Capturing moments with precision and creativity defines a professional photographer's craft, blending technical skill with artistic vision to produce stunning visuals. Mastery over lighting, composition, and post-processing transforms ordinary scenes into compelling stories that resonate with viewers. Dive deeper into the world of photography to elevate your skills and understand the nuances behind every remarkable shot.
Table of Comparison
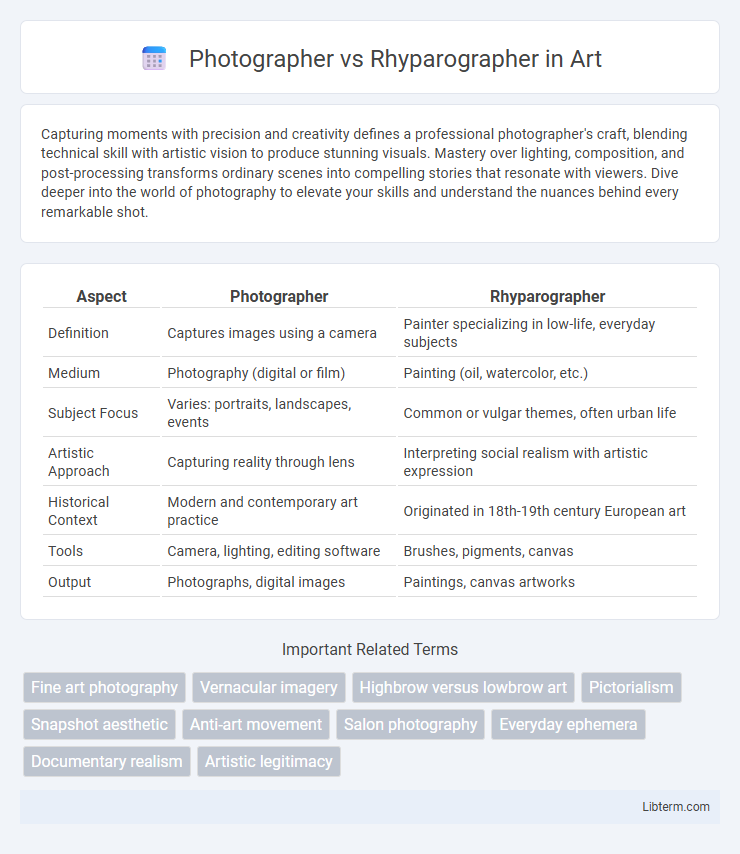
| Aspect | Photographer | Rhyparographer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Captures images using a camera | Painter specializing in low-life, everyday subjects |
| Medium | Photography (digital or film) | Painting (oil, watercolor, etc.) |
| Subject Focus | Varies: portraits, landscapes, events | Common or vulgar themes, often urban life |
| Artistic Approach | Capturing reality through lens | Interpreting social realism with artistic expression |
| Historical Context | Modern and contemporary art practice | Originated in 18th-19th century European art |
| Tools | Camera, lighting, editing software | Brushes, pigments, canvas |
| Output | Photographs, digital images | Paintings, canvas artworks |
Understanding the Terms: Photographer vs Rhyparographer
A photographer captures images using a camera to create artistic or documentary visual representations, emphasizing composition, lighting, and subject matter. In contrast, a rhyparographer specializes in painting or depicting commonplace, often mundane or lowly subjects, focusing on the everyday or vulgar aspects of life. Understanding these terms highlights the distinction between image creation through photography and thematic painting centered on ordinary realities.
Historical Origins and Etymology
The term "photographer" originates from the Greek words "photos," meaning light, and "graphein," meaning to draw, reflecting the process of capturing images using light. In contrast, "rhyparographer" derives from the Greek "rhyparos," meaning filthy or dirty, and "graphein," referring to the depiction of mundane or lowly subjects in painting, prevalent in 18th-century art criticism. Historical origins highlight "photographer" as a modern invention linked to 19th-century technological advances, whereas "rhyparographer" has roots in classical language describing a niche genre in fine art.
Artistic Intent: Capturing Beauty vs Everyday Reality
Photographers often aim to capture beauty through carefully composed images that highlight aesthetic appeal, lighting, and mood to evoke emotion. Rhyparographers focus on depicting everyday reality, emphasizing the ordinary and commonplace aspects of life with raw authenticity and unembellished detail. This distinction in artistic intent reflects contrasting priorities: one seeks idealized representation, while the other values truthful documentation of the mundane.
Subject Matter: What Each Artist Focuses On
Photographers capture real-world subjects through a lens, emphasizing moments in time, natural light, and composition across various themes such as portraits, landscapes, or events. Rhyparographers specialize in depicting everyday, commonplace objects and scenes, focusing on the mundane and often overlooked elements of daily life with detailed attention and artistic interpretation. The primary distinction lies in the medium and intent: photographers document reality while rhyparographers interpret ordinary subjects through painting or drawing.
Techniques and Tools Compared
Photographers utilize cameras, lenses, and digital editing software to capture and enhance images with precision in lighting, composition, and focus, emphasizing the moment's realism and aesthetics. Rhyparographers, historically focused on depicting everyday, often gritty scenes using traditional painting techniques such as oil on canvas and detailed brushwork, prioritize narrative and social commentary over photographic accuracy. While photographers rely on mechanical and digital tools for instant capture and manipulation, rhyparographers depend on manual craftsmanship and texture to convey mood and meaning in their work.
Influence on Art and Culture
Photographers revolutionized art and culture by capturing realistic images that document and shape societal narratives, influencing visual storytelling and media. Rhyparographers, specializing in mundane or lowly subjects in painting during the 18th century, challenged traditional artistic hierarchies, offering a counter-narrative that emphasized everyday life and common folk. Both roles expanded the boundaries of artistic expression, with photographers advancing modern visual culture and rhyparographers highlighting the cultural value of ordinary scenes.
Notable Figures in Both Fields
Notable photographers such as Ansel Adams revolutionized landscape photography with his mastery of light and dark, while Richard Avedon transformed portraiture through innovative composition. In the field of rhyparography, artists like Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot are recognized for their detailed and evocative depictions of everyday life and common people. Both fields emphasize the capture of reality, yet photographers use cameras and light technology, whereas rhyparographers rely on traditional painting techniques to convey their subjects.
Public Perception and Critique
Photographers are widely regarded for capturing reality through camera lenses, often praised for technical skill and artistic vision. Rhyparographers, artists specializing in painting or drawing low-life subjects, historically face critique for focusing on mundane or unsavory themes, which influences public perception as less prestigious. This distinction impacts cultural value judgments, where photography is seen as modern and innovative, while rhyparography is sometimes dismissed as genre art with limited aesthetic appeal.
Modern Interpretations and Trends
Modern photographers leverage advanced digital technology and AI-driven editing tools to create highly stylized images that push creative boundaries beyond traditional techniques. Rhyparographers, historically focused on depicting everyday scenes with raw realism, are now reinterpreted by contemporary artists blending social commentary with multimedia elements to resonate with current cultural themes. Trends in both fields emphasize narrative depth and emotional impact, often intersecting through hybrid practices that combine photography's precision with rhyparography's candid storytelling.
Choosing Your Path: Which Suits Your Vision?
Photographers capture images through cameras, focusing on framing, lighting, and timing to create visual stories that resonate with audiences. Rhyparographers specialize in depicting the mundane or everyday subjects, emphasizing realism and often highlighting overlooked details in painting or visual art. Choosing between these paths depends on your vision: if you seek to freeze moments in time with modern technology, photography aligns with your goals, while an interest in detailed, narrative-driven renderings of ordinary life leans toward rhyparography.
Photographer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com