Screen printing offers vibrant, durable designs ideal for customizing apparel, posters, and promotional materials. The process involves pushing ink through a mesh stencil onto various surfaces, ensuring high-quality replication of complex images. Explore the rest of the article to discover tips and techniques that can elevate your screen printing projects.
Table of Comparison
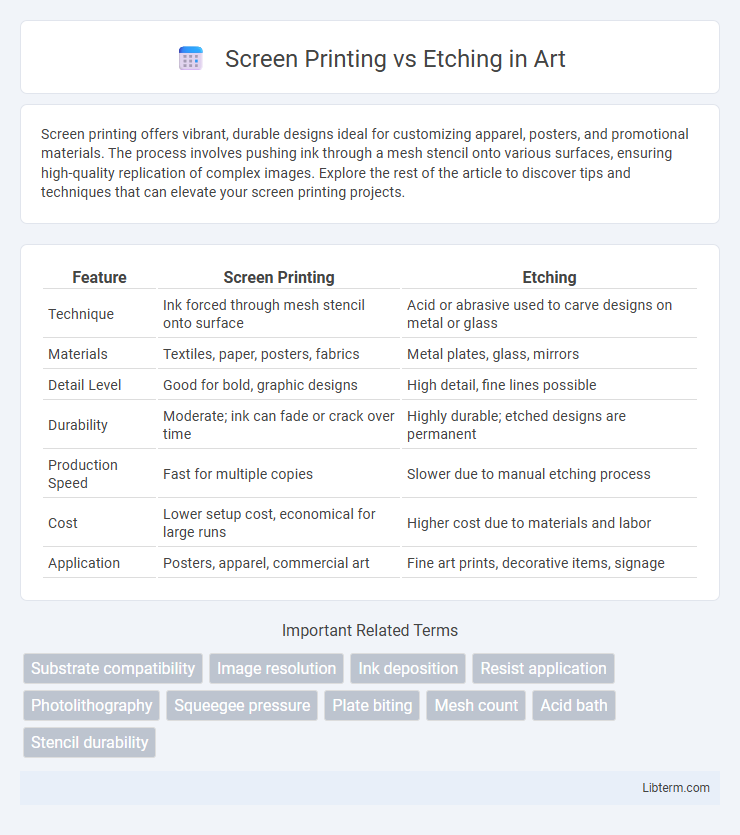
| Feature | Screen Printing | Etching |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Ink forced through mesh stencil onto surface | Acid or abrasive used to carve designs on metal or glass |
| Materials | Textiles, paper, posters, fabrics | Metal plates, glass, mirrors |
| Detail Level | Good for bold, graphic designs | High detail, fine lines possible |
| Durability | Moderate; ink can fade or crack over time | Highly durable; etched designs are permanent |
| Production Speed | Fast for multiple copies | Slower due to manual etching process |
| Cost | Lower setup cost, economical for large runs | Higher cost due to materials and labor |
| Application | Posters, apparel, commercial art | Fine art prints, decorative items, signage |
Introduction to Screen Printing and Etching
Screen printing involves pressing ink through a mesh stencil onto various surfaces, creating bold and vibrant designs commonly used on textiles, posters, and promotional items. Etching, a process primarily used on metal or glass, employs acid or abrasive substances to carve detailed patterns or images into the material's surface, offering precision and durability. Both techniques serve different artistic and industrial purposes, with screen printing emphasizing color application and etching focusing on intricate surface modification.
Historical Background of Both Techniques
Screen printing traces its origins back to ancient China during the Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD), where stencil techniques were utilized for textile patterns, evolving significantly in the early 20th century with the advent of synthetic mesh screens. Etching dates to the 16th century in Europe, pioneered by artists like Albrecht Durer who used acid to engrave designs onto metal plates for printmaking. Both methods have developed into key artistic and industrial processes, with screen printing favored for mass production and etching prized for fine detail and artistry.
Fundamental Processes Explained
Screen printing involves forcing ink through a mesh stencil directly onto a surface, creating vibrant and durable designs ideal for textiles and posters. Etching, by contrast, uses acid or laser to carve patterns into materials like metal or glass, offering precise and permanent markings suitable for fine details and industrial applications. These fundamental differences in technique define their distinct advantages in terms of texture, longevity, and application versatility.
Materials Used in Screen Printing vs Etching
Screen printing primarily uses mesh screens made from polyester or stainless steel and inks formulated with pigments and binders suitable for various substrates like fabric, paper, or metal. Etching involves materials such as metal plates--typically copper, zinc, or steel--and acid or mordant solutions like ferric chloride to create detailed designs by corroding the surface. Both processes require specific material combinations optimized for the medium and desired artwork durability.
Design Versatility and Application Range
Screen printing offers high design versatility with the ability to produce vibrant colors and intricate patterns on various surfaces including fabric, glass, and plastic. Etching provides a more precise and permanent design technique ideal for detailed and delicate patterns, primarily used on metals and glass. While screen printing suits mass production with diverse applications, etching excels in creating durable, high-fidelity designs for limited-run or specialty items.
Print Quality and Detail Comparison
Screen printing offers vibrant colors and sharp, bold designs but struggles with extremely fine detail due to ink spread and mesh limitations. Etching provides superior precision and finesse, capturing intricate lines and subtle textures with high durability in the design. For applications demanding intricate patterns and high-definition detail, etching is the preferred method, while screen printing excels in producing vivid, large-area prints efficiently.
Cost and Equipment Analysis
Screen printing generally incurs lower upfront equipment costs, utilizing mesh screens, squeegees, and inks, making it suitable for small to medium production runs with relatively affordable setup expenses. Etching requires specialized equipment such as acid tanks or laser etching machines, resulting in higher initial investment and maintenance costs, but offers precise, durable markings ideal for detailed or permanent applications. Cost-effectiveness depends on production volume and detail complexity, with screen printing favored for large runs and vibrant designs, while etching suits high-precision or small-batch work despite higher equipment outlay.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Screen printing generally uses plastisol inks and cleaning solvents that can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs), posing environmental and health risks if not properly managed, while etching processes often involve hazardous chemicals like acids and heavy metals that require careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination. Etching techniques demand stringent safety measures including fume extraction and protective gear due to corrosive substances, whereas screen printing also necessitates precautions against inhalation of ink particles and chemical exposure during cleaning. Sustainable alternatives such as water-based inks in screen printing and non-toxic etching solutions are increasingly adopted to minimize ecological footprint and enhance worker safety.
Common Uses in Industry and Art
Screen printing dominates in creating vibrant, large-scale graphics on textiles, posters, and commercial packaging, prized for its versatility and cost-effectiveness in mass production. Etching finds common uses in fine art prints, jewelry design, and industrial applications like circuit board manufacturing, where precision and detailed line work are essential. Both techniques are integral to industries demanding distinct visual and tactile qualities, with screen printing offering bold imagery and etching providing intricate, permanent markings.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
Screen printing offers vibrant color options and is ideal for high-volume production on textiles and flat surfaces, while etching provides precise, durable designs on metal, glass, and ceramics, making it suitable for intricate detailing. Consider the material type, design complexity, and desired durability when choosing between screen printing and etching, as screen printing excels in fast, cost-effective runs, whereas etching delivers long-lasting, professional-grade finishes. Projects requiring bold, colorful graphics benefit from screen printing, whereas those needing subtle, permanent markings lean towards etching.
Screen Printing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com