Collagraph and monotype are distinctive printmaking techniques that offer unique textures and visual effects; collagraph involves building a textured plate from various materials to create relief prints, while monotype produces a single, unique impression by painting or inking directly on a smooth surface. Each method provides vibrant opportunities for creative expression, ideal for artists seeking experimental and dynamic results. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these techniques can enhance your artistic practice.
Table of Comparison
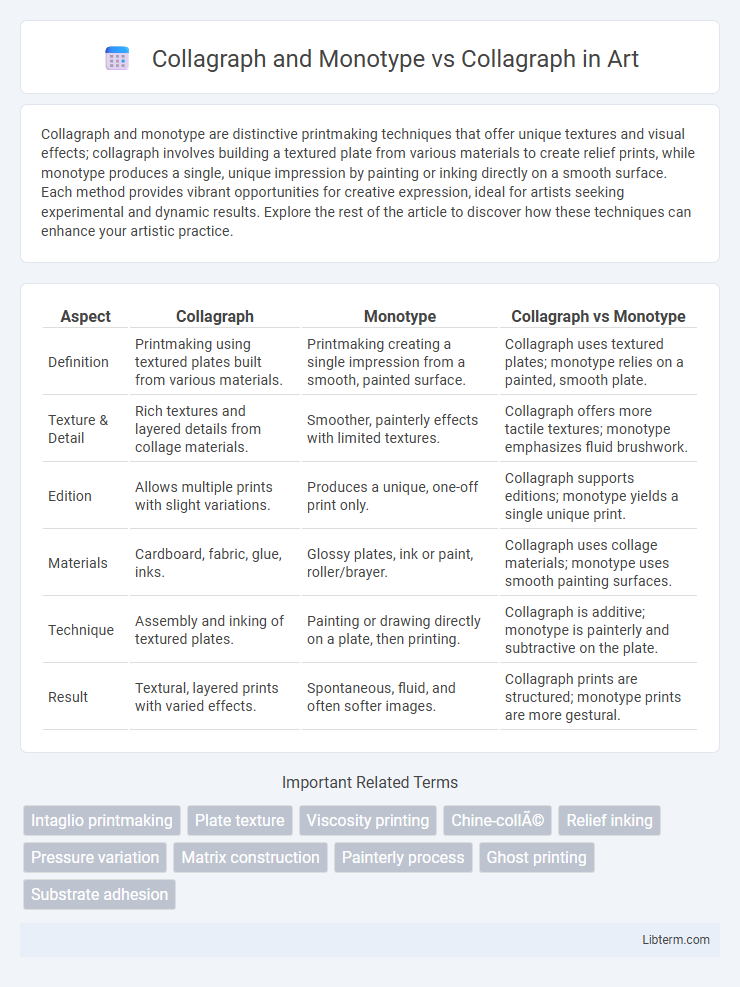
| Aspect | Collagraph | Monotype | Collagraph vs Monotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Printmaking using textured plates built from various materials. | Printmaking creating a single impression from a smooth, painted surface. | Collagraph uses textured plates; monotype relies on a painted, smooth plate. |
| Texture & Detail | Rich textures and layered details from collage materials. | Smoother, painterly effects with limited textures. | Collagraph offers more tactile textures; monotype emphasizes fluid brushwork. |
| Edition | Allows multiple prints with slight variations. | Produces a unique, one-off print only. | Collagraph supports editions; monotype yields a single unique print. |
| Materials | Cardboard, fabric, glue, inks. | Glossy plates, ink or paint, roller/brayer. | Collagraph uses collage materials; monotype uses smooth painting surfaces. |
| Technique | Assembly and inking of textured plates. | Painting or drawing directly on a plate, then printing. | Collagraph is additive; monotype is painterly and subtractive on the plate. |
| Result | Textural, layered prints with varied effects. | Spontaneous, fluid, and often softer images. | Collagraph prints are structured; monotype prints are more gestural. |
Introduction to Collagraph and Monotype Techniques
Collagraph and monotype are distinctive printmaking techniques that emphasize texture and unique image creation. Collagraph involves building up a plate with various materials to create raised surfaces, allowing for intricate texture and depth in prints. Monotype produces a single impression through painting or drawing directly on a smooth plate, offering spontaneity and rich tonal variation not found in collagraph prints.
What is Collagraph? Definition and Process
Collagraph is a printmaking technique where textured materials are glued onto a rigid surface, such as cardboard or wood, creating a printing plate that can be inked and pressed onto paper. The process involves building up layers of relief and intaglio textures to produce rich, detailed prints with a unique tactile quality. Unlike monotype, which produces a single impression from a smooth or painted surface, collagraph allows for multiple prints with varied effects due to its durable, textured plate.
Understanding Monotype Printing: An Overview
Monotype printing is a unique printmaking technique that produces a single, original impression by painting or drawing directly onto a smooth surface before transferring the image onto paper through a press. Unlike collagraph, which involves creating a textured printing plate from various materials to create multiple prints, monotype emphasizes spontaneity and one-of-a-kind artwork with no exact duplicates. This distinct approach makes monotype ideal for artists seeking expressive, fluid lines and rich tonal variations unattainable through collagraph methods.
Key Differences: Collagraph vs Monotype
Collagraph prints are created by building textured plates with various materials to produce multiple impressions, while monotypes generate a single unique print from a smooth surface without permanent plates. The primary distinction lies in repeatability; collagraphs allow for editioned prints, whereas monotypes are known for their one-of-a-kind, singular impressions. Collagraph techniques emphasize texture and relief, contrasting with monotype's emphasis on painterly effects and spontaneity.
Materials Used in Collagraph and Monotype Printing
Collagraph printing uses a variety of materials such as cardboard, fabric, leaves, and textured papers glued onto a stiff substrate to create a raised plate for inking. Monotype printing relies on a smooth plate--often glass or metal--coated with ink or paint directly applied for a single impression. The textured, relief-based materials in collagraphs produce rich, tactile prints, whereas monotypes emphasize painterly, one-of-a-kind images without fixed textural plates.
Artistic Possibilities: Textures and Effects
Collagraph offers rich textures through its collage-based printing plate, allowing artists to experiment with varied materials like fabric, cardboard, and textured papers for unique surface qualities. Monotype, distinguished by its singular print creation from a smooth plate, excels in delivering spontaneous, painterly effects with fluid ink application and blending. The combination of both techniques amplifies artistic possibilities, merging collagraph's tactile depth with monotype's softness and expressive brushstrokes for complex, multi-dimensional artworks.
Comparing Print Outcomes: Uniqueness and Edition Size
Collagraph prints exhibit rich texture and depth due to their collage-like plate construction, resulting in uniquely varied editions where no two prints are identical, emphasizing artistic experimentation over uniformity. Monotype prints, created using a smooth, non-permanent plate, yield singular, one-of-a-kind impressions with a painterly quality that cannot be exactly replicated, inherently limiting edition size to one or a few unique copies. Comparing both, collagraph editions can be larger with subtle variations across prints, while monotypes remain exclusive for their unmatched individuality and extremely limited edition size.
Suitability for Artists: Which Technique to Choose?
Collagraph printing offers tactile texture and rich depth, making it ideal for artists seeking expressive, hands-on experimentation with mixed media and intricate surfaces. Monotype printing provides unique, one-of-a-kind prints with fluid, painterly qualities suited for artists who prioritize spontaneity and individual expression in each impression. Artists should choose collagraph for controlled textural effects and monotype for versatile, singular artworks.
Combining Collagraph and Monotype Methods
Combining collagraph and monotype methods enhances textural complexity by merging relief printing with one-of-a-kind monoprint variations, allowing artists to create layered, rich compositions. Collagraph plates built with diverse materials produce tactile surfaces that capture ink differently, while the monotype process introduces spontaneous brushwork and unique color blends in each print. This fusion generates innovative prints featuring both defined relief marks and fluid, painterly qualities, expanding creative possibilities in contemporary printmaking.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Collagraph and Monotype
Collagraph offers rich texture and layered depth through printing plates made from various materials, while Monotype produces unique, one-of-a-kind prints by painting or inking directly onto a smooth surface. Artists seeking tactile, repeatable impressions benefit from Collagraph's versatility, whereas those valuing spontaneity and singular expression may prefer Monotype. Selecting between these techniques depends on whether the priority lies in textural complexity or singular visual impact.
Collagraph and Monotype Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com