Abstraction simplifies complex systems by focusing on essential features while hiding irrelevant details, enabling clearer understanding and efficient problem-solving. This approach is fundamental in software development and design, helping you manage complexity and improve code maintainability. Explore the rest of the article to discover how abstraction techniques can enhance your projects.
Table of Comparison
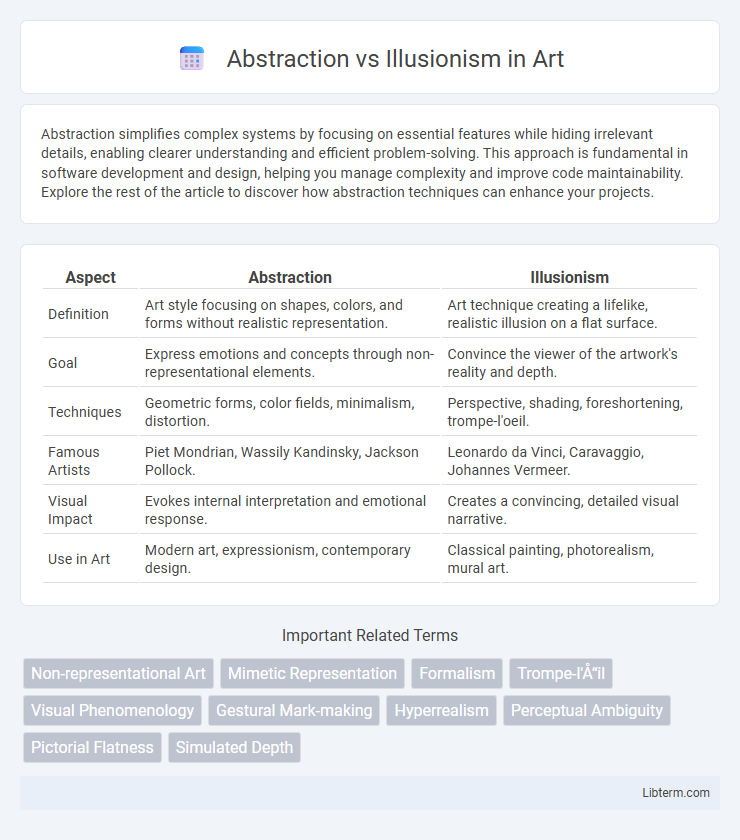
| Aspect | Abstraction | Illusionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art style focusing on shapes, colors, and forms without realistic representation. | Art technique creating a lifelike, realistic illusion on a flat surface. |
| Goal | Express emotions and concepts through non-representational elements. | Convince the viewer of the artwork's reality and depth. |
| Techniques | Geometric forms, color fields, minimalism, distortion. | Perspective, shading, foreshortening, trompe-l'oeil. |
| Famous Artists | Piet Mondrian, Wassily Kandinsky, Jackson Pollock. | Leonardo da Vinci, Caravaggio, Johannes Vermeer. |
| Visual Impact | Evokes internal interpretation and emotional response. | Creates a convincing, detailed visual narrative. |
| Use in Art | Modern art, expressionism, contemporary design. | Classical painting, photorealism, mural art. |
Understanding Abstraction: Core Concepts
Understanding abstraction involves recognizing the essence of forms by stripping away detailed representation to emphasize fundamental shapes, colors, and patterns. Core concepts include simplification, non-representational imagery, and the prioritization of emotional or conceptual expression over realistic portrayal. Unlike illusionism, which aims to create lifelike depth and perspective, abstraction focuses on conveying ideas through symbolic and minimalistic elements.
Defining Illusionism in Art and Thought
Illusionism in art and thought is defined by its emphasis on creating a convincing visual reality that mimics three-dimensional space and texture, often through techniques like perspective, chiaroscuro, and trompe-l'oeil. This approach prioritizes lifelike representation and sensory deception to engage viewers in a seemingly tangible experience. Illusionism contrasts with abstraction by seeking to replicate the external world rather than interpreting it through simplified or non-representational forms.
Historical Evolution: Abstraction and Illusionism
Abstraction emerged in the early 20th century as artists like Kandinsky and Malevich moved away from representational forms to emphasize colors, shapes, and emotions, marking a pivotal shift in modern art. Illusionism dates back to the Renaissance, with masters such as Leonardo da Vinci pioneering techniques like chiaroscuro and perspective to create lifelike representations and depth on a flat surface. The historical evolution reveals a dynamic tension where abstraction seeks to convey intrinsic meaning through non-representational forms, while illusionism focuses on mimicking reality with technical precision.
Key Differences Between Abstraction and Illusionism
Abstraction emphasizes simplified forms and colors that do not represent real-world objects, focusing on emotional or conceptual expression, while illusionism seeks to create a realistic, three-dimensional appearance on a two-dimensional surface through techniques like shading and perspective. Key differences lie in abstraction's departure from mimicking reality and illusionism's intent to deceive the eye by simulating texture, depth, and light. Abstraction highlights subjective interpretation, whereas illusionism relies on precise detail to produce lifelike imagery.
Philosophical Foundations of Abstraction
Philosophical foundations of abstraction emphasize distilling essential qualities and universal truths from sensory experiences, contrasting sharply with illusionism, which aims to replicate reality's perceptual details. Abstraction engages concepts like Plato's theory of forms, where abstract forms represent the truest reality beyond mere appearances. This ontological perspective prioritizes symbolic and conceptual integrity over mimetic fidelity, shaping modern art and epistemology by questioning what constitutes the essence of reality.
The Psychology Behind Illusionism
Illusionism leverages cognitive psychology principles to manipulate perception, creating visual experiences that challenge the brain's interpretation of reality. The psychological mechanisms involve depth cues, perspective, and contrast, which trick the mind into perceiving three-dimensionality on a flat surface. This exploitation of the brain's visual processing highlights how illusionism taps into subconscious neural pathways to evoke compelling, often deceptive, sensory responses.
Applications of Abstraction in Modern Disciplines
Abstraction plays a critical role in modern disciplines such as computer science, where it simplifies complex systems into manageable models, enhancing software development and algorithm design. In fields like architecture and industrial design, abstraction facilitates innovative problem-solving by emphasizing functional elements over detailed realism. Scientific research also relies heavily on abstraction to formulate theories and create simulations that represent essential aspects of natural phenomena without extraneous detail.
Illusionism’s Role in Perception and Creativity
Illusionism plays a crucial role in perception by manipulating visual cues to create a sense of depth, space, and realism that enhances cognitive engagement. This technique fosters creativity by challenging viewers' interpretations and encouraging new ways of seeing, often blurring the line between reality and imagination. In contrast to abstraction, illusionism relies on detailed representation to evoke emotional responses and stimulate intellectual curiosity through deceptive visual effects.
Contemporary Debates: Abstraction vs Illusionism
Contemporary debates on abstraction versus illusionism center on the tension between non-representational art and hyper-realistic techniques that challenge viewers' perception. Advocates of abstraction emphasize emotional expression and conceptual depth, while proponents of illusionism argue for technical mastery and immersive realism. This discourse shapes art movements, influencing critical reception, market dynamics, and evolving definitions of artistic authenticity.
Future Perspectives: Blurring Lines Between Abstraction and Illusionism
Emerging technologies in digital art and virtual reality are increasingly blurring the lines between abstraction and illusionism, creating immersive experiences that challenge traditional visual perceptions. Advances in AI-generated art contribute to hybrid forms where abstract shapes seamlessly blend with hyper-realistic elements, fostering new aesthetic dialogues. This convergence invites artists and audiences to explore fluid interpretations of reality, reshaping future artistic boundaries.
Abstraction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com