Wholeness represents the state of being complete and undivided, encompassing all aspects of your mind, body, and spirit in harmony. Achieving wholeness involves integrating your emotions, thoughts, and actions to foster inner balance and resilience. Explore this article to discover practical ways to cultivate wholeness in your life.
Table of Comparison
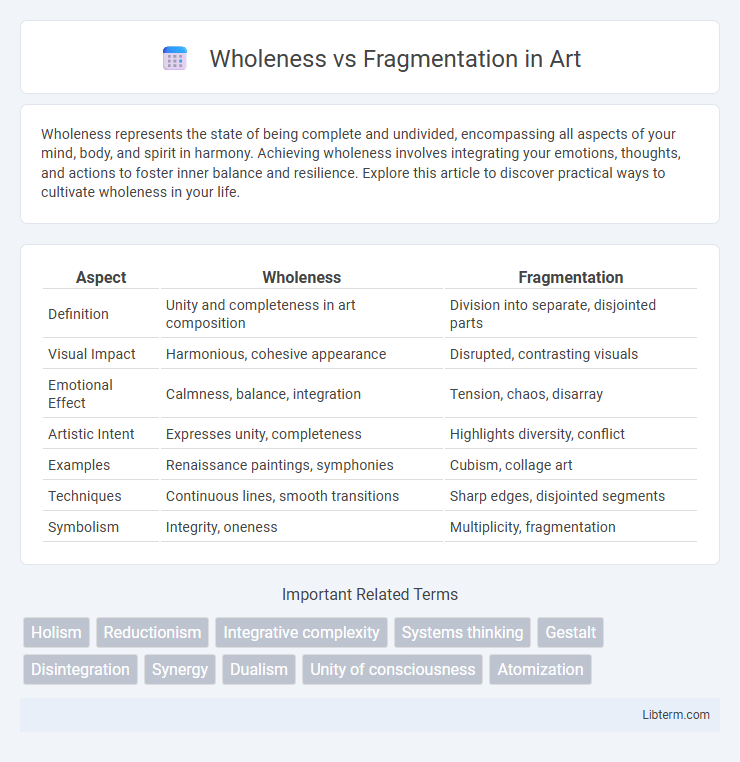
| Aspect | Wholeness | Fragmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unity and completeness in art composition | Division into separate, disjointed parts |
| Visual Impact | Harmonious, cohesive appearance | Disrupted, contrasting visuals |
| Emotional Effect | Calmness, balance, integration | Tension, chaos, disarray |
| Artistic Intent | Expresses unity, completeness | Highlights diversity, conflict |
| Examples | Renaissance paintings, symphonies | Cubism, collage art |
| Techniques | Continuous lines, smooth transitions | Sharp edges, disjointed segments |
| Symbolism | Integrity, oneness | Multiplicity, fragmentation |
Understanding Wholeness: A Holistic Perspective
Understanding wholeness involves recognizing the interconnectedness of all elements within a system, where each part contributes to the integrity of the whole. This holistic perspective emphasizes integration over isolation, promoting balance and synergy between physical, mental, and emotional components. Embracing wholeness fosters resilience and harmony, contrasting sharply with fragmentation that leads to disconnection and dysfunction.
The Nature of Fragmentation in Modern Life
Fragmentation in modern life manifests through the compartmentalization of work, social relationships, and personal identity, disrupting the sense of wholeness individuals seek. Constant digital distractions and rapid technological changes contribute to fragmented attention and experience, leading to decreased mindfulness and emotional disconnection. This pervasive separation challenges mental well-being by fostering feelings of isolation and undermining integrated self-awareness.
Psychological Impacts of Wholeness and Fragmentation
Wholeness fosters psychological resilience, enhancing emotional stability, self-awareness, and a cohesive sense of identity that promotes mental well-being. Fragmentation contributes to cognitive dissonance, emotional distress, and identity confusion, often increasing vulnerability to anxiety, depression, and dissociative disorders. Therapeutic approaches emphasizing integration and coherence aim to restore wholeness, improving overall psychological functioning and quality of life.
Wholeness in Relationships and Community
Wholeness in relationships and community fosters a deep sense of connection, trust, and mutual support that strengthens collective resilience and well-being. Emphasizing authenticity, empathy, and open communication encourages individuals to bring their full selves, creating unified and harmonious social bonds. This holistic approach reduces division and fragmentation by valuing interdependence and shared growth within diverse groups.
Fragmentation in Work and Productivity
Fragmentation in work and productivity occurs when tasks are frequently interrupted or divided into smaller, disjointed segments, leading to reduced focus and efficiency. This state causes cognitive overload, increasing the time required to complete projects and heightening the risk of errors due to constant context switching. Addressing fragmentation by implementing structured workflows and minimizing distractions can significantly enhance overall productivity and work quality.
The Role of Technology in Creating Fragmentation
Rapid advancements in technology contribute significantly to fragmentation by dispersing attention across multiple digital platforms, disrupting continuous focus and deep engagement. Constant notifications, multitasking demands, and the proliferation of specialized apps encourage fragmented cognitive processes, diminishing the sense of wholeness in personal and professional experiences. This technological environment challenges individuals' ability to maintain integrated perspectives, impacting mental well-being and holistic understanding.
Cultivating Wholeness: Practical Approaches
Cultivating wholeness involves integrating diverse aspects of the self through mindfulness practices, self-reflection, and intentional healing to overcome fragmentation. Techniques such as journaling, meditation, and therapy promote emotional coherence and psychological balance, fostering a unified sense of identity. Emphasizing holistic wellness enhances resilience, mental clarity, and overall well-being by synchronizing mind, body, and spirit.
Wholeness vs Fragmentation in Spiritual Practices
Wholeness in spiritual practices emphasizes the integration of mind, body, and spirit, fostering a harmonious connection that leads to inner peace and enlightenment. Fragmentation, by contrast, occurs when these aspects are disjointed, causing spiritual imbalance and emotional distress. Techniques such as meditation, mindfulness, and energy healing are pivotal in restoring wholeness, promoting spiritual growth and holistic well-being.
Overcoming Fragmentation for Personal Growth
Overcoming fragmentation is essential for achieving personal growth by fostering integration of conflicting emotions and thoughts into a cohesive self-concept. Embracing wholeness involves reconciling inner contradictions, promoting mental clarity and emotional resilience. Techniques such as mindfulness, self-reflection, and therapy enhance self-awareness, enabling seamless alignment of fragmented aspects for holistic development.
Building a Culture of Wholeness
Building a culture of wholeness emphasizes integration, authenticity, and collaboration, fostering resilient and motivated teams. Organizations prioritizing psychological safety and open communication reduce fragmentation and enhance collective well-being. Embedding values of inclusivity and trust contributes to sustained productivity and innovation.
Wholeness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com