Hatching is a fundamental shading technique in drawing that uses closely spaced parallel lines to create texture and depth. Mastering different hatching styles, such as cross-hatching and contour hatching, can significantly enhance the realism of your artwork. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to apply hatching effectively in your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
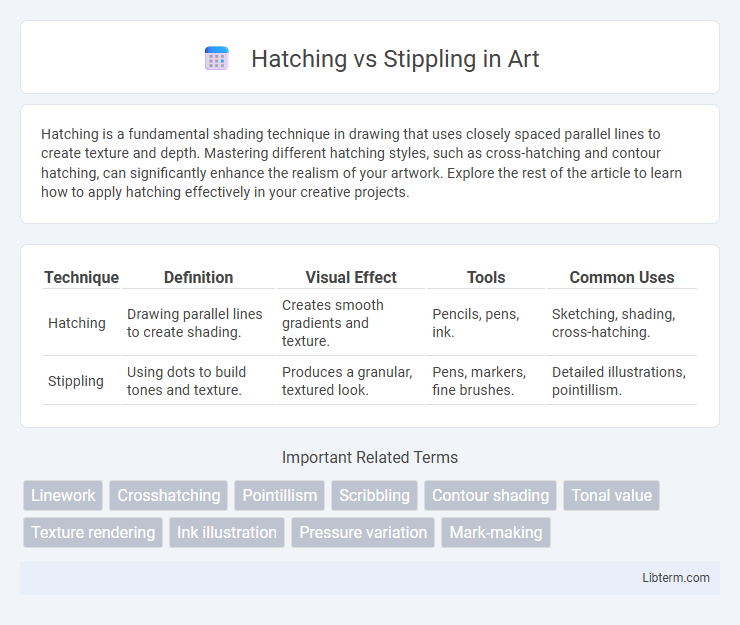
| Technique | Definition | Visual Effect | Tools | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hatching | Drawing parallel lines to create shading. | Creates smooth gradients and texture. | Pencils, pens, ink. | Sketching, shading, cross-hatching. |
| Stippling | Using dots to build tones and texture. | Produces a granular, textured look. | Pens, markers, fine brushes. | Detailed illustrations, pointillism. |
Understanding Hatching and Stippling
Hatching involves drawing closely spaced parallel lines to create shading and texture, while stippling uses numerous small dots to produce tonal variations and depth. Understanding the density and spacing in both hatching and stippling is crucial for controlling light, shadow, and form in artwork. Mastery of these techniques enhances the ability to create detailed and realistic illustrations in pen and ink or pencil drawings.
Historical Context of Line Art Techniques
Hatching and stippling are classic line art techniques that date back to Renaissance engravings and etchings, where artists like Albrecht Durer used hatching to create depth and texture through closely spaced parallel lines. Stippling emerged later, gaining prominence in the 18th century with naturalists such as Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon, who utilized dot patterns to achieve tonal variation in scientific illustrations. Both methods reflect the evolution of printmaking and drawing techniques aimed at enhancing realism and shading without color.
Key Differences Between Hatching and Stippling
Hatching uses closely spaced parallel lines to create shading and texture, while stippling relies on numerous small dots to build tone and depth. Hatching allows for smoother gradients and faster execution, whereas stippling provides more control over subtle variations in shading at the cost of being time-consuming. The key difference lies in their application techniques and the visual effect: hatching emphasizes line direction and density, whereas stippling emphasizes dot density and distribution.
Tools and Materials Required
Hatching requires tools such as fine-tipped pens, pencils, or ink brushes to create closely spaced parallel lines, typically on smooth paper or Bristol board to achieve precise line control. Stippling demands pens or markers with varying nib sizes, like technical pens or micron pens, used on textured or heavy-weight paper to allow for dense clusters of dots that build tonal value. Both techniques benefit from high-quality erasers and rulers for clean edges and corrections during detailed shading work.
Techniques for Effective Hatching
Effective hatching techniques in drawing involve varying line direction, length, and spacing to create texture, depth, and tonal range. Cross-hatching, where lines intersect at different angles, enhances shading and contrast by building up layers of value. Consistent pressure and controlled line flow contribute to smooth transitions and realistic effects compared to stippling's use of dots for texture and gradation.
Mastering Stippling Methods
Mastering stippling methods involves developing precision in applying countless tiny dots to create gradients and textures, distinguishing it from hatching's use of lines. Artists can achieve depth and subtle tonal transitions by varying dot density and spacing, requiring patience and steady control. Mastering stippling enhances the visual impact of drawings, making it ideal for detailed, textured illustrations in pen and ink art.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technique
Hatching offers quick shading and clear texture through parallel lines, making it ideal for dynamic sketches and emphasizing form, but it can appear less detailed in large, flat areas. Stippling provides precise control over tonal gradients using countless dots, resulting in richly detailed and smooth shading, though it demands significant time and patience for complex compositions. Both techniques enhance depth and texture in drawings, with hatching favoring speed and style, while stippling excels in subtlety and intricate detail.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Hatching and stippling are essential techniques for creating texture and depth in artwork; hatching uses parallel lines to build shading, while stippling employs dots to achieve gradual tonal variation. Choosing the right technique depends on the desired effect--hatching offers dynamic movement and can convey form more fluidly, whereas stippling provides precise control over light and shadow, ideal for detailed and subtle shading. Artists should consider the medium, subject matter, and time constraints when selecting between hatching and stippling to enhance visual impact and artistic expression.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common mistakes in hatching and stippling include uneven spacing and inconsistent pressure, leading to a patchy or unclear texture in artwork. Artists often apply too much pressure in hatching, causing harsh lines that disrupt the intended shading gradient, while in stippling, overcrowding dots can create unintended dark spots. To avoid these issues, practicing controlled, consistent strokes with deliberate spacing and varying pressure ensures smooth transitions and balanced tonal values.
Inspiring Examples and Artist Showcase
Hatching and stippling techniques demonstrate distinct artistic textures through lines and dots, respectively, offering unique avenues for shading and depth in sketches. Inspiring examples include Albrecht Durer's intricate hatching in "Knight, Death, and the Devil" and Georges Seurat's stippling mastery in "A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte." Contemporary artists like Marco Mazzoni harness hatching for detailed portraits, while pointillist stippling is showcased by artists like Darwin Brown, emphasizing fine tonal gradations and intricate detail.
Hatching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com