Digital art transforms creativity through technology, allowing artists to produce intricate designs, vibrant colors, and dynamic compositions with ease. This medium offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling quick edits, diverse styles, and global sharing that were once unimaginable. Explore how digital art can elevate your creative journey and discover its limitless possibilities in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
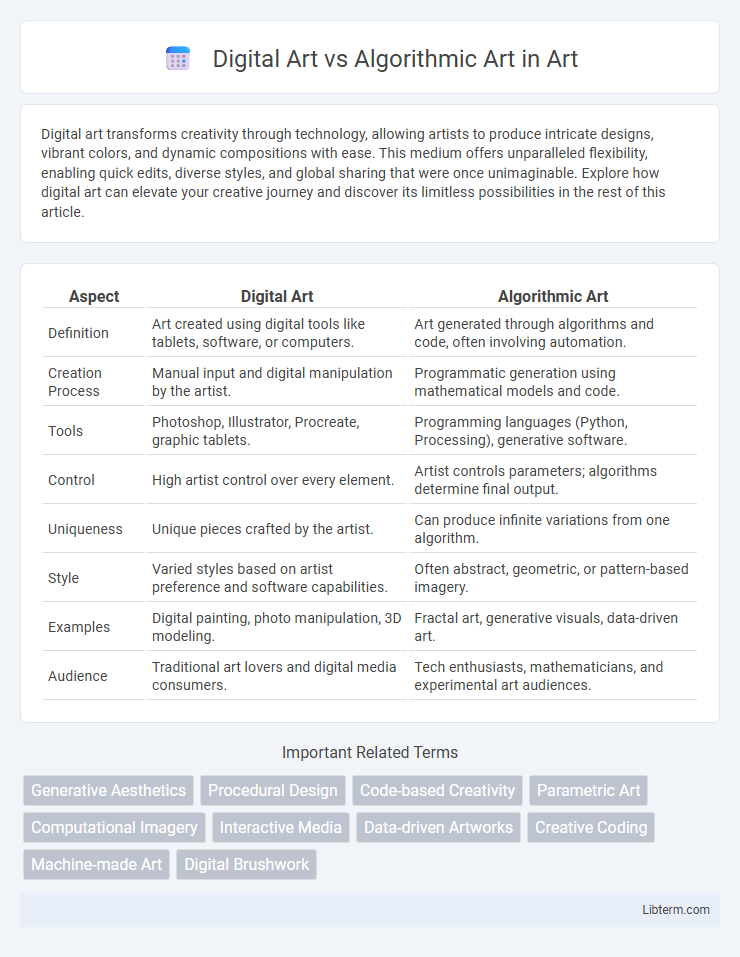
| Aspect | Digital Art | Algorithmic Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art created using digital tools like tablets, software, or computers. | Art generated through algorithms and code, often involving automation. |
| Creation Process | Manual input and digital manipulation by the artist. | Programmatic generation using mathematical models and code. |
| Tools | Photoshop, Illustrator, Procreate, graphic tablets. | Programming languages (Python, Processing), generative software. |
| Control | High artist control over every element. | Artist controls parameters; algorithms determine final output. |
| Uniqueness | Unique pieces crafted by the artist. | Can produce infinite variations from one algorithm. |
| Style | Varied styles based on artist preference and software capabilities. | Often abstract, geometric, or pattern-based imagery. |
| Examples | Digital painting, photo manipulation, 3D modeling. | Fractal art, generative visuals, data-driven art. |
| Audience | Traditional art lovers and digital media consumers. | Tech enthusiasts, mathematicians, and experimental art audiences. |
Understanding Digital Art: Definition and Scope
Digital art encompasses a broad range of creative expressions produced or enhanced through digital technology, including graphic design, digital painting, and multimedia installations. Its scope covers various techniques such as raster and vector graphics, 3D modeling, and animation, enabling artists to manipulate pixels and data to achieve innovative visual effects. Unlike algorithmic art, which relies on computer-generated algorithms to create patterns and forms, digital art prioritizes the artist's interaction with digital tools to produce unique and expressive works.
What Is Algorithmic Art? An Overview
Algorithmic art is a form of digital art created using computer algorithms that generate visual patterns or compositions based on mathematical formulas and rules. This art style leverages programming languages and computational processes to produce complex, often unpredictable imagery that can evolve over time or vary with each execution. Unlike traditional digital art, which is manually crafted by artists, algorithmic art emphasizes code-driven creativity and the interplay between human input and automated generation.
Tools and Techniques: Digital vs Algorithmic Creations
Digital art utilizes software like Adobe Photoshop, Procreate, and Corel Painter to create images through manual techniques such as brush strokes, layering, and digital painting. Algorithmic art employs code-based tools like Processing, p5.js, and Python libraries to generate visuals through mathematical algorithms, randomness, and iterative processes. These differing techniques highlight the manual craftsmanship in digital art versus the generative, rule-based approach in algorithmic art.
Creative Process: Human Touch vs Code-Driven Design
Digital art emphasizes the human touch, where artists use software tools to manually create and manipulate images, blending creativity with tactile control. Algorithmic art relies on code-driven design, generating visuals through mathematical algorithms and automated processes that often produce unexpected patterns. This contrast highlights the difference between intuitive, hands-on creation and systematic, computational generation in the artistic process.
Visual Styles and Aesthetic Differences
Digital art encompasses a broad spectrum of visual styles ranging from hyper-realistic renderings to abstract compositions created using software tools, emphasizing creative control and expressive freedom. Algorithmic art relies on computational procedures and generative algorithms, producing patterns, fractals, or complex geometries that often exhibit mathematical precision and repetitive aesthetics. The aesthetic difference lies in digital art's variability and artist-driven nuances versus algorithmic art's systematic, rule-based, and often emergent visual outcomes.
Applications and Practical Uses in Modern Media
Digital art integrates software tools like Photoshop and Procreate for creating visually compelling graphics used extensively in advertising, entertainment, and social media content. Algorithmic art harnesses mathematical algorithms and coding languages such as Python and Processing to generate dynamic visuals, often applied in data visualization, procedural animation, and interactive installations. Both forms significantly enhance modern media by enabling innovative storytelling, personalized content, and immersive user experiences across digital platforms.
Accessibility and Skill Requirements
Digital art offers broad accessibility through user-friendly software and intuitive interfaces, enabling artists with varying skill levels to create visually compelling works. Algorithmic art relies heavily on coding knowledge and mathematical understanding, making it less accessible to novices but highly rewarding for those skilled in programming. The skill requirements for algorithmic art emphasize logical thinking and algorithm design, while digital art prioritizes creativity and digital tool proficiency.
Artistic Intent: Expression vs Generative Systems
Digital art emphasizes artistic intent driven by human expression, where creators directly manipulate tools to convey emotions, ideas, and narratives. Algorithmic art relies on generative systems, using computer-coded rules and parameters to produce patterns and forms that evolve autonomously, often introducing randomness and complexity beyond manual design. The primary distinction lies in digital art's subjective creativity versus algorithmic art's procedural generation, blending human intention with computational logic.
The Future of Art: Hybrid Approaches and Emerging Trends
Digital art and algorithmic art increasingly converge through hybrid approaches that merge human creativity with computational processes, expanding artistic possibilities. Emerging trends highlight the integration of artificial intelligence, generative adversarial networks (GANs), and interactive installations that respond dynamically to audience input. These innovations redefine creative expression and challenge traditional boundaries, positioning hybrid art forms as a dominant force in the future art landscape.
Choosing Between Digital and Algorithmic Art: Key Considerations
Choosing between digital art and algorithmic art involves evaluating the level of creative control and technical expertise desired. Digital art offers artists direct manipulation of images through software like Photoshop or Procreate, appealing to those focused on visual expression and intuitive workflows. Algorithmic art requires programming knowledge to generate artwork via algorithms, ideal for creators interested in exploring procedural aesthetics and generative design techniques.
Digital Art Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com