Authenticity is the cornerstone of building genuine connections and fostering trust in both personal and professional relationships. Embracing your true self encourages transparency and inspires others to do the same, creating an environment of mutual respect and understanding. Discover how adopting authenticity can transform your interactions and elevate your success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
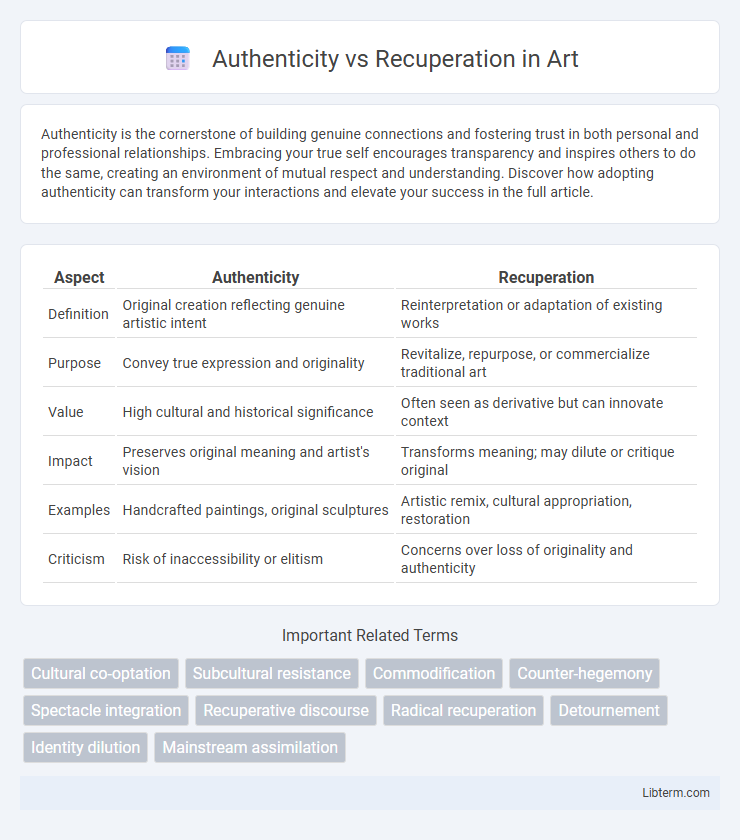
| Aspect | Authenticity | Recuperation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Original creation reflecting genuine artistic intent | Reinterpretation or adaptation of existing works |
| Purpose | Convey true expression and originality | Revitalize, repurpose, or commercialize traditional art |
| Value | High cultural and historical significance | Often seen as derivative but can innovate context |
| Impact | Preserves original meaning and artist's vision | Transforms meaning; may dilute or critique original |
| Examples | Handcrafted paintings, original sculptures | Artistic remix, cultural appropriation, restoration |
| Criticism | Risk of inaccessibility or elitism | Concerns over loss of originality and authenticity |
Understanding Authenticity: Definition and Importance
Authenticity refers to the genuine expression of one's true self, beliefs, and values, free from external influence or social pressure. It plays a crucial role in personal well-being, fostering self-esteem, emotional resilience, and meaningful relationships. Understanding authenticity helps individuals align actions with inner truths, enhancing life satisfaction and psychological health.
Recuperation: Meaning and Cultural Context
Recuperation refers to the process by which subversive or countercultural ideas are absorbed and transformed by dominant institutions, often neutralizing their original radical intent. In cultural contexts, this phenomenon manifests when avant-garde art, political dissent, or grassroots movements are co-opted by mainstream media or corporate interests, turning resistance into commodified trends. This dynamic challenges the preservation of genuine subversion by blurring the lines between authentic expression and institutional assimilation.
The Origins of Authenticity in Social Movements
The origins of authenticity in social movements trace back to the 1960s countercultural and civil rights movements, where genuine self-expression became a form of political resistance. Authenticity was valued as a means to challenge institutional norms and foster collective identity rooted in personal experience and social justice. This emphasis on authenticity contrasted with recuperation, which involves the co-optation of radical ideas by mainstream culture, diluting their transformative potential.
Recuperation: How Systems Absorb Radical Ideas
Recuperation refers to the process by which systems absorb and neutralize radical ideas, transforming them into mainstream, commodified concepts that lose their original subversive impact. This dynamic enables institutions to diffuse dissent by co-opting countercultural symbols, slogans, and practices, effectively integrating opposition into the status quo. The cycle of recuperation highlights the challenge for activists and innovators to maintain authenticity while resisting dilution by dominant structures.
Authentic Expression vs Market Appropriation
Authentic expression reflects genuine cultural, emotional, and individual identity, rooted in lived experience and original context. Market appropriation, by contrast, commodifies and reshapes these authentic expressions to fit consumer trends, often diluting their meaning and significance. This tension challenges creators to maintain integrity while navigating commercialization demands.
Case Studies: Authenticity Lost to Recuperation
Case studies reveal how authenticity is often compromised by recuperation, where original cultural expressions are sanitized or commodified to fit mainstream narratives. Examples include indigenous art forms appropriated for commercial use, stripping away their spiritual or historical significance. This loss highlights the tension between preserving genuine cultural identity and the pressures of market-driven adaptation.
Signs of Recuperation in Contemporary Culture
Signs of recuperation in contemporary culture include the commercialization and mainstream adoption of radical ideas, where countercultural symbols are repurposed for profit and mass appeal. Subversive art and political messages often get sanitized and integrated into consumer products, diluting their original intent. This process reflects how capitalist systems absorb dissent, turning authenticity into a marketable commodity.
The Impact of Recuperation on Identity and Community
Recuperation reshapes identity by absorbing and transforming subversive or countercultural elements into mainstream culture, often diluting original meanings and intentions. This process can undermine community cohesion by commodifying authentic expressions and turning radical ideas into marketable trends, weakening collective resistance. The tension between maintaining authenticity and the pressures of recuperation challenges communities to preserve their distinctiveness while navigating cultural assimilation.
Strategies to Preserve Authenticity
Strategies to preserve authenticity include engaging deeply with local cultures through immersive experiences and supporting genuine community-led initiatives. Prioritizing transparent storytelling and ethical sourcing helps maintain original values while preventing cultural dilution. Implementing sustainable practices ensures that traditions are respected and safeguarded for future generations.
The Ongoing Tension: Authenticity vs Recuperation
The ongoing tension between authenticity and recuperation centers on the struggle to maintain genuine cultural or ideological expressions while facing pressures for mainstream assimilation and commodification. Authenticity often resists dilution by dominant narratives, whereas recuperation attempts to neutralize radical or subversive elements by reinterpreting them within acceptable societal frameworks. This dynamic creates continuous friction in movements seeking to preserve original meanings amid external attempts at appropriation or normalization.
Authenticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com