Parquetry is a decorative woodworking technique involving geometric patterns created by fitting together small pieces of wood veneer. This craftsmanship enhances flooring, furniture, and cabinetry with intricate, visually striking designs that combine artistic detail with durable construction. Explore the rest of the article to discover how parquetry can elevate your space with timeless elegance.
Table of Comparison
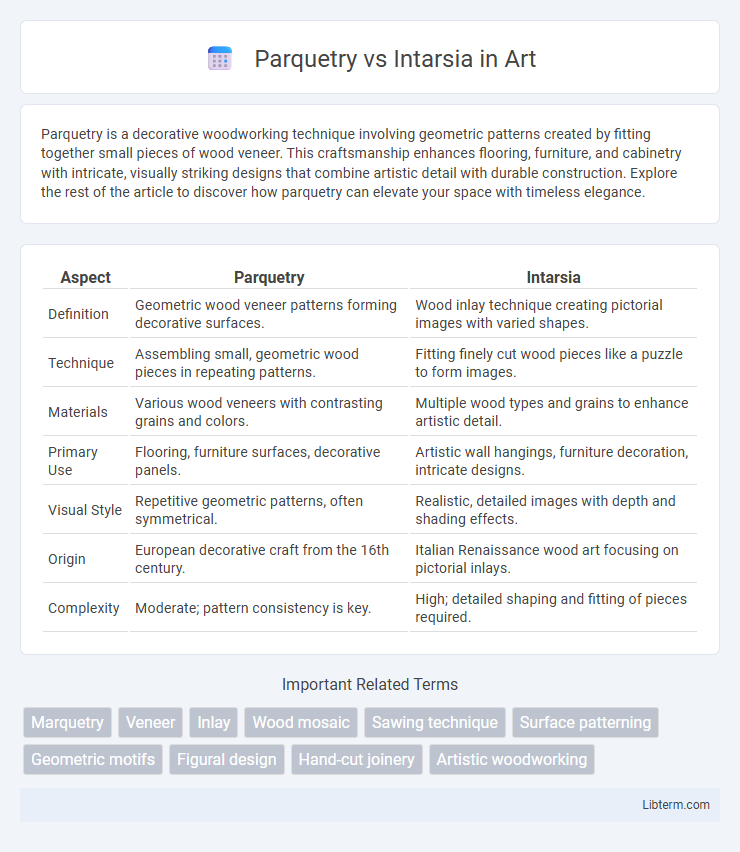
| Aspect | Parquetry | Intarsia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Geometric wood veneer patterns forming decorative surfaces. | Wood inlay technique creating pictorial images with varied shapes. |
| Technique | Assembling small, geometric wood pieces in repeating patterns. | Fitting finely cut wood pieces like a puzzle to form images. |
| Materials | Various wood veneers with contrasting grains and colors. | Multiple wood types and grains to enhance artistic detail. |
| Primary Use | Flooring, furniture surfaces, decorative panels. | Artistic wall hangings, furniture decoration, intricate designs. |
| Visual Style | Repetitive geometric patterns, often symmetrical. | Realistic, detailed images with depth and shading effects. |
| Origin | European decorative craft from the 16th century. | Italian Renaissance wood art focusing on pictorial inlays. |
| Complexity | Moderate; pattern consistency is key. | High; detailed shaping and fitting of pieces required. |
Introduction to Parquetry and Intarsia
Parquetry is a woodworking technique that involves creating geometric patterns by assembling small pieces of veneer, typically used for decorating furniture and flooring. Intarsia is an intricate wood-inlay process where different wood pieces are shaped and fitted together to create a detailed, pictorial design. Both methods enhance wood surfaces with artistic patterns, but parquetry emphasizes repetitive geometric shapes, while intarsia focuses on more complex, three-dimensional images.
Historical Origins: Parquetry vs Intarsia
Parquetry traces its origins to ancient Egypt and was prominently used during the Renaissance in Europe for flooring and furniture, characterized by geometric patterns formed from wood veneers. Intarsia, emerging in 14th-century Italy, developed as a specialized woodworking technique for creating detailed pictorial inlays using various wood species to achieve color and texture variations. Both techniques reflect rich artistic traditions but differ in their historical contexts and intended decorative applications.
Materials and Tools Used in Each Technique
Parquetry primarily utilizes thin veneer sheets of wood or synthetic materials, which are cut into geometric shapes and assembled to create intricate patterns; tools include veneer cutters, saws, and sanders. Intarsia involves thicker wood pieces of varied species, often shaped and carved individually before fitting together like a puzzle, requiring chisels, scroll saws, and files for detailed work. Both techniques demand precise cutting instruments but differ significantly in material thickness and the dimensionality of the final artwork.
Crafting Methods: Step-by-Step Comparison
Parquetry involves arranging small geometric wood pieces in repeating patterns, relying on precision cutting, gluing, and sanding to create flat, decorative surfaces. Intarsia uses individually shaped wood pieces fitted together like a puzzle, requiring careful contouring, shading, and layering to achieve a three-dimensional effect. Both crafts demand meticulous planning and skilled handwork but differ in complexity and visual depth due to their distinct assembly and finishing techniques.
Common Design Patterns and Motifs
Parquetry commonly features geometric patterns such as chevrons, herringbone, and basketweave, utilizing repeated wood veneer segments to create intricate floor and furniture surfaces. Intarsia incorporates pictorial motifs like floral designs, animals, and landscapes, achieved by fitting varied shapes of wood pieces together to form detailed images. Both techniques emphasize precision craftsmanship but differ in pattern complexity, with parquetry favoring repetitive symmetry and intarsia highlighting artistic, representational imagery.
Applications in Modern Interior Design
Parquetry and intarsia both enhance modern interior design by adding intricate wooden patterns that elevate aesthetic appeal and texture. Parquetry, with its geometric and repetitive designs, is ideal for flooring, wall panels, and cabinetry, creating a sophisticated and harmonious environment. Intarsia offers more pictorial and sculptural wood inlays, making it perfect for accent walls, custom furniture, and statement pieces, adding depth and artistic flair to contemporary spaces.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Parquetry, made from geometric wood pieces glued on surfaces, offers higher durability due to its dense and stable construction, making it resistant to wear and easier to maintain with regular cleaning and occasional refinishing. Intarsia involves intricate, inlaid wood designs that are more susceptible to damage from moisture and physical impact, requiring careful handling and specialized maintenance to preserve its detailed artistry. Choosing parquetry enhances longevity and simplifies upkeep, while intarsia demands mindful care to maintain its decorative appeal.
Aesthetic Differences Between Parquetry and Intarsia
Parquetry features geometric patterns created by arranging small wood veneers in repetitive, angular designs that emphasize symmetry and precision. Intarsia showcases detailed, pictorial images made from varied wood pieces with different textures and grains, creating a three-dimensional effect and depth. The contrasting aesthetic appeal lies in parquetry's structured visual rhythm versus intarsia's intricate, sculptural artistry.
Cost Implications and Value Addition
Parquetry generally incurs lower costs due to its repetitive geometric patterns and use of uniform wood veneers, making it more budget-friendly for large surface areas. Intarsia demands higher investment because of its intricate, hand-cut wood pieces and the craftsmanship required, which significantly increases labor and material expenses. The value addition of intarsia is often superior, as its detailed, artistic designs elevate the uniqueness and aesthetic appeal, which can enhance property or furniture resale value compared to the more standardized parquetry patterns.
Choosing Between Parquetry and Intarsia for Your Project
Choosing between parquetry and intarsia depends on the project's complexity and desired visual effect; parquetry features geometric patterns created from wood veneers, ideal for flooring and furniture with repetitive designs, while intarsia involves assembling intricately shaped wood pieces to form detailed, pictorial images suitable for artistic wall panels or decorative accents. Consider parquetry for surfaces requiring durability and uniformity, as its veneer layers provide stability and resistance to warping. Intarsia suits projects prioritizing texture and depth, allowing for customized, three-dimensional imagery using varying wood types and grains.
Parquetry Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com