Surrealism unlocks the subconscious mind, blending dreamlike imagery with reality to challenge conventional perceptions and spark creativity. This art movement influences various forms, including painting, literature, and film, pushing boundaries to evoke emotional and intellectual responses. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how surrealism can transform your understanding of art and imagination.
Table of Comparison
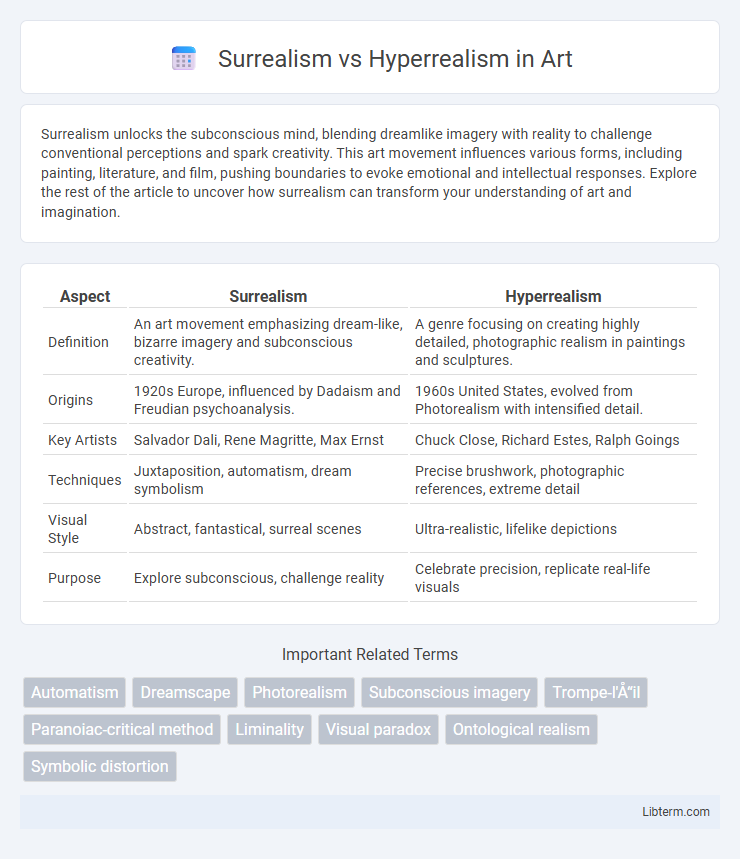
| Aspect | Surrealism | Hyperrealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An art movement emphasizing dream-like, bizarre imagery and subconscious creativity. | A genre focusing on creating highly detailed, photographic realism in paintings and sculptures. |
| Origins | 1920s Europe, influenced by Dadaism and Freudian psychoanalysis. | 1960s United States, evolved from Photorealism with intensified detail. |
| Key Artists | Salvador Dali, Rene Magritte, Max Ernst | Chuck Close, Richard Estes, Ralph Goings |
| Techniques | Juxtaposition, automatism, dream symbolism | Precise brushwork, photographic references, extreme detail |
| Visual Style | Abstract, fantastical, surreal scenes | Ultra-realistic, lifelike depictions |
| Purpose | Explore subconscious, challenge reality | Celebrate precision, replicate real-life visuals |
Introduction to Surrealism and Hyperrealism
Surrealism emerged in the early 20th century as an avant-garde movement emphasizing dreamlike scenes and unconscious imagery to challenge reality and logic. Hyperrealism, developing in the late 1960s, focuses on creating artwork with extreme precision and detail, often resembling high-resolution photographs. Both movements explore reality but differ fundamentally in expression: Surrealism distorts and transcends, while Hyperrealism replicates and intensifies.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Surrealism originated in the early 1920s as an avant-garde movement led by Andre Breton, emphasizing the unconscious mind and dreamlike imagery to challenge reality. Hyperrealism emerged in the late 1960s as an evolution of Photorealism, focusing on meticulous detail to create lifelike representations that often highlight social and cultural themes. Both movements reflect distinct artistic responses to perception and reality, evolving through significant historical contexts such as post-World War I psychological exploration and postmodern skepticism.
Key Characteristics of Surrealism
Surrealism is characterized by dream-like scenes, unexpected juxtapositions, and illogical compositions that explore the subconscious mind. It emphasizes symbolic imagery, spontaneous techniques, and the exploration of fantasies and irrational concepts. Artists like Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte exemplify these features by blending reality with imagination in bizarre, thought-provoking ways.
Defining Features of Hyperrealism
Hyperrealism is characterized by its meticulous attention to detail, creating artworks that resemble high-resolution photographs with extraordinary precision. This art movement emphasizes lifelike representations, often highlighting textures, reflections, and subtle nuances of light and shadow to evoke a heightened sense of reality. Unlike Surrealism, which explores dreamlike and fantastical imagery, Hyperrealism strives to replicate reality with scientific accuracy, pushing the boundaries of visual perception.
Influential Artists in Both Movements
Salvador Dali and Rene Magritte stand as towering figures in Surrealism, renowned for their dreamlike imagery and exploration of the subconscious mind, influencing generations of artists and writers. In contrast, Chuck Close and Richard Estes exemplify Hyperrealism with their meticulous attention to photographic detail, pushing the boundaries of realism to new heights. Both movements, though distinct in style and philosophy, have significantly shaped contemporary art through these influential artists.
Techniques and Artistic Approaches
Surrealism employs techniques such as automatism, dream imagery, and unexpected juxtapositions to explore the subconscious mind and irrational scenes. Hyperrealism focuses on meticulous detailing, photorealistic precision, and advanced rendering methods to create artwork that closely resembles high-resolution photographs. While Surrealism emphasizes imaginative and symbolic content, Hyperrealism prioritizes accuracy and lifelike representation through controlled brushwork and texture replication.
Thematic Contrasts: Dreams vs Reality
Surrealism explores themes centered on dreams, the unconscious, and fantastical imagery that defies logical boundaries, creating a world where imagination transcends reality. Hyperrealism, in contrast, focuses on depicting reality with meticulous detail and precision, often emphasizing everyday scenes or objects with photographic clarity. This thematic contrast highlights Surrealism's embrace of the irrational and dreamlike, against Hyperrealism's dedication to portraying the tangible and observable world.
Impact on Contemporary Art
Surrealism revolutionized contemporary art by challenging perceptions of reality through dreamlike, fantastical imagery, inspiring artists to explore subconscious themes and abstract symbolism. Hyperrealism, emphasizing meticulous detail and photographic precision, pushed the boundaries of technical skill and heightened the visual experience of everyday life in art. Both movements significantly influenced contemporary art by expanding creative expression--Surrealism through psychological depth and Hyperrealism through technical mastery.
Reception and Criticism Over Time
Surrealism faced early criticism for its dreamlike, irrational imagery, which some saw as nonsensical or politically subversive, though it gained acclaim for its innovative exploration of the unconscious mind. Hyperrealism emerged later, initially challenged for its painstaking replication of reality, yet praised for technical prowess and its commentary on perception and reality. Over time, both movements secured influential positions in modern art discourse, with Surrealism celebrated for expanding artistic boundaries and Hyperrealism for elevating figurative precision to a new conceptual level.
Surrealism vs Hyperrealism: Which Resonates Today?
Surrealism challenges perception by blending dreamlike elements with reality, creating imaginative and thought-provoking visuals, while Hyperrealism emphasizes meticulous detail to produce lifelike representations that blur the line between art and photography. Surrealism resonates today for its bold exploration of subconscious and abstract concepts, appealing to audiences seeking emotional depth and symbolic meaning. Hyperrealism attracts those who appreciate technical skill and precision, yet Surrealism's influence on contemporary culture and digital media secures its stronger relevance in modern artistic expression.
Surrealism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com