Marquetry transforms ordinary furniture into exquisite art by intricately inlaying wood veneers to create detailed patterns and images. This craftsmanship demands precision and creativity, making each piece unique and highly valued in interior design. Discover how marquetry can elevate your decor by exploring the techniques and styles in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
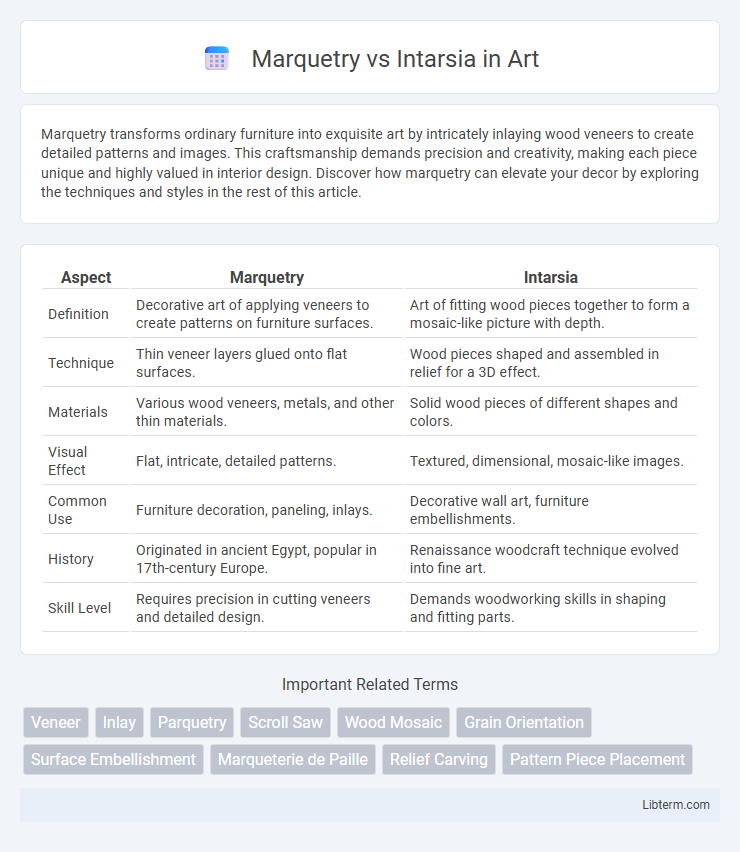
| Aspect | Marquetry | Intarsia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decorative art of applying veneers to create patterns on furniture surfaces. | Art of fitting wood pieces together to form a mosaic-like picture with depth. |
| Technique | Thin veneer layers glued onto flat surfaces. | Wood pieces shaped and assembled in relief for a 3D effect. |
| Materials | Various wood veneers, metals, and other thin materials. | Solid wood pieces of different shapes and colors. |
| Visual Effect | Flat, intricate, detailed patterns. | Textured, dimensional, mosaic-like images. |
| Common Use | Furniture decoration, paneling, inlays. | Decorative wall art, furniture embellishments. |
| History | Originated in ancient Egypt, popular in 17th-century Europe. | Renaissance woodcraft technique evolved into fine art. |
| Skill Level | Requires precision in cutting veneers and detailed design. | Demands woodworking skills in shaping and fitting parts. |
Introduction to Marquetry and Intarsia
Marquetry involves creating intricate designs by applying thin veneers of wood, shell, or other materials onto surfaces, emphasizing decorative artistry and precision. Intarsia is a woodworking technique that forms detailed images by fitting together individual pieces of wood, highlighting depth and texture through three-dimensional effects. Both crafts showcase skilled craftsmanship but differ in their approach to assembling materials and creating visual impact.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Marquetry and intarsia both originated during the Renaissance period, with marquetry evolving in Italy and intarsia developing primarily in Tuscany as intricate wood inlay techniques. Marquetry involves applying thin veneers of various woods on flat surfaces to create detailed pictorial designs, while intarsia focuses on fitting individually carved wood pieces together like a puzzle to form a three-dimensional effect. Over centuries, these crafts have influenced furniture and decorative art, showcasing a progression from simple geometric patterns to complex, realistic imagery reflecting the cultural and artistic advancements of their eras.
Core Techniques and Methods
Marquetry involves creating intricate patterns by veneering thin slices of wood, shell, or other materials onto a flat substrate, emphasizing precision cutting and layering for detailed surface designs. Intarsia focuses on assembling three-dimensional, puzzle-like wood pieces of varying thicknesses to form a textured, relief image, utilizing shaping and sanding to achieve depth and contour. Both techniques require meticulous craftsmanship but differ in dimensionality, with marquetry producing flat decorative surfaces and intarsia crafting sculptural wood art.
Materials Used in Marquetry vs Intarsia
Marquetry primarily uses thin veneers of wood, metal, or shell carefully cut and glued onto a flat surface to create intricate patterns, emphasizing delicate and lightweight materials. Intarsia involves fitting together thicker pieces of wood, often solid hardwoods like walnut, cherry, and oak, shaped and assembled tightly to form a three-dimensional mosaic. The choice of materials in marquetry supports fine detail and intricate imagery, while intarsia materials provide depth, texture, and a sculptural quality to the finished piece.
Key Differences in Design Approaches
Marquetry involves creating intricate, flat patterns by applying thin veneer slices of various woods onto a surface, emphasizing detailed, pictorial designs. Intarsia uses thicker wood pieces individually shaped and assembled to form a three-dimensional mosaic with varied depth and texture. The primary design difference lies in marquetry's focus on flat veneer layering for visual complexity, while intarsia prioritizes sculptural assembly for tactile and dimensional effects.
Popular Applications and Uses
Marquetry is predominantly used in fine furniture, decorative panels, and luxury cabinetry, showcasing intricate patterns with thin veneers. Intarsia is favored in artistic woodworking projects such as wall art, small boxes, and musical instruments, emphasizing detailed, three-dimensional effects with solid wood pieces. Both techniques enhance visual appeal but differ in material layering and application scope.
Artistic Styles and Influences
Marquetry involves applying thin veneers of wood to create intricate, flat patterns, often influenced by Baroque and Rococo artistic styles emphasizing elaborate detail and symmetry. Intarsia, by contrast, uses thicker wood pieces assembled to form a mosaic-like, three-dimensional effect rooted in Renaissance and Medieval art traditions, highlighting depth and texture. Both techniques reflect cultural influences but differ in visual impact and dimensionality due to their unique construction methods.
Skills Required for Each Craft
Marquetry demands precise skills in veneer cutting and pattern alignment to create intricate, flat surface designs often involving fine motor control and detailed planning. Intarsia requires advanced wood shaping and fitting abilities, emphasizing three-dimensional craftsmanship to assemble varied wood pieces into a sculptural mosaic. Both crafts necessitate patience and artistic vision, but intarsia often involves more complex woodworking techniques and textural creativity.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Marquetry and intarsia both require careful maintenance to preserve their intricate designs and wood veneers, with marquetry being more susceptible to damage from moisture and direct sunlight due to its thin veneer layers. Intarsia, constructed from thicker solid wood pieces, generally offers greater durability and easier repair options when compared to marquetry's delicate surface. Regular dusting with a soft cloth and controlled humidity levels are essential for extending the lifespan of both techniques, but intarsia's robust nature typically withstands wear better in high-traffic environments.
Choosing Between Marquetry and Intarsia
Choosing between marquetry and intarsia depends on the desired visual effect and project complexity. Marquetry involves applying thin veneer pieces to create intricate, flat patterns on surfaces, ideal for detailed and delicate designs. Intarsia uses thicker wood pieces assembled like a puzzle, producing a three-dimensional appearance suited for sculptural or textured woodworking projects.
Marquetry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com