Mosaic art transforms ordinary materials into captivating visual stories through intricate patterns and vibrant colors. This timeless technique enhances aesthetics in architecture, interior design, and public spaces, creating unique and lasting impressions. Explore the article to discover how mosaic can elevate your space with artful elegance.
Table of Comparison
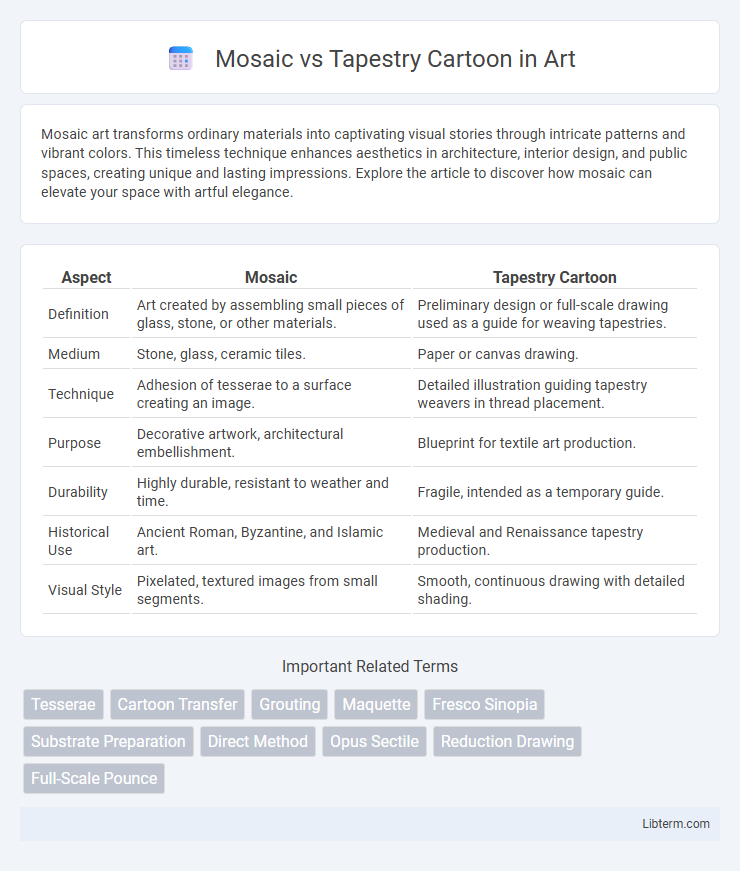
| Aspect | Mosaic | Tapestry Cartoon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created by assembling small pieces of glass, stone, or other materials. | Preliminary design or full-scale drawing used as a guide for weaving tapestries. |
| Medium | Stone, glass, ceramic tiles. | Paper or canvas drawing. |
| Technique | Adhesion of tesserae to a surface creating an image. | Detailed illustration guiding tapestry weavers in thread placement. |
| Purpose | Decorative artwork, architectural embellishment. | Blueprint for textile art production. |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to weather and time. | Fragile, intended as a temporary guide. |
| Historical Use | Ancient Roman, Byzantine, and Islamic art. | Medieval and Renaissance tapestry production. |
| Visual Style | Pixelated, textured images from small segments. | Smooth, continuous drawing with detailed shading. |
Introduction to Mosaic and Tapestry Cartoon
Mosaic and tapestry cartoons serve as detailed design templates for creating intricate art forms; mosaics use small pieces of colored glass, stone, or ceramic to form patterns, while tapestry cartoons are full-scale illustrations guiding textile weavers. Mosaics date back to ancient Mesopotamia and Rome, where craftsmen meticulously arranged tesserae for both decorative and narrative purposes. Tapestry cartoons emerged prominently in the medieval period, especially in Europe, providing weavers with precise outlines to produce elaborate woven artworks used in palaces and churches.
Historical Background of Mosaic Cartoon
Mosaic cartoons trace their origins to ancient civilizations where artisans used small pieces of colored glass, stone, or ceramic known as tesserae to create detailed images and narratives on architectural surfaces, predominantly in Roman and Byzantine cultures. These works served both decorative and didactic purposes, often depicting religious themes, mythological scenes, or social ideals with durable and vibrant detail. The technique evolved through centuries, influencing Renaissance mosaic art and modern interpretations that blend traditional craftsmanship with contemporary design.
Evolution of Tapestry Cartoon Art
The evolution of tapestry cartoon art showcases a progression from the intricate, grid-based mosaic techniques to more fluid, dynamic designs that emphasize storytelling and texture. Early tapestry cartoons combined detailed sketches with color-coded patterns, allowing weavers to translate complex images into woven form efficiently. Over time, this art form integrated diverse artistic styles and cultural motifs, enhancing visual narratives and refining craftsmanship in both European and global tapestry traditions.
Key Differences Between Mosaic and Tapestry Cartoons
Mosaic cartoons consist of small, individual pieces of glass or stone called tesserae arranged to form images with vibrant color contrasts, while tapestry cartoons are large-scale, detailed drawings or designs used as templates for weaving intricate textile artworks. The key difference lies in medium and technique: mosaics are permanent, rigid compositions created from solid materials, whereas tapestry cartoons serve as guides for weaving thread-based artworks with softer textures. Mosaic art emphasizes light reflection and durability, whereas tapestry cartoons focus on color gradation and fabric texture replication.
Materials and Techniques in Mosaic Cartoon
Mosaic cartoons utilize small pieces of colored glass, stone, or ceramic called tesserae, arranged meticulously to create detailed images with vibrant textures and depth. Techniques in mosaic cartoon making include precise cutting of tesserae and embedding them into mortar or adhesive to form durable, moisture-resistant surfaces ideal for architectural decoration. Unlike tapestry cartoons, mosaics emphasize durability and light reflection, offering longevity and intricate color blending through material selection and placement.
Artistic Styles in Tapestry Cartoon
Tapestry cartoons showcase intricate artistic styles characterized by meticulous detailing and vibrant color palettes that bring woven narratives to life. The use of fine lines and textured shading techniques enhances depth, creating a rich visual experience distinct from the fragmented imagery typical of mosaics. This style emphasizes craftsmanship and storytelling through fabric, highlighting the skillful interplay of light, shadow, and pattern inherent in tapestry art.
Cultural Significance of Mosaic and Tapestry Cartoons
Mosaic and tapestry cartoons serve as vital cultural artifacts that reflect the artistic techniques and societal values of their respective eras. Mosaic cartoons, often used as detailed full-scale designs for intricate stone or glass mosaics, demonstrate the ancient civilizations' emphasis on durability and public storytelling through visual symbolism. Tapestry cartoons, typically detailed preparatory drawings for woven tapestries, highlight the medieval and Renaissance focus on narrative richness and textile craftsmanship as a means to convey political power and religious themes.
Modern Adaptations of Mosaic and Tapestry Cartoons
Modern adaptations of mosaic and tapestry cartoons integrate advanced digital techniques and contemporary art styles to revitalize traditional motifs and narratives. Artists employ high-resolution printing and 3D modeling to enhance texture and color vibrancy, bridging the classical craftsmanship with present-day aesthetic demands. These innovations foster new interpretations while preserving the intricate design principles characteristic of historic mosaic and tapestry cartoons.
Iconic Examples: Mosaic vs Tapestry Cartoon
Mosaic art is epitomized by the intricate Byzantine mosaics of Ravenna, featuring luminous glass pieces arranged to depict religious scenes with vibrant color and detailed patterns. Tapestry cartoons, exemplified by the famed Bayeux Tapestry, serve as full-scale preparatory designs that guided the weaving of narrative-driven textile art, showcasing historical events through embroidered imagery. Both art forms transform raw materials into storytelling mediums, with mosaics emphasizing durable, light-reflective surfaces and tapestry cartoons focusing on detailed, hand-woven pictorial sequences.
Choosing Between Mosaic and Tapestry for Artistic Projects
Mosaic art uses small pieces of glass, stone, or ceramics to create detailed, durable images ideal for outdoor and architectural projects, while tapestry relies on woven threads offering rich textures and warmth suited for interior decor and storytelling. Choosing between mosaic and tapestry depends on factors like desired visual impact, installation environment, and material longevity; mosaics excel in moisture-prone or high-traffic areas, whereas tapestries provide flexible, portable artwork with intricate patterns. Budget considerations and maintenance also influence the decision, as mosaics often require skilled labor and higher upfront costs, but demand minimal upkeep compared to tapestries, which may need careful preservation.
Mosaic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com