Professional installations ensure that your equipment functions efficiently and safely, reducing the risk of malfunctions and costly repairs. Proper setup tailored to your specific needs enhances performance and longevity of the system. Discover key tips and expert advice to achieve flawless installations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
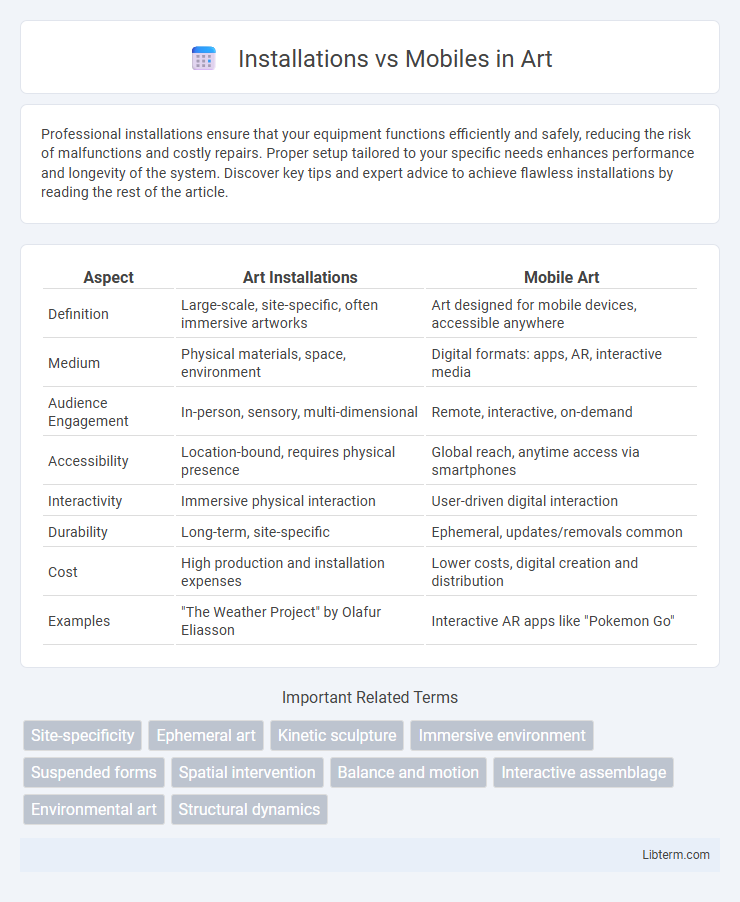
| Aspect | Art Installations | Mobile Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large-scale, site-specific, often immersive artworks | Art designed for mobile devices, accessible anywhere |
| Medium | Physical materials, space, environment | Digital formats: apps, AR, interactive media |
| Audience Engagement | In-person, sensory, multi-dimensional | Remote, interactive, on-demand |
| Accessibility | Location-bound, requires physical presence | Global reach, anytime access via smartphones |
| Interactivity | Immersive physical interaction | User-driven digital interaction |
| Durability | Long-term, site-specific | Ephemeral, updates/removals common |
| Cost | High production and installation expenses | Lower costs, digital creation and distribution |
| Examples | "The Weather Project" by Olafur Eliasson | Interactive AR apps like "Pokemon Go" |
Understanding Installations and Mobiles
Installations refer to software setups on fixed devices such as desktops or servers, characterized by stable environments and consistent hardware configurations. Mobiles involve applications designed for portable devices like smartphones and tablets, optimized for varying screen sizes, touch interfaces, and intermittent connectivity. Understanding the distinct requirements of installations and mobiles enhances application performance, user experience, and resource management across platforms.
Key Differences Between Installations and Mobiles
Installations are fixed systems designed for permanent placement in specific locations, whereas mobiles are portable devices intended for easy transportation and on-the-go use. Installations typically offer greater stability, higher capacity, and enhanced performance due to their robust infrastructure, while mobiles prioritize compactness, flexibility, and wireless connectivity. Key differences include mobility, power supply dependency, and installation complexity, with mobiles relying on batteries and wireless networks, in contrast to the wired and anchored nature of installations.
Historical Evolution of Installations and Mobiles
Installations have evolved from early mechanical systems to complex digital infrastructures, reflecting advancements in industrial technology and urban development since the Industrial Revolution. Mobile devices transformed from basic mobile phones introduced in the 1980s to sophisticated smartphones integrating high-speed internet, GPS, and multimedia functions by the 2010s. The parallel evolution highlights a shift from fixed, large-scale systems essential for infrastructure to portable, personalized technology driving connectivity and mobility in the digital age.
Artistic Intent: Purpose of Installations vs Mobiles
Installations prioritize immersive environments designed to engage viewers through spatial interaction, emphasizing the artist's intention to create a holistic experience. Mobiles focus on balance, movement, and the dynamic interplay of forms, reflecting the artist's exploration of kinetic principles and change over time. Both forms serve distinct artistic purposes, with installations aiming to transform perception within a fixed space, while mobiles highlight fluidity and the ephemeral nature of art.
Materials and Techniques Used
Installations often utilize durable materials such as metal, wood, and acrylic, employing techniques like welding, carving, and mixed-media assembly to create large-scale, often site-specific works. Mobiles primarily consist of lightweight materials like aluminum, wire, and paper, with techniques centered on balancing, suspension, and delicate joining to achieve kinetic movement. The choice of materials and techniques for installations prioritizes stability and permanence, whereas mobiles emphasize flexibility and dynamic interaction with air currents.
Spatial Impact in Art: Installations vs Mobiles
Installations transform spatial environments by immersing viewers within a constructed three-dimensional context, altering perception through scale, texture, and interaction. Mobiles engage space dynamically, relying on movement and balance to create constantly shifting spatial relationships that animate the environment. The spatial impact of installations tends to be immersive and often stationary, while mobiles emphasize kinetic interaction and spatial fluidity.
Audience Interaction and Engagement
Installations provide immersive, large-scale environments that captivate audiences through multi-sensory experiences and physical interaction, fostering deeper emotional engagement and extended dwell time. Mobile devices offer personalized, on-the-go access with interactive features like touch, voice, and augmented reality, enabling real-time audience participation and social sharing. Both mediums enhance engagement differently: installations excel in creating memorable collective experiences, while mobiles drive continuous, personalized interaction and immediate feedback.
Notable Artists and Iconic Works
Notable artists who excel in installations include Yayoi Kusama, known for her immersive Infinity Mirror Rooms, while mobiles are famously associated with Alexander Calder, whose kinetic sculptures revolutionized modern art. Kusama's installations often utilize vibrant colors and repetitive patterns to create immersive environments, whereas Calder's mobiles rely on balance and movement to engage viewers dynamically. Both art forms emphasize spatial experience, yet installations offer layered sensory engagement, contrasting with the elegant motion intrinsic to mobiles.
Challenges in Creating Installations vs Mobiles
Creating installations presents challenges such as securing stable structural support, managing large-scale spatial logistics, and integrating complex multimedia components to ensure immersive experiences. Mobile projects demand efficient optimization for varying device specifications, seamless user interface adaptability, and maintaining performance across diverse environments with limited hardware resources. Both require distinct considerations in design, development, and deployment to address scalability and user interaction effectively.
Future Trends in Installations and Mobiles
Installations are evolving with the integration of smart technology and IoT, enabling more efficient energy management and automation in residential and commercial buildings. Mobile devices continue to advance with 5G connectivity and augmented reality (AR) capabilities, enhancing user interaction and real-time data access. Future trends indicate a convergence where mobile platforms will increasingly control and optimize installations remotely, driving smarter, interconnected environments.
Installations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com