Montage is a powerful filmmaking technique that combines a series of short shots to convey information, emotions, or passage of time efficiently. This method enhances storytelling by creating a dynamic visual narrative that captures attention and evokes specific moods. Discover how mastering montage can elevate your visual projects by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
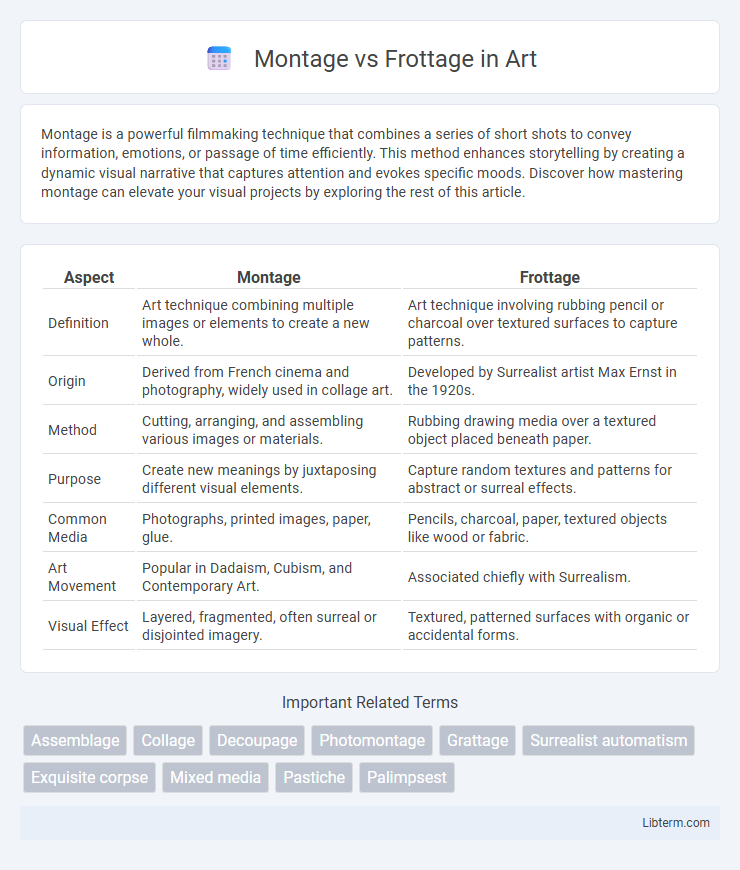
| Aspect | Montage | Frottage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art technique combining multiple images or elements to create a new whole. | Art technique involving rubbing pencil or charcoal over textured surfaces to capture patterns. |
| Origin | Derived from French cinema and photography, widely used in collage art. | Developed by Surrealist artist Max Ernst in the 1920s. |
| Method | Cutting, arranging, and assembling various images or materials. | Rubbing drawing media over a textured object placed beneath paper. |
| Purpose | Create new meanings by juxtaposing different visual elements. | Capture random textures and patterns for abstract or surreal effects. |
| Common Media | Photographs, printed images, paper, glue. | Pencils, charcoal, paper, textured objects like wood or fabric. |
| Art Movement | Popular in Dadaism, Cubism, and Contemporary Art. | Associated chiefly with Surrealism. |
| Visual Effect | Layered, fragmented, often surreal or disjointed imagery. | Textured, patterned surfaces with organic or accidental forms. |
Definition of Montage
Montage is a film editing technique that combines a series of short shots into a cohesive sequence to condense space, time, and information, emphasizing thematic connections rather than continuous narrative. Frottage, in contrast, is a visual art method involving rubbing pencil or other media over textured surfaces to capture their patterns. Montage serves as a powerful tool in cinema for enhancing storytelling efficiency and emotional impact through juxtaposition.
Definition of Frottage
Frottage is an artistic technique that involves creating a textured image by rubbing a pencil or other drawing tool over paper placed on a rough surface, capturing its patterns and details. In contrast, montage is a collage method that assembles various images or materials to form a cohesive composition. Frottage emphasizes the direct impression of physical textures, often used to explore abstract or surreal visual effects.
Historical Origins of Montage
Montage, originating from early 20th-century Soviet cinema, particularly the works of Sergei Eisenstein and Dziga Vertov, emphasizes the collision of independent shots to create new meanings through juxtaposition. Frottage, developed by Max Ernst in the 1920s as a surrealist art technique, involves creating textures by rubbing pencil or other materials over a textured surface. The historical origins of montage highlight its evolution as a cinematic tool for narrative and emotional impact, contrasting with frottage's roots in visual texture experimentation.
Historical Origins of Frottage
Frottage, developed by German artist Max Ernst in the 1920s, originated as a Surrealist technique involving the creation of textured rubbings from various surfaces to unlock the subconscious. This method contrasts with montage, which assembles different visual elements into a cohesive image, primarily emerging from early 20th-century Dada and Cubist practices. Frottage's historical significance lies in its innovative use of chance and texture to challenge traditional artistic composition and explore deeper psychological themes.
Artistic Techniques in Montage
Montage in artistic techniques involves assembling diverse visual elements to create a cohesive composition that conveys a narrative or conceptual message, often emphasizing contrast and juxtaposition. This method allows artists to manipulate time, space, and perspective by integrating photographs, drawings, or digital images, enhancing emotional and thematic impact. Unlike Frottage, which relies on texture and impression through rubbing, Montage centers on deliberate composition and layering to construct meaning.
Artistic Techniques in Frottage
Frottage is an artistic technique that involves creating textures and patterns by rubbing a pencil or crayon over paper placed on a textured surface, capturing the tactile qualities directly onto the artwork. This method, popularized by surrealist Max Ernst, emphasizes spontaneity and the discovery of hidden images within natural or man-made textures. Frottage contrasts with montage, which assembles multiple visual elements into a collage, as it relies on physical interaction with surfaces to produce imagery.
Key Differences Between Montage and Frottage
Montage involves assembling various visual elements from different sources to create a cohesive composition, emphasizing deliberate placement and thematic unity. Frottage is a textural technique that captures surface patterns by rubbing a pencil or crayon over paper placed on textured objects, highlighting spontaneous texture reproduction. The key difference lies in montage's focus on combining distinct images for a conceptual message, while frottage concentrates on extracting natural textures for abstract or expressive effects.
Prominent Artists Using Montage and Frottage
Montage, pioneered by artists like Sergei Eisenstein and Dziga Vertov, utilizes the technique of juxtaposing multiple images or shots to create a cohesive narrative or emotional impact, fundamentally shaping cinematic storytelling. Frottage, popularized by Max Ernst, involves rubbing pencil or other media over textured surfaces to create unique patterns, reflecting surrealist exploration of subconscious imagery. Prominent montage artists expanded visual narratives in film and photography, while frottage artists emphasized texture and chance in visual art, both methods innovating artistic expression.
Applications in Contemporary Art
Montage integrates diverse visual elements to create complex, layered compositions often used in contemporary digital art and mixed media installations, enhancing narrative depth and visual impact. Frottage, a technique involving texture rubbing from surfaces, is employed by contemporary artists to introduce tactile authenticity and spontaneity in paintings and printmaking, often evoking natural or urban environments. Both techniques play crucial roles in expanding artistic expression and material experimentation within modern art practices.
Choosing Between Montage and Frottage
Choosing between montage and frottage depends on the desired artistic effect and medium. Montage involves assembling diverse images or elements to create a cohesive visual narrative, ideal for film, photography, and graphic design. Frottage, a tactile technique using rubbings from textured surfaces, suits fine art and experimental projects emphasizing texture and abstraction.
Montage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com