Blending enhances the flavor, texture, and consistency of various food and beverage products, making them more enjoyable and appealing. Whether you're mixing ingredients for a smoothie, sauce, or soup, the right blending technique ensures optimal results. Discover effective blending methods and tips in the rest of this article to elevate your culinary skills.
Table of Comparison
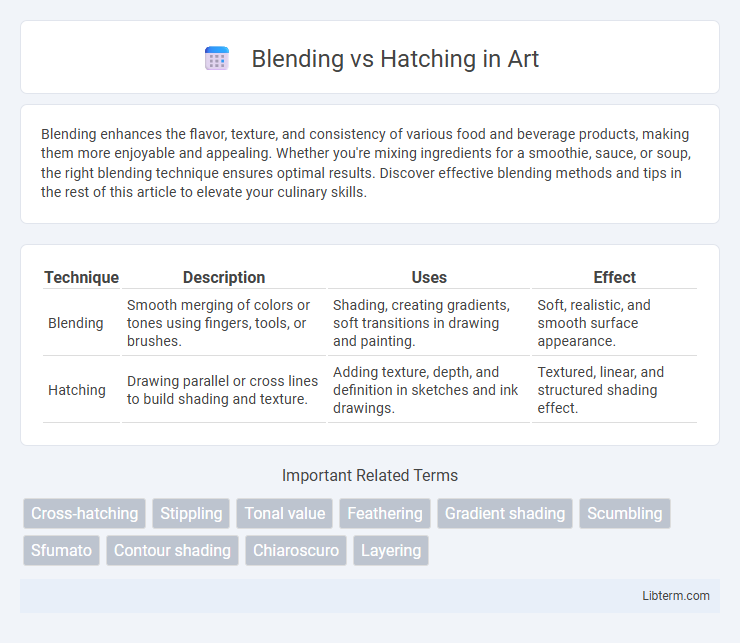
| Technique | Description | Uses | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blending | Smooth merging of colors or tones using fingers, tools, or brushes. | Shading, creating gradients, soft transitions in drawing and painting. | Soft, realistic, and smooth surface appearance. |
| Hatching | Drawing parallel or cross lines to build shading and texture. | Adding texture, depth, and definition in sketches and ink drawings. | Textured, linear, and structured shading effect. |
Understanding Blending and Hatching Techniques
Blending and hatching are fundamental shading techniques in drawing, each creating distinct textures and depth. Blending involves smoothly merging tones to produce gradients and soft transitions, ideal for realistic skin and subtle shadows. Hatching uses parallel or intersecting lines to build value and texture, offering a dynamic and structured approach for rendering form and contrast.
Key Differences Between Blending and Hatching
Blending creates smooth transitions between tones by merging colors or shades seamlessly, while hatching uses closely spaced parallel lines to build texture and value. Blending often produces softer, more realistic effects ideal for gradual shading, whereas hatching emphasizes structure and form through line direction and density. Artists choose blending to achieve subtle gradients, whereas hatching excels in rendering contrast and dynamic patterns.
Tools Required for Blending and Hatching
Blending requires tools such as blending stumps, tortillons, soft brushes, or even tissue paper to smooth out pencil or charcoal strokes for a seamless gradient effect. Hatching relies primarily on fine-tipped pencils, pens, or brushes to create closely spaced parallel lines that build texture and shading. Both techniques demand precise control of pressure and direction to achieve the desired tonal variations and depth.
Step-by-Step Guide to Blending in Art
Blending in art involves smoothly merging colors or shades to create seamless transitions and realistic textures, often achieved using tools like blending stumps, brushes, or fingers. Begin by applying light layers of your chosen medium, then gradually build up tones while softly smoothing the edges to avoid harsh lines. Maintain consistent pressure and work in small circular motions for even blending, enhancing depth and softness in your artwork.
Mastering the Basics of Hatching
Mastering the basics of hatching involves understanding how to create texture, depth, and shading through closely spaced parallel lines. Unlike blending, which smooths tones for gradual transitions, hatching emphasizes directional strokes to build form and volume. Effective hatching requires control over line density, spacing, and angle to achieve realistic lighting effects and enhance dimensionality in drawing.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Drawing
Choosing between blending and hatching depends on the desired texture and depth in your drawing; blending creates smooth gradients ideal for realistic shading, while hatching uses parallel lines to convey texture and form. Blending techniques work best with materials like charcoal, graphite, or pastels to achieve soft transitions, whereas hatching excels with ink or pen for a more graphic, structured look. Assess the subject matter and artistic style to determine whether the softness of blending or the detailed line work of hatching enhances your visual storytelling.
Visual Effects: Smooth vs. Textured Shading
Blending creates smooth, gradient transitions between tones, resulting in soft and realistic shading ideal for capturing subtle light and shadow nuances. Hatching employs closely spaced or intersecting lines to build texture and volume, producing a more textured, dynamic appearance that emphasizes form and contrast. The choice between blending and hatching directly impacts the visual effect, with blending offering seamless gradation and hatching providing a tactile, structured shading style.
Common Mistakes in Blending and Hatching
Common mistakes in blending include overworking the medium, which can lead to muddy colors and loss of texture, and neglecting to gradually layer tones, resulting in uneven transitions. In hatching, errors often involve inconsistent line spacing and pressure, causing unintended tonal values and disrupting the sense of depth. Both techniques require controlled application and attention to detail to achieve smooth gradients and accurate shading.
Combining Blending and Hatching for Mixed Effects
Combining blending and hatching techniques creates dynamic textures and depth in artwork by merging smooth transitions with structured lines. Blending softens color edges for subtle gradients, while hatching uses parallel or cross lines to build tone and texture, resulting in rich, layered visual effects. Employing both methods strategically enhances dimensionality and visual interest in drawings and paintings.
Tips for Improving Shading Skills
Mastering shading techniques involves practicing both blending and hatching to create depth and texture effectively. Utilize soft pencils and smooth strokes for seamless blending, while varying line direction and pressure enhances hatching detail and dimension. Experiment with layering multiple hatching styles or combining them with blending can enrich shading complexity and realism.
Blending Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com