Sgraffito is a decorative technique that involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, often used in pottery, wall decoration, and art. This method enhances texture and depth, making designs stand out with intricate detail and historical charm. Explore the article to discover how sgraffito can transform your creative projects.
Table of Comparison
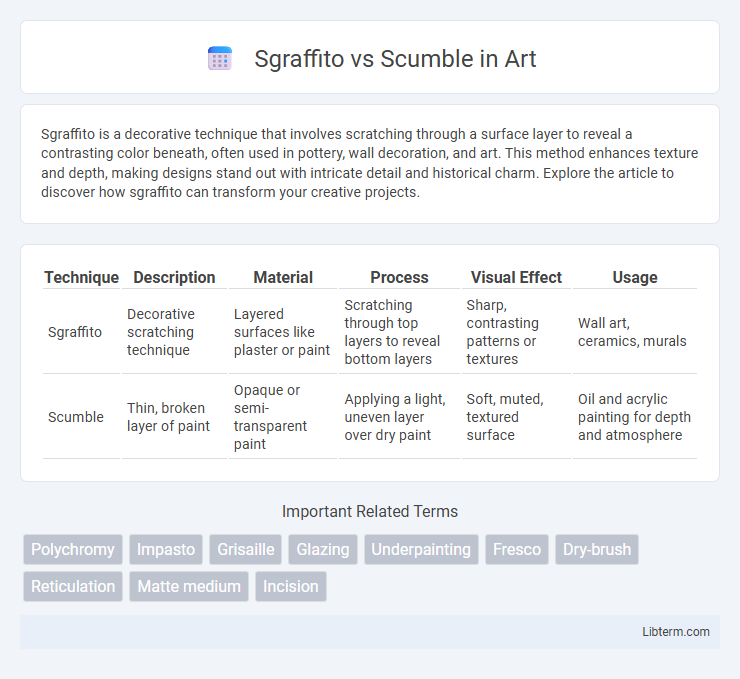
| Technique | Description | Material | Process | Visual Effect | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sgraffito | Decorative scratching technique | Layered surfaces like plaster or paint | Scratching through top layers to reveal bottom layers | Sharp, contrasting patterns or textures | Wall art, ceramics, murals |
| Scumble | Thin, broken layer of paint | Opaque or semi-transparent paint | Applying a light, uneven layer over dry paint | Soft, muted, textured surface | Oil and acrylic painting for depth and atmosphere |
Introduction to Sgraffito and Scumble
Sgraffito is a decorative technique involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color or material beneath, commonly used in pottery, wall decor, and fine art. Scumble refers to a painting method where a thin, semi-opaque layer of paint is applied over another to create a textured, softened effect, enhancing depth and luminosity. Both techniques serve distinct artistic purposes, with sgraffito emphasizing contrast and texture through incised lines, while scumble focuses on subtle color blending and surface modulation.
Historical Origins and Artistic Evolution
Sgraffito originated during the Renaissance, characterized by scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, mainly used in pottery and fresco decoration across Italy and the Netherlands. Scumble emerged in the Baroque period as a technique of applying thin, opaque layers of paint to create depth and soften colors, gaining popularity among European painters such as Rembrandt. Both techniques evolved through artistic innovation, with sgraffito maintaining its tactile texture in decorative arts and scumbling advancing as a key tool in expressive brushwork and atmospheric effects in oil painting.
Defining Sgraffito: Techniques and Materials
Sgraffito is a decorative technique involving scratching through a surface layer of wet plaster, paint, or slip to reveal a contrasting color beneath, commonly used in ceramics and wall art. Artists typically apply multiple layers of differently colored materials and use tools such as knives or styluses to create intricate designs by carefully removing portions of the top layer. Materials for sgraffito often include pigmented plaster, clay slips, and oil or acrylic paints, which provide a durable and textured finish that enhances the visual contrast.
Understanding Scumble: Methods and Mediums
Scumble involves applying a thin, semi-transparent layer of paint over a dried layer to create depth and texture, commonly using oil or acrylic mediums. This technique requires careful control of brushstrokes and paint dilution to achieve a soft, misty effect that enhances underlying colors. Unlike sgraffito, which focuses on scratching through layers to reveal contrasts, scumbling emphasizes subtle color blending and atmospheric nuances.
Key Differences Between Sgraffito and Scumble
Sgraffito involves scratching through a top layer of paint to reveal a contrasting color beneath, creating textures and intricate designs, while scumble uses a thin, semi-transparent layer of paint applied over a dry layer to soften or lighten the color underneath without exposing it. Sgraffito emphasizes texture and layering with high contrast, whereas scumble focuses on subtle color blending and tonal variation. Artists choose sgraffito for bold, graphic effects and scumble for atmospheric depth and muted transitions.
Visual Effects: Texture and Depth
Sgraffito creates striking visual effects by scratching through a surface layer to reveal underlying colors, resulting in distinct textured lines and dramatic depth contrasts. Scumble employs a semi-transparent, broken color application, softening edges and producing a rich, layered depth with subtle texture variations. Both techniques enhance the tactile quality of artwork but differ in approach: Sgraffito emphasizes pronounced linear texture, while Scumble builds nuanced luminosity and surface complexity.
Applications in Fine Art and Decorative Work
Sgraffito and scumble techniques both enhance texture and depth in fine art and decorative work, with sgraffito involving scratching through a surface layer to reveal underlying colors, ideal for intricate designs and layered effects. Scumble employs a thin, semi-transparent layer of paint brushed lightly over a dry layer, creating soft transitions and atmospheric effects often used in glazing and aging finishes. Artists and decorators select sgraffito for bold, graphic contrasts in ceramics and murals, while scumble is preferred for subtle color modulation in oil and acrylic paintings.
Popular Artists and Iconic Examples
Sgraffito, employed by artists like Pablo Picasso and Jean Dubuffet, involves scratching through a surface layer to reveal a contrasting color beneath, exemplified in Picasso's ceramics and Dubuffet's textured paintings. Scumble, favored by artists such as J.M.W. Turner and John Constable, uses a thin, opaque layer of paint to create softened effects and atmospheric depth, as seen in Turner's seascapes and Constable's landscapes. These techniques remain iconic for their distinctive textural qualities and contributions to modern and classical art.
Advantages and Challenges of Each Technique
Sgraffito offers precise textural contrast by scratching through a top layer to reveal underlying colors, enabling fine detail and intricate designs that enhance depth, though it requires careful timing and control to avoid tearing the substrate. Scumbling creates soft, broken color effects by applying semi-opaque layers with a dry brush, ideal for subtle tonal variations and atmospheric qualities, but achieving consistent opacity can be challenging and may require multiple layers. Both techniques offer distinct advantages for artistic expression, with Sgraffito excelling in sharp delineation and Scumble providing a delicate interplay of light and texture.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Artwork
Selecting between sgraffito and scumble depends on the texture and detail desired in your artwork; sgraffito involves scratching through layers of paint to reveal underlying colors, creating sharp, defined lines, while scumble applies a thin, semi-opaque layer of paint to soften and blend surfaces. Artists aiming for intricate textures or pronounced contrasts benefit from sgraffito's precise incisions, whereas those seeking subtle, atmospheric effects find scumble ideal for adding depth and luminosity. Understanding the visual impact and layering potential of each technique enables informed decisions tailored to the artistic vision and medium used.
Sgraffito Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com