Alcohol ink art transforms vibrant, fluid colors into stunning abstract designs that captivate the eye. This medium, known for its fast drying time and bold pigments, allows artists to create unique textures and depth on non-porous surfaces such as Yupo paper and ceramics. Discover how you can master this expressive art form by exploring our detailed guide ahead.
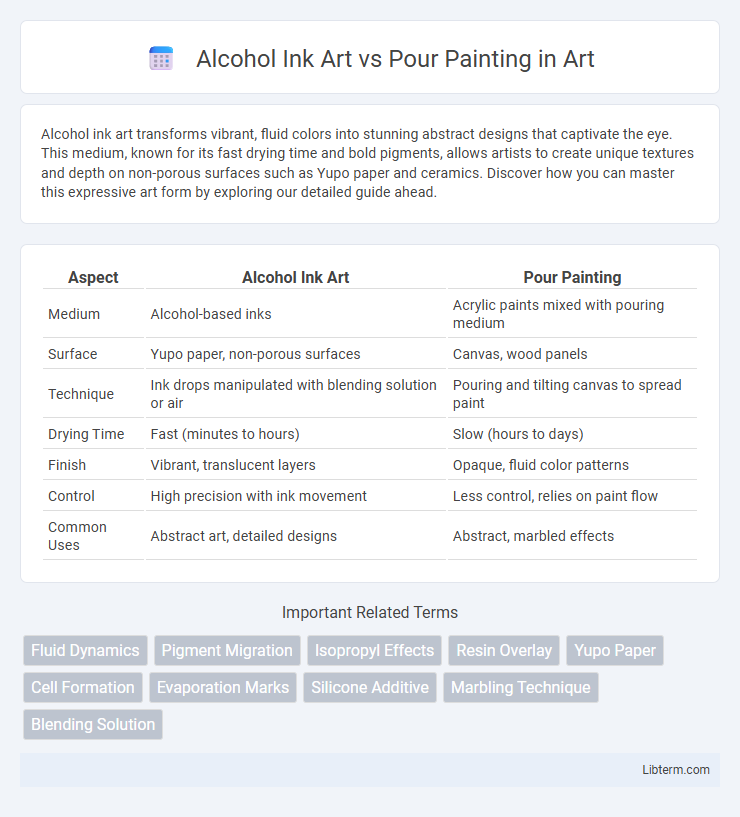
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alcohol Ink Art | Pour Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Alcohol-based inks | Acrylic paints mixed with pouring medium |
| Surface | Yupo paper, non-porous surfaces | Canvas, wood panels |
| Technique | Ink drops manipulated with blending solution or air | Pouring and tilting canvas to spread paint |
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slow (hours to days) |
| Finish | Vibrant, translucent layers | Opaque, fluid color patterns |
| Control | High precision with ink movement | Less control, relies on paint flow |
| Common Uses | Abstract art, detailed designs | Abstract, marbled effects |
Introduction to Alcohol Ink Art and Pour Painting
Alcohol ink art involves using highly pigmented, fast-drying alcohol-based inks on non-porous surfaces like Yupo paper or ceramic tiles, creating vibrant, fluid patterns with rich color blending and translucency. Pour painting, also known as acrylic pouring, entails combining acrylic paints with pouring mediums to achieve a fluid consistency that flows and interacts freely on canvas, producing abstract, marbled effects with cells and intricate color mixing. Both techniques emphasize the unpredictable movement of liquid mediums but differ in material properties and surface textures, offering unique aesthetic outcomes for abstract art enthusiasts.
Key Differences Between Alcohol Ink Art and Pour Painting
Alcohol Ink Art features vibrant, translucent pigments that reactively blend on non-porous surfaces like Yupo paper, creating fluid and dynamic effects, whereas Pour Painting involves pouring acrylic paints mixed with pouring mediums onto canvas to achieve marbled, textured patterns. Alcohol Ink Art dries quickly and allows for intricate manipulation with tools or air, while Pour Painting requires longer drying times and emphasizes layering and cell formation through chemical additives. The materials and techniques used distinctly influence the final aesthetics and creative process in each medium.
Materials and Tools Required for Each Technique
Alcohol ink art requires isopropyl alcohol, vibrant alcohol-based inks, Yupo paper or non-porous surfaces, blending solution, and tools such as brushes, droppers, and air blowers for manipulating the ink. Pour painting involves acrylic paints, pouring mediums like Floetrol or Liquitex Pouring Medium, primed canvases or wood panels, cups for mixing, stir sticks, and optional silicone oil to create cells and texture. Both techniques demand specific materials tailored to their fluid dynamics, with alcohol ink art emphasizing fast-drying, translucent inks on slick surfaces, while pour painting relies on thicker, slower-drying acrylic mixtures for layered, textured effects.
Surface Choices: What Works Best for Both Methods
Alcohol ink art thrives on non-porous, glossy surfaces such as Yupo paper, ceramic tiles, and glass, which allow the inks to flow and blend seamlessly. Pour painting excels on primed canvases or wooden panels, providing a grip that holds the fluid paint without excessive absorption while supporting vibrant color retention. Choosing the right surface is critical for both methods to achieve optimal fluidity, color intensity, and longevity of the artwork.
Color Behavior and Effects: Alcohol Ink vs Pour Paints
Alcohol ink art features vibrant, translucent colors that rapidly spread and blend with high fluidity, creating intricate patterns and organic textures due to the ink's alcohol base evaporating quickly. Pour painting utilizes thicker acrylic paints mixed with pouring mediums, resulting in slower drying times and the formation of cells and marbling effects as pigments layer and interact on the canvas surface. Color behavior in alcohol inks emphasizes bright, saturated hues with sharp edges and dynamic flow, while pour paints offer more muted blends, depth, and texture through pigment density and surface tension manipulation.
Techniques and Application Processes
Alcohol ink art uses highly pigmented, fast-drying alcohol-based dyes applied on non-porous surfaces like Yupo paper, allowing for vibrant, fluid effects created through techniques such as blowing, tilting, and layering. Pour painting relies on mixing acrylic paints with pouring mediums to achieve a viscous consistency, which is then poured onto a canvas and manipulated by tilting or using tools to create abstract patterns and cells. Both techniques emphasize color flow and spontaneity but differ in medium properties, surface interaction, and drying times, impacting the final texture and visual outcome.
Drying Times and Finish: What to Expect
Alcohol ink art typically dries within minutes, offering a vibrant, glossy finish that enhances color intensity and fluidity. Pour painting requires several hours to days to dry, resulting in a thicker, more textured finish with a matte or glossy surface depending on the medium used. Understanding these differences in drying times and finish helps artists choose the best technique for their desired visual effects and project timelines.
Artistic Styles and Popular Patterns
Alcohol Ink Art features vibrant, fluid designs with high saturation and organic shapes created by manipulating alcohol-based dyes on non-porous surfaces, emphasizing bold color blending and abstract forms. Pour Painting relies on pouring layers of acrylic paint mixed with pouring mediums onto a canvas, forming cells, marbled effects, and dynamic, flowing patterns that highlight spontaneity and texture. Popular patterns in Alcohol Ink Art include blooming flowers and landscapes, while Pour Painting showcases geode-inspired swirls and cosmic abstracts.
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
Alcohol ink art and pour painting both demand careful control over fluid dynamics and drying times to avoid common challenges like color blending and uneven textures. Troubleshooting alcohol ink art often involves managing ink dilution and alcohol evaporation rates to prevent unwanted bleeding or blooming effects. Pour painting requires precise mixing ratios of paint and pouring medium to maintain flow consistency and minimize cracking or separation during drying.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Art Goals
Choosing between alcohol ink art and pour painting depends on your desired artistic effect and workflow preferences; alcohol ink art offers vibrant colors with precise control and fast-drying properties, ideal for detailed, fluid designs on non-porous surfaces. Pour painting emphasizes creating abstract, organic patterns through fluid dynamics on canvas or wood, with a longer drying time that allows for blending and layering techniques. Understanding the characteristics of each medium helps artists align their creative goals with the most suitable technique, enhancing both process satisfaction and final outcomes.
Alcohol Ink Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com