Traditional painting techniques use time-honored methods such as oil, acrylic, and watercolor to create lasting works of art characterized by rich textures and vibrant colors. Mastering brushwork, blending, and layering allows artists to convey depth and emotion in their subjects. Discover how embracing these classic approaches can elevate your artistic skills by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
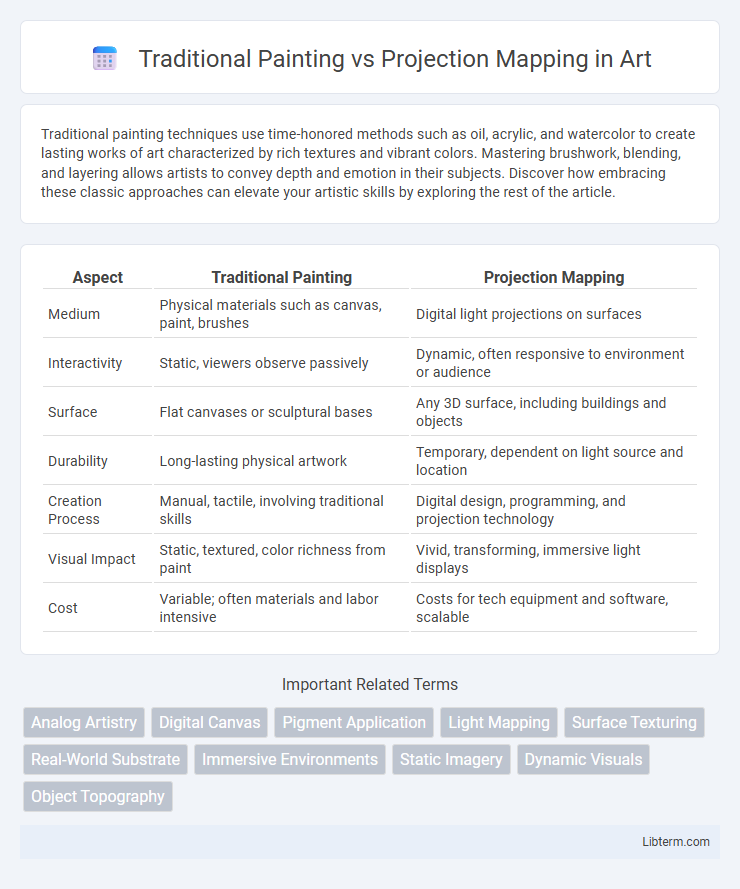
| Aspect | Traditional Painting | Projection Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials such as canvas, paint, brushes | Digital light projections on surfaces |
| Interactivity | Static, viewers observe passively | Dynamic, often responsive to environment or audience |
| Surface | Flat canvases or sculptural bases | Any 3D surface, including buildings and objects |
| Durability | Long-lasting physical artwork | Temporary, dependent on light source and location |
| Creation Process | Manual, tactile, involving traditional skills | Digital design, programming, and projection technology |
| Visual Impact | Static, textured, color richness from paint | Vivid, transforming, immersive light displays |
| Cost | Variable; often materials and labor intensive | Costs for tech equipment and software, scalable |
Introduction to Traditional Painting and Projection Mapping
Traditional painting involves the application of pigments on surfaces such as canvas, wood, or paper, using tools like brushes, knives, or sponges to create static visual art characterized by texture, color, and form. Projection mapping, a contemporary digital technique, uses projectors to cast images or animations onto irregularly shaped objects or architectural structures, transforming them into dynamic canvases that interact with the environment. Both mediums serve artistic expression, with traditional painting emphasizing tactile craftsmanship and projection mapping offering immersive, time-based visual experiences.
Historical Evolution of Visual Art Forms
Traditional painting, dating back to prehistoric cave art and flourishing through Renaissance masterpieces, represents the foundational visual art form characterized by manual application of pigments on surfaces such as canvas and wood. Projection mapping, emerging in the late 20th century, revolutionized visual art by using digital technology to project images onto complex surfaces, transforming architecture and objects into dynamic visual displays. The historical evolution from static, tactile mediums to immersive, digital experiences illustrates a significant paradigm shift in artistic expression driven by technological advancements and changing audience engagement.
Core Techniques of Traditional Painting
Traditional painting relies on core techniques such as brushwork, color mixing, and layering to create texture, depth, and detail on physical surfaces like canvas or wood. Artists master skills like blending, glazing, and impasto to manipulate light and shadow, achieving realism or expressive effects. These techniques require manual precision and an intimate understanding of materials, contrasting with the digital projection mapping process that uses technology to project images onto three-dimensional objects.
Technology Behind Projection Mapping
Projection mapping leverages advanced technology such as high-resolution projectors, 3D mapping software, and real-time rendering to transform irregular surfaces into dynamic visual displays. Unlike traditional painting, which relies on physical pigments and static imagery, projection mapping uses computer-generated graphics that adapt to the contours and movements of the display surface, enhancing viewer engagement. This technology enables seamless integration of light, color, and motion, creating immersive experiences unattainable through conventional painting methods.
Artistic Expression: Canvas vs Digital Surfaces
Traditional painting offers tactile engagement with physical canvas, allowing artists to manipulate texture and medium for nuanced, hand-crafted expression. Projection mapping transforms digital surfaces into dynamic art installations, enabling interactive and immersive experiences that evolve in real-time. Both mediums expand artistic boundaries, with traditional painting emphasizing permanence and materiality, while projection mapping prioritizes versatility and temporal fluidity.
Viewer Experience: Physical Presence and Immersion
Traditional painting offers a tangible physical presence that engages viewers through texture, brushstrokes, and the materiality of the canvas, creating a direct sensory connection. Projection mapping transforms surfaces with dynamic visuals and motion, immersing viewers in a multi-sensory environment that blurs the line between reality and digital art. The immersive experience of projection mapping often induces a heightened sense of participation, while traditional painting provides a solitary, contemplative engagement rooted in physical space.
Accessibility and Portability of Artworks
Traditional painting offers high accessibility through physical presence in galleries and private collections but is limited by the artist's location and the artwork's fixed size. Projection mapping enhances portability by transforming any surface into a dynamic canvas, allowing large-scale, interactive displays that can be easily relocated and adapted to different environments. While traditional art relies on tangible materials, projection mapping leverages digital technology, making it more versatile for public events and temporary installations.
Challenges and Limitations in Both Mediums
Traditional painting faces challenges such as limited dynamic interaction and static visual appeal, requiring extensive time and meticulous skill for detailed artworks. Projection mapping encounters limitations like dependency on surface geometry, ambient lighting conditions, and technology constraints, which can affect image clarity and viewer engagement. Both mediums demand careful planning and adaptation to overcome issues of permanence and environmental interaction.
Future Trends in Art Creation and Display
Traditional painting continues to evolve with advanced pigments and digital tools enhancing texture and color richness. Projection mapping integrates augmented reality and AI to create immersive, interactive art experiences in public spaces and galleries. Future trends emphasize hybrid techniques where classic craftsmanship meets real-time digital manipulation, expanding artistic possibilities and audience engagement.
Conclusion: Bridging Tradition and Innovation
Traditional painting preserves cultural heritage through tactile craftsmanship and timeless techniques, while projection mapping revolutionizes visual experiences by integrating digital technology and dynamic imagery. Bridging tradition and innovation, artists increasingly combine hand-painted elements with projection mapping to create immersive, multifaceted artworks that honor historical artistry while embracing modern creativity. This fusion expands artistic expression and engages audiences with vibrant, interactive narratives that transcend conventional mediums.
Traditional Painting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com