Casein is a protein found in milk that binds effectively with oil, improving texture and stability in food products and cosmetics. This natural interaction enhances emulsification, creating smoother blends and more consistent formulations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your products can benefit from the unique properties of casein and oil combinations.
Table of Comparison
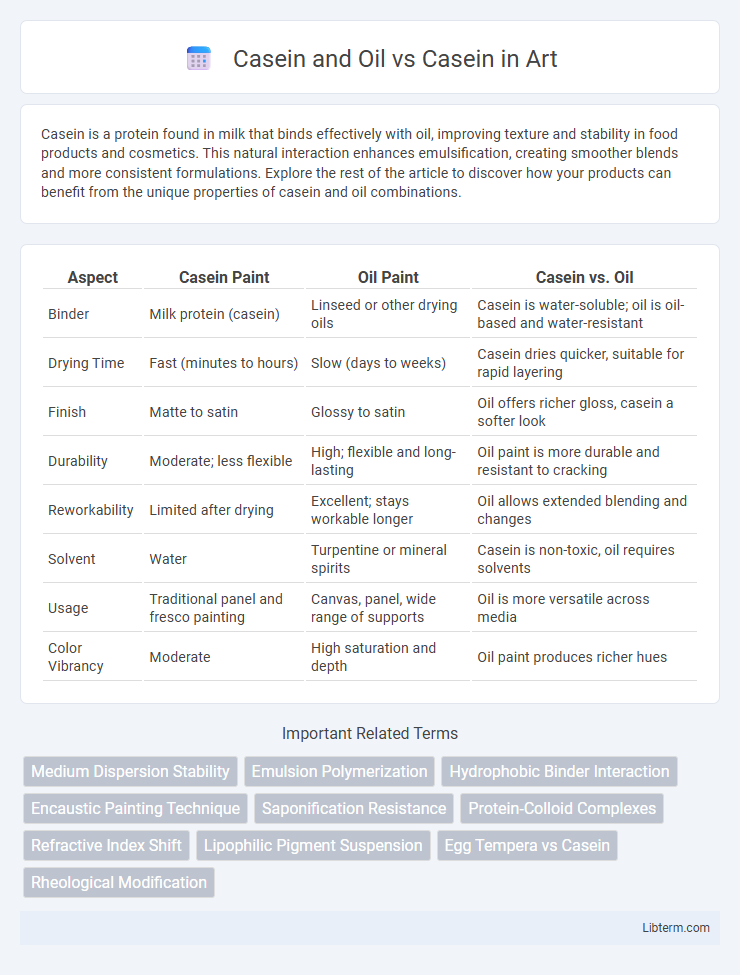
| Aspect | Casein Paint | Oil Paint | Casein vs. Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Binder | Milk protein (casein) | Linseed or other drying oils | Casein is water-soluble; oil is oil-based and water-resistant |
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slow (days to weeks) | Casein dries quicker, suitable for rapid layering |
| Finish | Matte to satin | Glossy to satin | Oil offers richer gloss, casein a softer look |
| Durability | Moderate; less flexible | High; flexible and long-lasting | Oil paint is more durable and resistant to cracking |
| Reworkability | Limited after drying | Excellent; stays workable longer | Oil allows extended blending and changes |
| Solvent | Water | Turpentine or mineral spirits | Casein is non-toxic, oil requires solvents |
| Usage | Traditional panel and fresco painting | Canvas, panel, wide range of supports | Oil is more versatile across media |
| Color Vibrancy | Moderate | High saturation and depth | Oil paint produces richer hues |
Understanding Casein: Composition and Properties
Casein, a phosphoprotein constituting about 80% of milk proteins, exhibits unique properties such as high emulsification, water-binding capacity, and slow digestibility, which influence its functional applications in food and pharmaceuticals. Casein micelles, primarily composed of as1-, as2-, b-, and k-casein fractions, form stable colloidal structures that facilitate controlled release and improve texture in casein-based formulations. When combined with oils, casein acts as an efficient emulsifier, enhancing the stability and bioavailability of lipid nutrients through the formation of casein-oil complexes, unlike pure casein which lacks these lipid interaction benefits.
What is Oil-Based Casein Paint?
Oil-based casein paint combines the protein-based binder casein with natural oils like linseed or walnut oil to enhance durability and drying time. This hybrid formulation offers superior adhesion, water resistance, and a smooth finish compared to traditional water-based casein paint. Artists and conservators prefer oil-based casein for its vibrant matte appearance and archival quality on wood, canvas, and paper surfaces.
Key Differences: Casein and Casein-Oil Paints
Casein paint is a water-soluble medium made from milk protein, known for its fast drying time, matte finish, and excellent adhesion to porous surfaces. Casein-oil paints combine casein with oil, typically linseed oil, enhancing durability, flexibility, and water resistance while slowing drying time compared to pure casein. The addition of oil increases the paint's gloss and allows for richer texture and layering options, making casein-oil suitable for artists seeking a balance between watercolor and oil paint properties.
Historical Uses of Casein vs Casein-Oil Mixtures
Casein has been historically used as a durable and water-resistant adhesive in woodworking, paper bonding, and painting, dating back to ancient Egypt. The development of casein-oil mixtures enhanced these properties by combining the protein's strong adhesive qualities with the drying and protective benefits of oils, resulting in more flexible and weather-resistant coatings. These mixtures found significant applications in pioneering early paint formulations and industrial adhesives throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Advantages of Pure Casein Paint
Pure casein paint offers superior durability and moisture resistance compared to casein mixed with oil, making it ideal for long-lasting applications. Its fast-drying properties and matte finish enhance color retention and surface texture without the yellowing commonly seen in oil-blended paints. High protein content in pure casein ensures excellent adhesion on porous surfaces, providing a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for artists and craftsmen.
Benefits of Adding Oil to Casein
Adding oil to casein improves the texture and moisture retention in food products, making them creamier and enhancing palatability. The incorporation of healthy oils, such as omega-3 rich sources, boosts the nutritional profile by providing essential fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins alongside casein's high-quality protein. This combination supports better nutrient absorption and sustained energy release, benefiting muscle repair and overall metabolic health.
Workability and Drying Times Compared
Casein paint combined with oil exhibits extended drying times but offers enhanced workability due to the oil's slow oxidation process, allowing smoother blending and greater manipulation on the canvas. In contrast, pure casein paint dries faster through protein coagulation, providing quicker layering but reduced open time for blending. Artists prioritize casein with oil when extended drying suits detailed work, while pure casein is favored for rapid coverage and prompt overpainting.
Durability and Longevity: Casein Versus Casein-Oil
Casein-oil paints exhibit enhanced durability compared to pure casein paints due to the added oil content, which improves water resistance and flexibility. The oil component forms a stronger, more resilient film that extends the longevity of the paint surface, reducing susceptibility to cracking and environmental damage. Consequently, casein-oil formulations are favored for applications requiring long-term durability and sustained protection.
Best Applications: When to Use Each Formulation
Casein and oil formulations excel in skincare products requiring deep hydration and barrier repair, making them ideal for dry or mature skin types. Casein-only formulations suit lightweight moisturizers and treatments focused on protein nourishment without added oils, preferred in oily or acne-prone skin care. Choosing between these depends on desired texture, absorption rate, and specific skin needs for optimal results.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Considerations
Casein and oil mixtures often pose greater health risks due to potential allergenic reactions and lipid oxidation compared to pure casein, which is generally recognized as safe and non-toxic. From a safety perspective, casein alone maintains higher stability and lower flammability, while addition of oils can increase the product's susceptibility to spoilage and microbial growth. Environmentally, producing casein with oil involves higher carbon emissions and water usage due to oil extraction processes, whereas pure casein production typically generates less ecological impact, making it a more sustainable option in dairy-based applications.
Casein and Oil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com