Opposition plays a vital role in democratic systems by challenging government decisions and offering alternative viewpoints. It ensures accountability and helps prevent the abuse of power through rigorous debate and scrutiny. Explore the rest of the article to understand how opposition shapes political landscapes and impacts your society.
Table of Comparison
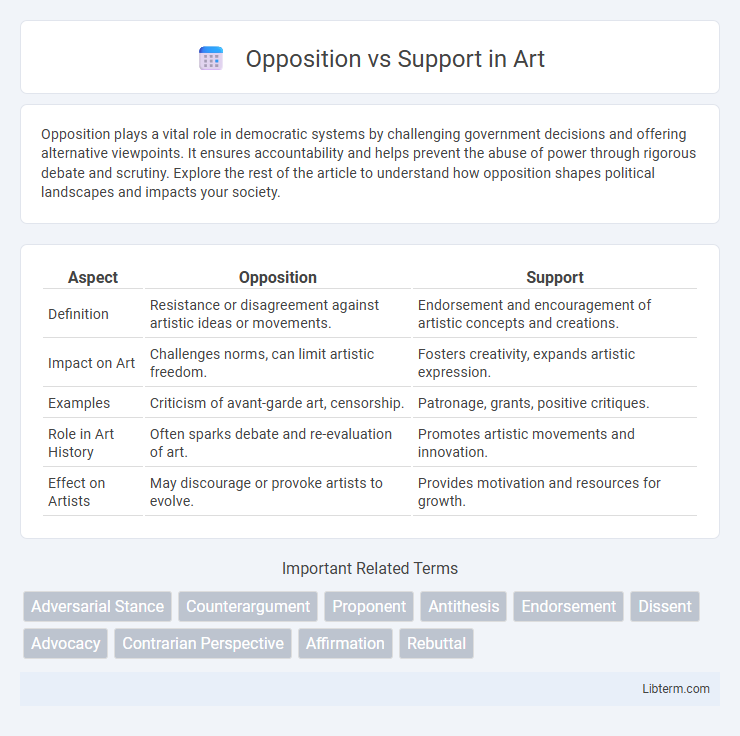
| Aspect | Opposition | Support |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resistance or disagreement against artistic ideas or movements. | Endorsement and encouragement of artistic concepts and creations. |
| Impact on Art | Challenges norms, can limit artistic freedom. | Fosters creativity, expands artistic expression. |
| Examples | Criticism of avant-garde art, censorship. | Patronage, grants, positive critiques. |
| Role in Art History | Often sparks debate and re-evaluation of art. | Promotes artistic movements and innovation. |
| Effect on Artists | May discourage or provoke artists to evolve. | Provides motivation and resources for growth. |
Understanding Opposition and Support
Understanding opposition involves recognizing the reasons individuals or groups resist ideas, policies, or changes, often stemming from conflicting interests, values, or misinformation. Support is rooted in shared goals, trust, and perceived benefits, reinforcing alignment with a cause or initiative. Analyzing the underlying motivations and emotional drivers aids in addressing concerns and fostering collaboration.
Historical Perspectives on Opposition vs Support
Historical perspectives on opposition versus support reveal how political movements and social reforms often hinge on public sentiment and power dynamics. Landmark events such as the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s exemplify strong opposition met with growing support, highlighting the clash between entrenched systems and progressive change. Understanding these shifts offers insight into the cyclical nature of resistance and endorsement in shaping societal progress.
Psychological Roots of Support and Opposition
Support and opposition toward ideas or groups are deeply rooted in psychological factors such as identity, cognition, and emotional investment. Social identity theory explains how individuals align with groups that reinforce their self-concept, leading to strong support or opposition based on perceived in-group or out-group dynamics. Cognitive biases like confirmation bias and motivated reasoning further entrench these positions by filtering information to align with existing beliefs.
Factors Influencing Opposition
Factors influencing opposition include ideological conflicts, perceived threats to economic interests, and cultural or social identity concerns. Political polarization and misinformation can exacerbate resistance by reinforcing existing biases and undermining trust. Social media platforms amplify opposing voices, creating echo chambers that intensify dissent and hinder constructive dialogue.
Drivers Behind Support
Drivers behind support for a cause or policy often include perceived personal benefits, alignment with core values, and trust in the endorsing entities. Economic incentives, social identity, and information sources significantly shape individuals' support levels, enhancing their commitment and advocacy. Understanding these factors enables more targeted strategies to mobilize and sustain active support bases.
Social Impacts of Opposition vs Support
Opposition to social initiatives often generates resistance that hinders policy implementation, increases social division, and delays positive community outcomes. Support, conversely, fosters collaboration, enhances social cohesion, and accelerates the achievement of shared goals such as equity, inclusion, and sustainability. Empirical studies reveal that robust support networks contribute to improved mental health, economic stability, and overall societal well-being.
Opposition vs Support in Politics
Opposition and support in politics define the dynamics of governance and policy-making, with opposition challenging ruling parties' decisions and advocating for alternative policies. Political opposition holds governments accountable through critique, debate, and proposing reforms, while support ensures the enactment and stability of policies aligned with prevailing party ideologies. The balance between opposition and support influences democratic processes, legislative effectiveness, and public trust in political systems.
The Role of Media in Shaping Opposition and Support
The role of media in shaping opposition and support is pivotal, as it influences public opinion through framing, agenda-setting, and selective coverage of political events. Media outlets can amplify dissent by highlighting protests and criticisms, while also fostering support by showcasing positive government actions or endorsements from influential figures. The rise of social media platforms has intensified this dynamic, enabling rapid dissemination of opposing views and mobilizing both opposition and support groups effectively.
Conflict Resolution: Balancing Opposition and Support
Effective conflict resolution involves balancing opposition and support by actively listening to opposing viewpoints while fostering a supportive environment that encourages open dialogue. Strategies like mediation and collaborative negotiation help address disagreements by validating concerns and jointly developing solutions. Maintaining this equilibrium reduces tension and promotes mutual understanding, leading to sustainable conflict resolution.
Cultivating Constructive Opposition and Meaningful Support
Cultivating constructive opposition involves encouraging critical thinking while maintaining respect, fostering an environment where diverse perspectives challenge ideas without personal attacks. Meaningful support emphasizes active listening, validating contributions, and providing actionable feedback that empowers growth and collaboration. Balancing these dynamics enhances decision-making, drives innovation, and strengthens team cohesion by leveraging the strengths of both opposition and support.
Opposition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com