Organic products offer a healthier alternative by avoiding synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, promoting environmental sustainability. They often contain higher levels of essential nutrients and antioxidants, benefiting your overall well-being. Discover how choosing organic can transform your lifestyle in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
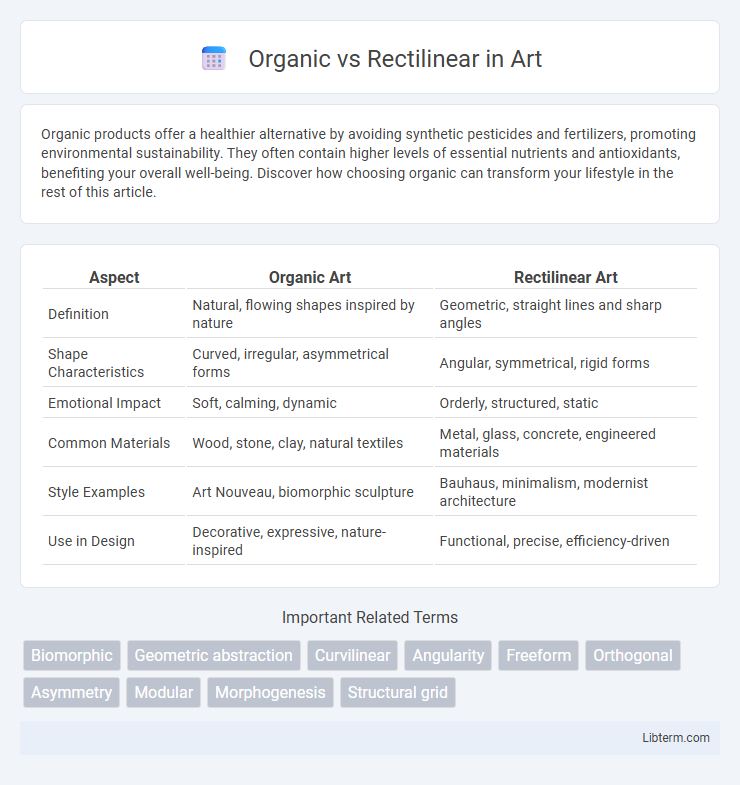
| Aspect | Organic Art | Rectilinear Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural, flowing shapes inspired by nature | Geometric, straight lines and sharp angles |
| Shape Characteristics | Curved, irregular, asymmetrical forms | Angular, symmetrical, rigid forms |
| Emotional Impact | Soft, calming, dynamic | Orderly, structured, static |
| Common Materials | Wood, stone, clay, natural textiles | Metal, glass, concrete, engineered materials |
| Style Examples | Art Nouveau, biomorphic sculpture | Bauhaus, minimalism, modernist architecture |
| Use in Design | Decorative, expressive, nature-inspired | Functional, precise, efficiency-driven |
Introduction to Organic and Rectilinear Design
Organic design emphasizes natural, flowing shapes inspired by nature, characterized by curves, asymmetry, and irregular forms that create a sense of harmony and movement. Rectilinear design focuses on straight lines, right angles, and geometric shapes, promoting structure, order, and simplicity. These contrasting design philosophies influence architecture, interior design, and product development by prioritizing either natural aesthetics or precise, clean lines.
Defining Organic Design: Characteristics and Origins
Organic design is characterized by natural, flowing lines, asymmetrical shapes, and forms that mimic nature, promoting harmony between the built environment and its surroundings. Originating from movements like Art Nouveau and reinforced by designers such as Frank Lloyd Wright, this style emphasizes curves, irregular shapes, and integration with natural landscapes. Its principles contrast sharply with rectilinear design, which relies on straight lines, right angles, and geometric precision.
Understanding Rectilinear Forms: Key Features
Rectilinear forms are characterized by straight lines and sharp angles, creating a sense of order and structure commonly found in modern architecture and urban planning. These geometric shapes maximize space efficiency and facilitate straightforward construction processes due to their predictable and repetitive patterns. Key features include right angles, parallel lines, and uniform dimensions, distinguishing rectilinear designs from organic forms that emphasize curves and irregularity.
Historical Context: Evolution of Design Styles
Organic design, rooted in the Arts and Crafts Movement of the late 19th century, emphasizes natural forms, flowing curves, and asymmetry inspired by nature. Rectilinear design gained prominence during the Bauhaus era in the early 20th century, showcasing geometric shapes, straight lines, and functional simplicity aligned with modernist principles. These contrasting styles reflect cultural shifts from handcrafted articulation to industrial efficiency in architectural and graphic design history.
Material Choices in Organic vs Rectilinear Architecture
Material choices in organic architecture emphasize natural, sustainable elements such as wood, stone, and rammed earth to harmonize with the environment and create fluid, curved forms. Rectilinear architecture typically favors industrial materials like steel, glass, and concrete, supporting sharp angles and geometric precision. The selection of materials in both styles directly influences structural integrity, aesthetic expression, and environmental impact.
Functional Impacts of Each Design Approach
Organic design fosters fluid, adaptable spaces that promote natural movement and comfort, enhancing occupant well-being and flexibility in use. Rectilinear design emphasizes efficiency and predictability through straight lines and right angles, supporting functional clarity and ease of space organization. Each approach impacts lighting, circulation, and spatial perception differently, influencing user experience and operational performance.
Aesthetic Appeal: Visual Differences Explored
Organic design features flowing, curvilinear shapes that evoke natural forms and create a sense of softness and fluidity in visual compositions. Rectilinear design relies on straight lines and right angles, producing a structured, geometric, and orderly aesthetic with a modern, minimalist appeal. The visual contrast between organic curves and rectilinear grids offers distinct emotional responses, with organic shapes often perceived as more inviting and dynamic, while rectilinear forms convey stability and precision.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Organic architecture emphasizes harmony with natural landscapes, utilizing sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs that reduce environmental impact. Rectilinear architecture often employs modular construction techniques that can optimize material usage and facilitate recycling, contributing to sustainability goals. Both approaches prioritize reducing carbon footprints through innovative design strategies tailored to specific ecosystem contexts.
Popular Examples Around the World
Organic architecture is exemplified by structures like Frank Lloyd Wright's Fallingwater in the USA and Antoni Gaudi's Sagrada Familia in Spain, characterized by flowing lines and integration with natural surroundings. Rectilinear architecture is prominently seen in the modernist works such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe's Farnsworth House and the International Style skyscrapers like New York's Seagram Building, emphasizing straight lines and geometric forms. These contrasting styles highlight global architectural diversity, where organic designs prioritize harmony with nature and rectilinear forms emphasize precision and functionality.
Choosing the Right Style: Factors to Consider
Choosing between organic and rectilinear design styles depends on factors such as the intended ambiance, spatial functionality, and personal preferences. Organic styles emphasize natural, flowing shapes that promote comfort and relaxation, ideal for spaces aiming for warmth and creativity. Rectilinear designs feature clean lines and geometric forms, offering a modern, structured look suited for professional or minimalist environments.
Organic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com