathematical formulas for design. Future possibilities in art generation include enhanced interactivity and real-time adaptation through AI-driven creativity, enabling dynamic artworks that respond to user input or environmental changes. Advances in neural networks and deep learning promise increasingly sophisticated, personalized artistic experiences that bridge human creativity with computational innovation.
Generative Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com