Sculptures transform spaces by adding depth, texture, and artistic expression, enriching both indoor and outdoor environments. Different materials and styles create diverse visual experiences that can evoke emotions and tell stories. Discover how sculpture can enhance your surroundings and inspire creativity by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
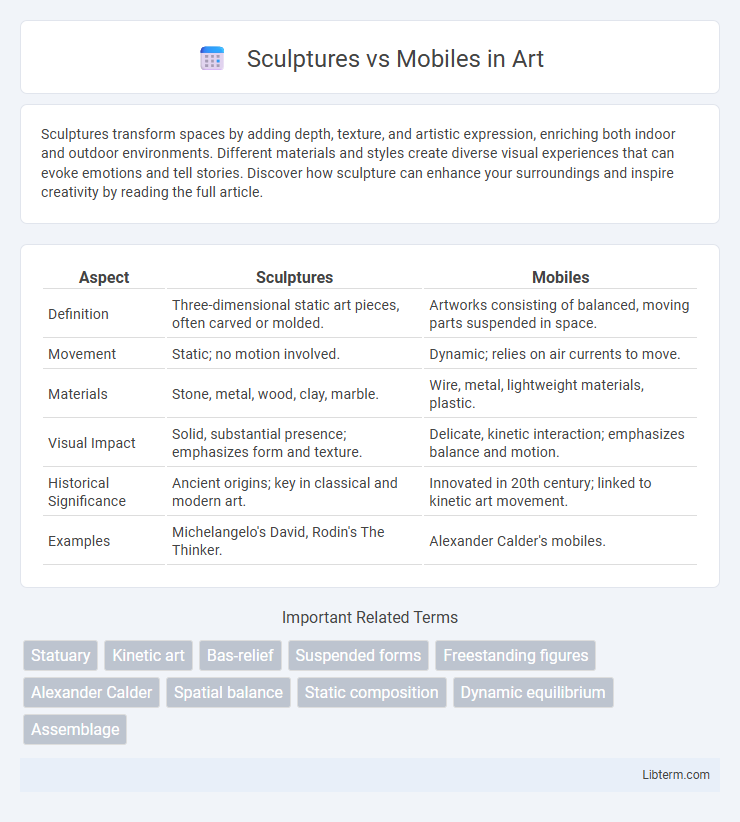
| Aspect | Sculptures | Mobiles |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional static art pieces, often carved or molded. | Artworks consisting of balanced, moving parts suspended in space. |
| Movement | Static; no motion involved. | Dynamic; relies on air currents to move. |
| Materials | Stone, metal, wood, clay, marble. | Wire, metal, lightweight materials, plastic. |
| Visual Impact | Solid, substantial presence; emphasizes form and texture. | Delicate, kinetic interaction; emphasizes balance and motion. |
| Historical Significance | Ancient origins; key in classical and modern art. | Innovated in 20th century; linked to kinetic art movement. |
| Examples | Michelangelo's David, Rodin's The Thinker. | Alexander Calder's mobiles. |
Introduction to Sculptures and Mobiles
Sculptures are three-dimensional art forms created from materials such as stone, metal, or wood that emphasize mass, volume, and texture. Mobiles, invented by Alexander Calder in the early 20th century, are kinetic sculptures designed to move gracefully with air currents, combining balance and motion. Both art forms explore spatial relationships but differ fundamentally in their interaction with the environment and viewer engagement.
Defining Traditional Sculptures
Traditional sculptures are three-dimensional artworks created from materials such as stone, metal, wood, or clay, characterized by their static and solid forms. These sculptures often depict figures, animals, or abstract shapes that remain fixed in position, emphasizing texture, volume, and mass. Unlike mobiles, traditional sculptures do not include moving parts or rely on balance and motion to create visual interest.
The Evolution of Mobiles
Mobiles evolved from traditional sculptures by incorporating movement and balance, pioneered by artist Alexander Calder in the 1930s. These kinetic sculptures introduced dynamic spatial relationships, engaging viewers through shifting forms and shadows. Modern mobiles integrate advanced materials and motorized elements, further expanding their interactive and aesthetic dimensions.
Key Materials in Sculptures vs Mobiles
Sculptures primarily utilize robust materials such as marble, bronze, wood, and clay, chosen for their durability and ability to hold intricate details. Mobiles rely on lightweight materials like wire, metal rods, and suspended elements made from plastic, glass, or thin metal sheets to enable balanced movement and dynamic interaction with air currents. The contrasting material properties reflect their distinct artistic purposes: permanence in sculptures versus kinetic motion in mobiles.
Artistic Techniques and Processes
Sculptures primarily involve subtractive or additive techniques such as carving, modeling, and casting to create three-dimensional static forms, often utilizing materials like stone, metal, or clay. Mobiles employ dynamic construction methods, balancing elements suspended by wires to achieve kinetic movement, relying on principles of physics and spatial harmony. The artistic process of mobiles emphasizes engineering and motion integration, contrasting with the tactile and material manipulation central to traditional sculpture.
Visual Impact and Movement
Sculptures offer a static visual impact characterized by solid forms and textures that invite detailed observation from multiple angles, creating a sense of permanence and weight. Mobiles, designed by artists like Alexander Calder, incorporate kinetic movement that changes the viewer's perception as they shift with air currents, generating dynamic interactions between balance, light, and shadow. The interplay of mobility in mobiles contrasts with the fixed presence of sculptures, highlighting different approaches to engaging audiences through visual and spatial experience.
Influential Artists in Both Art Forms
Alexander Calder revolutionized mobiles by introducing kinetic art that blends movement and balance, transforming traditional sculpture into dynamic forms. Constantin Brancusi's minimalist sculptures emphasize smooth, organic shapes and simplicity, influencing modernist sculpture profoundly. Both artists redefined space and form, with Calder focusing on motion and Brancusi on timeless stillness, each leaving a lasting impact on their respective art forms.
Sculptures and Mobiles in Modern Spaces
Sculptures in modern spaces serve as focal points, blending artistic expression with architectural design to enhance aesthetic appeal and spatial harmony. Mobiles, characterized by their kinetic movement and lightness, introduce dynamic visual interest and subtle interactivity, often transforming room ambiance through changing shadows and forms. Both sculptures and mobiles contribute uniquely to contemporary interiors, offering static grandeur and fluid movement respectively, enriching the modern artistic landscape.
Collecting and Display Considerations
Sculptures often require stable bases and spatial consideration for optimal display, favoring solid pedestals or plinths to highlight their three-dimensional form. Mobiles need ceiling mounts or overhead suspension points, allowing for kinetic movement and interaction with airflow, which adds dynamic visual interest but demands careful placement to prevent damage. Collectors prioritize lighting, environmental conditions, and available space differently for sculptures and mobiles to preserve material integrity and enhance aesthetic impact.
Future Trends: Sculptures vs Mobiles
Future trends in sculptures emphasize the integration of interactive digital elements and sustainable materials, while mobiles are evolving with advancements in lightweight, flexible components and kinetic energy harnessing technologies. Sculptures increasingly incorporate augmented reality and sensor-based interactivity to engage viewers, whereas mobiles focus on dynamic motion enhanced by smart materials and IoT connectivity. Both art forms are converging toward immersive, eco-conscious designs that blend physical artistry with technological innovation.
Sculptures Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com