Cropping is a fundamental technique in photography and graphic design that enhances composition by removing unwanted outer areas of an image. It helps to focus attention on the subject, improve framing, and eliminate distractions, making your visuals more impactful. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective cropping tips that will elevate your visual storytelling.
Table of Comparison
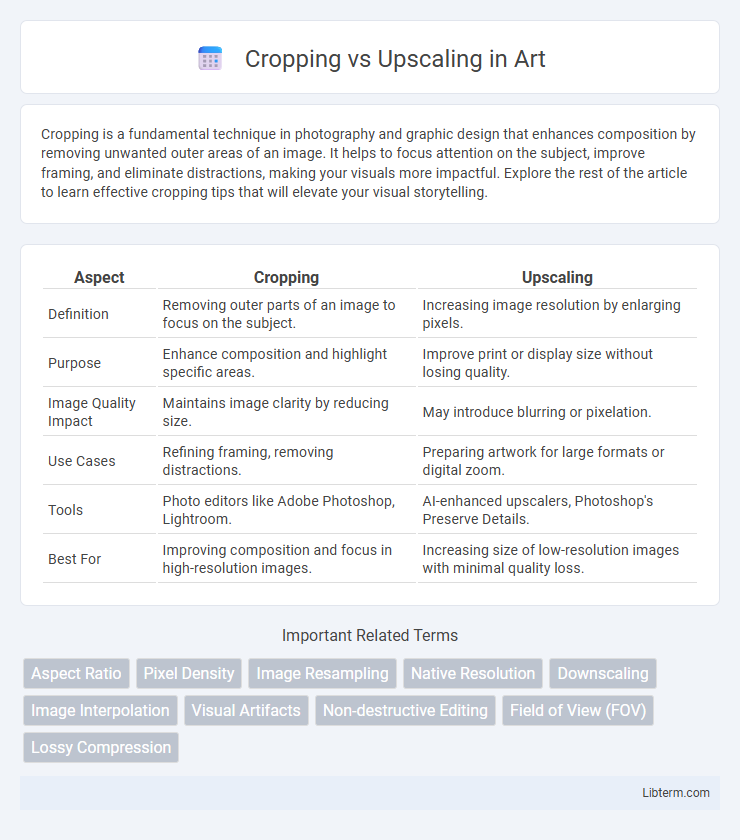
| Aspect | Cropping | Upscaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Removing outer parts of an image to focus on the subject. | Increasing image resolution by enlarging pixels. |
| Purpose | Enhance composition and highlight specific areas. | Improve print or display size without losing quality. |
| Image Quality Impact | Maintains image clarity by reducing size. | May introduce blurring or pixelation. |
| Use Cases | Refining framing, removing distractions. | Preparing artwork for large formats or digital zoom. |
| Tools | Photo editors like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom. | AI-enhanced upscalers, Photoshop's Preserve Details. |
| Best For | Improving composition and focus in high-resolution images. | Increasing size of low-resolution images with minimal quality loss. |
Introduction to Cropping and Upscaling
Cropping involves removing outer parts of an image to focus on a specific area, often improving composition without altering original resolution. Upscaling increases an image's size by adding pixels through interpolation techniques like bicubic or AI-based algorithms, aiming to preserve quality at higher resolutions. Both methods are essential in image editing, with cropping refining content and upscaling enhancing display size.
Understanding Image Cropping
Image cropping involves removing unwanted outer areas to focus on the central subject, enhancing composition and framing without altering resolution. Unlike upscaling, which increases image size by adding pixels and risks quality loss, cropping maintains original image sharpness within the selected area. Mastery of image cropping techniques ensures a balanced, high-quality visual presentation by emphasizing key details and eliminating distractions.
What is Image Upscaling?
Image upscaling enhances the resolution of a digital image by increasing its pixel count, allowing for larger display sizes without losing visual quality. Advanced algorithms, such as deep learning-based super-resolution, reconstruct finer details to improve clarity and sharpness beyond simple interpolation techniques. This process contrasts with cropping, which reduces image size by trimming edges, often compromising composition or context.
Key Differences: Cropping vs Upscaling
Cropping reduces an image's dimensions by cutting out portions, which decreases resolution and focuses on a specific area, while upscaling enlarges the entire image, increasing pixel count through interpolation but may introduce blurriness or loss of detail. Cropping maintains original pixel quality within the selected region, whereas upscaling relies on algorithms like bicubic or neural network-based methods to estimate missing pixels. The choice between cropping and upscaling impacts image clarity, composition, and usability depending on the intended application or display size.
When to Use Cropping
Cropping is ideal when the goal is to remove unwanted areas of an image to improve composition, focus on the subject, or fit specific dimensions without distorting the original resolution. It is particularly useful for eliminating distractions or achieving a tighter framing that highlights key elements in photography and graphic design. Use cropping when maintaining image clarity is critical, especially if enlarging the image through upscaling would result in loss of sharpness or pixelation.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Upscaling
Upscaling enhances image resolution by increasing pixel count, allowing for larger displays without loss of original data, which benefits detailed viewing on high-resolution screens. However, it can introduce artifacts like blurriness and noise due to interpolation algorithms guessing missing information, reducing image clarity. While cropping improves composition by focusing on specific elements, upscaling is essential when maintaining full image content at larger sizes is required.
Impact on Image Quality
Cropping reduces image resolution by removing pixels, resulting in a smaller but often sharper composition, while upscaling increases pixel count through interpolation, which can introduce blurriness and artifacts. Cropping preserves original image sharpness but limits print size or display scale, whereas upscaling allows larger prints or screens but at the cost of reduced clarity and possible pixelation. High-quality upscaling algorithms such as AI-based models can mitigate quality loss, but true image detail cannot be fully recovered like in original uncropped photos.
Cropping and Upscaling in Digital Photography
Cropping in digital photography involves trimming the edges of an image to improve composition or focus on a subject, often resulting in a smaller pixel count that can reduce image resolution. Upscaling uses algorithms to increase an image's pixel dimensions, enhancing its size while attempting to maintain detail, but it may introduce artifacts or softness if overdone. Balancing cropping and upscaling is essential to preserve image quality, especially for printing or displaying on high-resolution screens.
Tools and Software for Cropping and Upscaling
Top tools for cropping include Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and Lightroom, which offer precise control over image dimensions and composition. For upscaling, AI-powered software like Topaz Gigapixel AI, Adobe Photoshop's Preserve Details 2.0, and Let's Enhance use machine learning algorithms to enhance image resolution while minimizing quality loss. These specialized tools leverage advanced interpolation and neural networks to optimize image clarity during resizing processes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Needs
Cropping enhances image composition by removing unwanted areas, ideal for focusing on specific details without altering resolution. Upscaling increases image size using AI algorithms or interpolation, suitable for printing or displaying on higher-resolution screens but may introduce artifacts. Selecting the right approach depends on balancing the desired detail retention, output quality, and final use case of the image.
Cropping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com