Futurism explores the impact of emerging technologies, innovative designs, and avant-garde ideas shaping tomorrow's world. It emphasizes dynamic change, speed, and the fusion of art and technology to envision new possibilities. Discover how futurism can inspire Your view of society and innovation in the full article ahead.
Table of Comparison
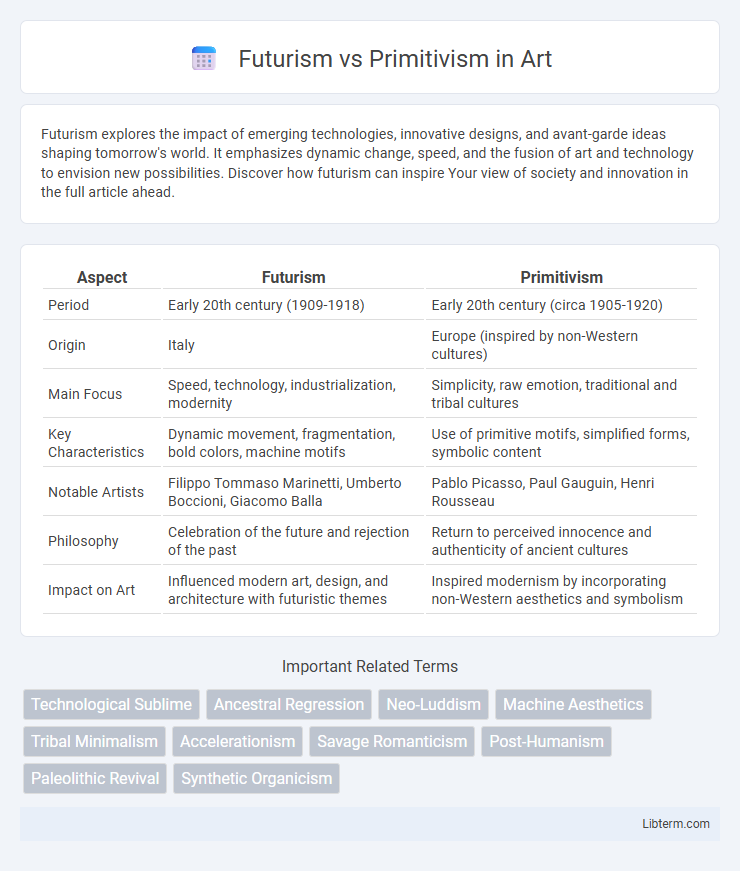
| Aspect | Futurism | Primitivism |
|---|---|---|
| Period | Early 20th century (1909-1918) | Early 20th century (circa 1905-1920) |
| Origin | Italy | Europe (inspired by non-Western cultures) |
| Main Focus | Speed, technology, industrialization, modernity | Simplicity, raw emotion, traditional and tribal cultures |
| Key Characteristics | Dynamic movement, fragmentation, bold colors, machine motifs | Use of primitive motifs, simplified forms, symbolic content |
| Notable Artists | Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, Giacomo Balla | Pablo Picasso, Paul Gauguin, Henri Rousseau |
| Philosophy | Celebration of the future and rejection of the past | Return to perceived innocence and authenticity of ancient cultures |
| Impact on Art | Influenced modern art, design, and architecture with futuristic themes | Inspired modernism by incorporating non-Western aesthetics and symbolism |
Defining Futurism and Primitivism
Futurism is an early 20th-century avant-garde movement emphasizing speed, technology, and modernity, celebrating industrial progress and dynamic urban life. Primitivism, by contrast, draws inspiration from non-Western and prehistoric art, valuing simplicity, raw emotion, and a return to nature. Both movements challenge traditional aesthetics but diverge in their sources of inspiration and artistic goals.
Historical Origins of Both Movements
Futurism emerged in early 20th-century Italy, driven by the manifesto published by Filippo Tommaso Marinetti in 1909, emphasizing speed, technology, and modernity as core themes. Primitivism, rooted in late 19th-century European art, drew inspiration from non-Western and prehistoric cultures, valuing simplicity and rawness as a reaction against industrialization and urbanization. Both movements challenged traditional aesthetics but diverged in focus: Futurism celebrated the machine age, while Primitivism idealized perceived purity in ancient or tribal cultures.
Key Philosophies: Progress versus Simplicity
Futurism champions relentless progress, embracing technology, innovation, and the mechanization of society as pathways to a better future. Primitivism, in contrast, idealizes simplicity and a return to pre-industrial, often nature-centric ways of life, criticizing modernity's complexities and environmental degradation. These opposing philosophies fundamentally debate whether human advancement is best achieved through technological evolution or by reconnecting with basic, ancestral lifestyles.
Artistic Expressions and Aesthetics
Futurism emphasizes dynamic movement, technology, and industrial progress through bold lines, fragmented shapes, and vibrant colors that convey speed and mechanization. Primitivism draws inspiration from indigenous and ancient art forms, utilizing simplified shapes, raw textures, and earthy tones to evoke a sense of authenticity and emotional depth. Both movements challenge classical aesthetics but diverge in their focus: Futurism celebrates modernity and innovation, while Primitivism seeks to reconnect with primal human essence.
Technological Embrace versus Natural Return
Futurism emphasizes the technological embrace, celebrating industrial innovation, machinery, and speed as symbols of progress and modernity. Primitivism advocates a natural return to simplicity, valuing raw, organic forms and traditional, often pre-industrial cultural expressions. The tension between Futurism's forward-looking technological optimism and Primitivism's nostalgic reverence for nature highlights divergent artistic and philosophical responses to the rapidly changing modern world.
Influence on Modern Culture
Futurism and Primitivism have each left distinct imprints on modern culture, with Futurism championing technological progress, rapid urbanization, and dynamic movement, influencing contemporary architecture, fashion, and digital art. Primitivism draws from indigenous art forms and ancient aesthetics, inspiring modern artists to explore raw, organic motifs and challenge industrialized society's norms, evident in avant-garde visual arts and music. Both movements contribute to the cultural dialogue on modernization, identity, and the relationship between humanity and technology.
Criticism and Controversies
Futurism faced criticism for its aggressive glorification of technology and war, often being associated with fascist ideologies and the rejection of traditional values. Primitivism sparked controversies due to its romanticized and sometimes exploitative portrayal of non-Western cultures, raising ethical concerns about cultural appropriation and erasure. Both movements challenged artistic norms but were scrutinized for their ideological implications and social impacts.
Influential Figures and Works
Futurism, spearheaded by Filippo Tommaso Marinetti and exemplified in works like Umberto Boccioni's sculpture "Unique Forms of Continuity in Space," emphasized speed, technology, and the dynamism of modernity. Primitivism, championed by artists such as Pablo Picasso and Paul Gauguin, drew inspiration from African, Oceanic, and indigenous art forms, as seen in Picasso's groundbreaking painting "Les Demoiselles d'Avignon." Both movements significantly impacted 20th-century art, challenging traditional aesthetics through their distinct approaches to form, culture, and modern experience.
Societal Impact and Relevance Today
Futurism's emphasis on technology, speed, and industrial progress reshaped early 20th-century society by promoting modernity and innovation, influencing art, architecture, and cultural attitudes toward urbanization and mechanization. Primitivism, in contrast, sought a return to simplicity and a critique of industrial society by idealizing indigenous cultures, highlighting ongoing debates about authenticity and cultural appropriation. Both movements remain relevant today as society navigates the tension between rapid technological advancement and the desire to preserve cultural roots and sustainable ways of living.
Future Trends: Synthesis or Conflict?
Futurism's emphasis on technological innovation and speed contrasts with Primitivism's valorization of simplicity and nature, creating a complex dynamic in contemporary art and culture. Emerging trends indicate a synthesis where digital technology integrates organic forms, reflecting a hybrid aesthetic that embraces both progress and tradition. This fusion challenges the binary opposition by promoting a dialogue that blends futuristic visions with primal elements, shaping future creative expressions.
Futurism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com