A well-defined frontal profile enhances facial symmetry and highlights your natural features, creating a balanced and attractive appearance. Proper understanding of this profile is essential for makeup application, hairstyling, and cosmetic procedures tailored to your unique face shape. Discover how mastering your frontal profile can transform your style and confidence by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
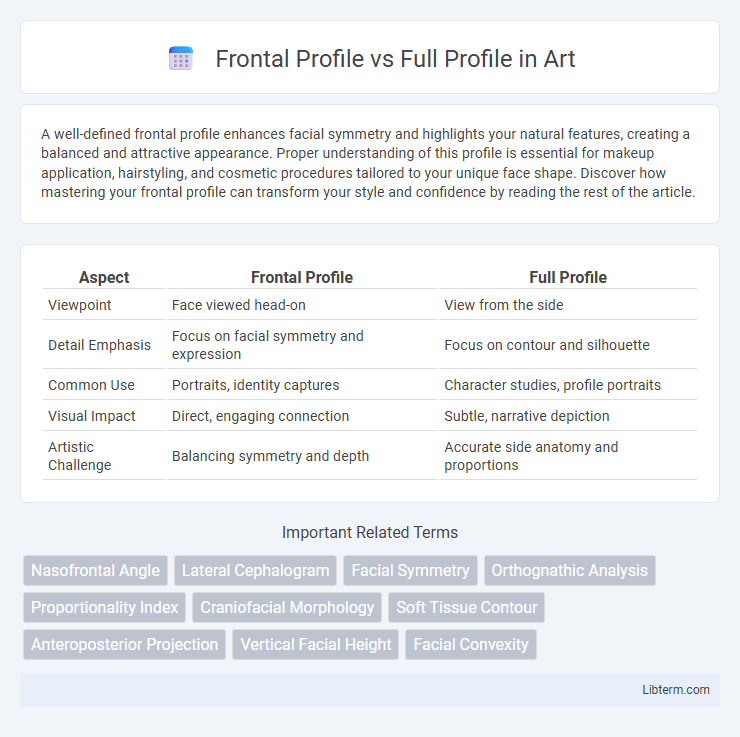
| Aspect | Frontal Profile | Full Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Viewpoint | Face viewed head-on | View from the side |
| Detail Emphasis | Focus on facial symmetry and expression | Focus on contour and silhouette |
| Common Use | Portraits, identity captures | Character studies, profile portraits |
| Visual Impact | Direct, engaging connection | Subtle, narrative depiction |
| Artistic Challenge | Balancing symmetry and depth | Accurate side anatomy and proportions |
Understanding Frontal Profile and Full Profile
Understanding the frontal profile involves analyzing a subject's face directly from the front, highlighting symmetrical facial features, eye alignment, and nose shape. The full profile captures the side view, emphasizing the shape of the forehead, nose bridge, and jawline contours. Comparing frontal and full profiles aids in comprehensive facial recognition, forensic analysis, and detailed anthropometric studies.
Key Differences Between Frontal and Full Profiles
Frontal profiles capture a face directly from the front, emphasizing symmetry and facial features like eyes, nose, and mouth, whereas full profiles showcase the side view, highlighting the outline of the face including the nose, forehead, and chin. The key differences lie in perspective and detail; frontal profiles are ideal for identification and expression clarity, while full profiles provide unique spatial information and contour shapes. Both perspectives are crucial in fields such as biometrics, art, and facial recognition technology for comprehensive analysis.
When to Use a Frontal Profile Image
A frontal profile image is ideal for professional settings such as LinkedIn profiles or corporate websites where clear facial recognition is crucial. Use a frontal profile to convey approachability, confidence, and trustworthiness, enhancing personal branding in industries like finance, law, or customer service. This image type is also effective for identification purposes in passports, ID cards, and security badges.
Benefits of Full Profile Photography
Full profile photography captures the subject's side view, emphasizing facial contours and bone structure, which enhances visual storytelling and character depth in portraits. This perspective provides a more dynamic and three-dimensional representation, making it ideal for modeling portfolios and artistic projects requiring detailed facial analysis. Full profile shots also minimize distractions from background elements, focusing attention solely on the subject's unique profile features for a refined and professional appearance.
Applications in Professional Settings
Frontal profile photographs are essential in professional settings for tasks like ID badges, corporate headshots, and facial recognition systems due to their clear visibility of facial features and symmetrical alignment. Full profile images are typically used in forensic analysis, security protocols, and anthropological studies where side views help capture facial contours and structural details not visible from the front. Selecting between frontal and full profiles depends on the application's need for either comprehensive facial feature analysis or detailed structural examination.
Impact on Facial Recognition Technology
Frontal profile images provide optimal data for facial recognition technology, ensuring higher accuracy due to clear visibility of key facial features such as eyes, nose, and mouth. Full profile images often result in reduced identification performance as they capture a side view, limiting the algorithm's ability to match facial landmarks effectively. Combining both frontal and full profile images in datasets enhances robustness by improving recognition systems' adaptability to various angles and lighting conditions.
Aesthetics: Which Profile is More Appealing?
Frontal profiles highlight facial symmetry, often perceived as more attractive due to balanced features and direct eye contact, which enhances emotional connection. Full profiles emphasize facial contours such as the nose, cheekbones, and jawline, adding depth and character but may obscure symmetrical balance. Aesthetically, preferences depend on context, with frontal profiles favored in portrait photography for engagement while full profiles suit artistic and sculptural presentations.
Effects on Personal Branding
Frontal profile photographs create a direct visual connection, conveying confidence and approachability, which enhances personal branding by fostering trust and transparency. Full profile images emphasize uniqueness and individuality, highlighting distinctive features that can help establish a memorable and authoritative brand identity. Choosing between frontal and full profile shots depends on whether the goal is to project openness or distinctiveness in personal branding strategies.
Industry Examples: Frontal vs Full Profile
Frontal profile captures a subject facing directly forward, ideal for security systems like facial recognition in banking and retail industries, ensuring clear visibility of facial features. Full profile shows the side view, commonly utilized in law enforcement and biometrics for identifying unique ear or nose shapes. Combining both frontal and full profiles enhances accuracy in industries such as healthcare and aviation security where precise identification is critical.
Choosing the Right Profile for Your Needs
Selecting between a frontal profile and a full profile depends on the intended purpose and visual impact. A frontal profile captures direct facial features, ideal for identification and formal portraits, while a full profile offers a side view highlighting facial contours, commonly used in art and medical assessments. Analyzing the context, such as documentation, artistic expression, or clinical evaluation, ensures the right profile type enhances clarity and meets specific requirements.
Frontal Profile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com